Electron Distribution - Mrs. Loweke AP Chemistry
advertisement

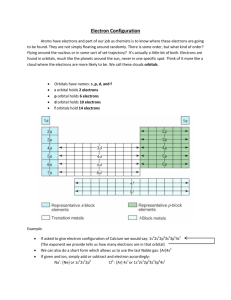
Electron Distribution LEQs How do electron configurations and the four quantum numbers illustrate electron placement using the quantum model? Electrons are located in energy levels which are subdivided into sublevels and orbitals Energy Levels(n): 1 through 7 Electrons held= 2n2 Sublevels: s: 1 orbital: holds up to 2 electrons p: 3 orbitals: holds up to 6 electrons d: 5 orbitals: holds up to 10 electrons f: 7 orbitals: holds up to 14 electrons Order 1s2s2p3s3p4s3d4p5s4d5p6s4f5d6p7s5f6d7p Rules Aufbau Principle: electrons fill lower energy levels before filling higher energy levels Hund’s Rule: electrons in a sublevel will fill each orbital before pairing up. Pauli’s Exclusion Principle: electrons in the same orbital will have different spins Orbital Notation Graphically represents the distribution of electrons. Steps: 1. Determine number of electrons to be distributed. 2. Determine the ending sublevel/orbital for the atom. 3. Draw boxes, circles, or lines to represent the orbitals. 4. Draw arrows (up or down) to represent the electrons. Ex: Magnesium Ex: Sulfur Ex: Nitrogen Ex: Iron Electron Configuration “Shorthand” for orbital notation Steps: 1. Determine the number of electrons 2. Determine the ending energy level/sublevel 3. Write out order until the ending sublevel 4. Represent electrons as exponents Ex: Potassium Ex: Scandium (Sc) Ex: Neon Ex: Zirconium (Zr) Noble Gas Electron Configuration Shortened version of electron configuration Steps: 1. Determine the number of electrons and ending energy level/sublevel. 2. Determine the nearest noble gas with LESS electrons 3. Write the noble gas in brackets 4. Write the rest of the electron configuration using exponents for electrons. Ex: Rubidium Ex: Tin Ex: Sodium Ex: Niobium (Nb)