Legal Aspects of the Practice of Medicine
advertisement

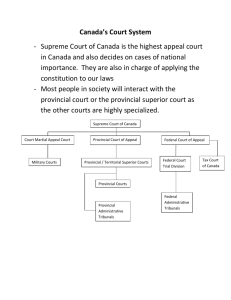
Introduction to Health Law B. Barrowman September 2002 Outline • what is health law? • forces shaping evolution of Canadian health law in the 21st century • health law and ethics • overview of Canadian legal system, terminology, etc. • some areas of health law we will cover in the curriculum Health Law • field of legal practice, scholarship and law reform relating to the delivery of health care • deals with health care delivery at macro and micro level • rapidly expanding and dynamic field scientific, social, economic, legal, philosophical and political influences Why Study Health Law in Medical School? • all aspects of the practice of medicine, and healthcare more broadly, are affected by the law • important for physicians to have an awareness of how the law affects them and their patients • Medical Council of Canada expects competency in this area Influences on the Development of Health Law in Canada • health care reform movement (re organization and financing of health care system) • increasing litigation and new types of litigation – e.g. class action suits re medical devices – wrongful life lawsuits Influences on the Development of Health Law in Canada • advances in science and technology – e.g. genetic research – reproductive technologies • advances in information technology – computerized patient information – vast amount of health info on the internet • evolution of field of bioethics, increasing influence of new perspectives Law and Ethics • law influenced by ethics and to some extent the converse is true • obviously important to comply with the law, but what the law says may not be the ultimate answer to a moral question • many ethical principles re medical practice now codified - tends to blur the distinction (rules-based vs. virtue ethics) • some similarities in reasoning - clarifying facts, principles and their application Overview of the Canadian Legal System • • • • where does the law come from? areas of law Canadian constitutional framework the court system Sources of Law • Legislation – statutes – regulations – federal and provincial • Judicial Decisions – sometimes referred to as the “common law” – precedents Nature of the Law • degree of uncertainty • role of judicial interpretation • constantly evolving Divisions of Law • Public Law – disputes between individual and state – e.g. criminal law, administrative law, constitutional law • Private Law – sometimes referred to as “civil law” – disputes between individuals – e.g. torts, contracts, property law Canadian Constitutional Framework • Constitution Act 1867 (British North America Act) - division of powers between federal and provincial governments • Charter of Rights and Freedoms 1982 legislation and actions of government can be challenged, based on the rights granted in the Charter Structure of the Courts • superior provincial court --> provincial Court of Appeal --> Supreme Court of Canada • (federal courts) • (inferior courts) • administrative tribunals, e.g. NF Medical Board Health Law Topics • Canada’s health care system – structure, funding, supply of and access to health services • • • • regulation of health professionals e.g. MD’s medical negligence consent confidentiality and disclosure of health information Health Law Topics • medical care of minors • medical care of patients with mental disabilities • abortion • regulation of reproductive technologies • genetics and the law • end of life decision making • medical research 1. Structure and Dynamics of Canadian Health Care System • complex legal framework • areas of federal and provincial jurisdiction • Canada Health Act - establishes criteria that provincial health plans are supposed to meet • provinces responsible for administration of health care - hospitals, insurance for and supply of services • the future? 2. Regulation of the Medical Profession • provincial responsibility • “self-regulating” professions • body created by statute in each province – e.g. NF Medical Board – standards for licensure – deals with allegations of incompetence, incapacity or misconduct – can generate its own policies, guidelines 3. Civil Liability • a.k.a. negligence, “malpractice”, “getting sued” • law in this area mostly “judge-made” • informed consent • standard of care 4. Complex Emerging Issues – e.g. reproductive technologies – electronic health care records - privacy issues – cost constraints - impact on insured services and on individual care • complex issues affected by several sources and divisions of law (courts, legislatures, federal, provincial, criminal, civil, Charter of Rights) as well as ethics, public policy