Alcohol to Alkyl Bromide Conversion Lab Experiment
advertisement

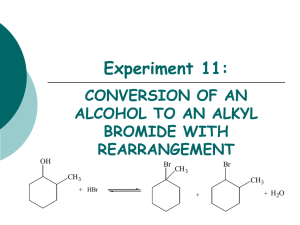
Experiment 11: OH CONVERSION OF AN ALCOHOL TO AN ALKYL BROMIDE WITH REARRANGEMENT Br CH3 + HBr Br CH3 CH3 + + H2O Objectives To synthesize isomeric alkyl halides from an alcohol using an SN1 dehydration reaction. To determine product substitution based on reaction rate with AgNO3. To characterize reactants and products using IR spectroscopy. SN1 MECHANISM 1. hydroxyl oxygen attacks and removes a proton from hydrobromic acid. H 2. Forms new O-H bond, oxygen bears a positive charge (oxonium ion). OH CH3 H H 3. Water is eliminated-forms 2o carbocation. H O Br H H H CH3 CH3 H H + H2O + Br secondary carbocation H H H H CH3 H H H H a a Br- 5. Reaction of the carbocation with the bromide ion yields the alkyl halide. CH3 Hydride Shift 4. Products may form from the 2o carbocation, but it is more likely that the 2o C+ will rearrange to a 3o C+. b b Br- Br Br CH3 CH3 5. Reaction of the carbocation with the bromide ion yields the alkyl halide. EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE (Synthesis) • Add 2-methylcyclohexanol, 48% HBr and 3 boiling chips to flask. water out • Clamp flask to ring stand. • Attach clear hoses to condenser and place condenser on top of flask. water in heating mantle to voltage regulator iron ring • Begin water flow through condenser and apply heat. • Reflux the solution for 30 minutes. • Cool flask in beaker of tap water. EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE (Purification) • Transfer solution to separatory funnel. • Add concentrated sulfuric acid. • Stir solution gently with glass rod. Do NOT agitate. • Draw off bottom acidic layer into an Erlenmeyer flask. • Transfer the top layer to a preweighed beaker using a glass Pasteur pipet. • Reweigh beaker to obtain final mass. • Perform silver nitrate test. Table 11.1 Must determine which reactant is your limiting reagent first, 48% HBr or 2-methylcyclohexanol. Calculate the amount of product that can be formed based on the limiting reagent. Theoretical Yield (g) This mass will be obtained by weighing an empty small beaker, then reweighing after the product has been added. The difference in mass is the actual product yield. Actual Yield (g) % Yield Product Appearance Actual yield (g) Theoretical yield (g) X 100 Physical state and color of product. EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE (Silver Nitrate Test) When an alkyl halide is treated with a solution of alcoholic silver nitrate, a precipitate of silver halide forms. The rate limiting step is the formation of the carbocation. Br + AgNO3 ethanol + C + NO3- + AgBr(s) Rate of reaction: 3o > 2o > 1o Alkyl Bromides Table 11.2 Test Solution 1-bromobutane 2-bromobutane 2-bromo-2-methylpropane Product sample Reaction Rate (min/sec) You only need 3 drops of each of these! Get ONLY what you need! IR SPECTROSCOPY OH CH3 Br CH3 Table 11.3 Functional Group Base Values (cm-1) OH stretch 3200-3600 C-O stretch 1000-1200 sp3 CH stretch 2850-3000 C-Br stretch 500-700 2-methylcyclohexanol Alkyl halide product Frequency (cm-1) Frequency (cm-1) SAFETY CONCERNS Sulfuric acid is very corrosive and must be used with EXTREME caution! Silver nitrate will stain the skin! Use gloves at all times! Alkyl bromides are lachrymators! Keep covered at all times to avoid inhalation! WASTE MANAGEMENT Place the acidic solution from extraction in bottle labeled “AQUEOUS ACIDIC WASTE”. Place alkyl bromide product in the bottle labeled “ALKYL BROMIDE WASTE”. Pour the contents of the test tubes used in the silver nitrate test in the container labeled “SILVER NITRATE WASTE”. For Next Lab… Experiment 12 Pre-lab notebook entry will be due at the beginning of lab!