Intermolecular Forces
advertisement

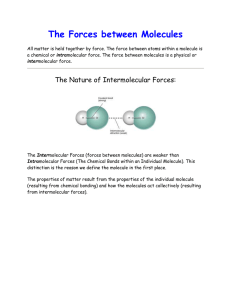
Intermolecular Forces Pages 112-113; 167-169 Intermolecular Forces Forces of attraction between molecules Link molecules together instead of atoms Not very strong Three Types Dispersion Forces (AKA London Dispersion Forces) Dipole Interactions Hydrogen Bonding Dispersion Forces Weakest of the three intermolecular forces Occur between nonpolar molecules Caused by the movement of electrons around the molecule Dispersion Forces H-H share electrons equally, but as electrons are zipping around the orbitals, they might both be found in the same area at the same time. This would give the molecule a temporary or instantaneous dipole. Dispersion Forces The larger the molecule (the more electrons it contains), the stronger the dispersion force becomes. Nonpolar Molecule Boiling Point (°C, 1 atm) # electrons Comparison of strength H2 -253 2 weakest O2 -183 16 Cl2 -34 34 Br2 59 70 strongest Dipole Interactions Also known as dipole-dipole Occur when polar molecules are attracted to one another Positive end of a polar molecule attracts to the negative end of another polar molecule Dipole Interactions Dipole Interactions Dipoles can be induced on nonpolar molecules as well. Example: Water and Oxygen O H H O O Dipole Interactions O H H O Induced dipoles O Hydrogen Bonding The intermolecular attraction between a hydrogen atom which is covalently bonded to N, O or F AND an unshared pair of electrons on another N, O, or F atom H-F H-O H-N Hydrogen Bonding Because H is so small, it can approach the unshared pair of electrons very closely. Dotted lines are used to show hydrogen bonding Hydrogen bonding is a very strong IMF. Hydrogen Bonding in Water O O H H H H O H H O O H H H H Practice Problem 1 What type of intermolecular force will happen between the following molecules? F2 ICl CCl4 H2S NH3 HF Practice Problem 3 Water (H2O) and ammonia (NH3) are both relatively small polar molecules. Using IMF, explain why water’s boiling point is 100°C while ammonia’s is -33°C. Practice Problem 2 Rank the molecules below in order of lowest boiling point to highest boiling point. H2O CH4 HBr