Nuclear Chemistry
advertisement

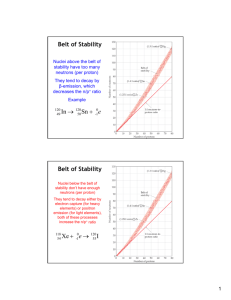
Mini Quiz- Half Sheet H = 1.01 g/mol, O = 16.00 g/mol S = 32.07 g/mol, N = 14.01 g/mol, I = 126.90 g/mol 1. How many grams in 3.4 x 1023 molecules of H2SO4? 2. How many molecules are there in 0.40 g of N2I6? Nuclear Chemistry Unstable Nuclei Often nuclei of very large atoms are unstable… Unstable Nuclei Stable Nuclei + Energy Cause of Instability A p+ to no ratio that is not close to 1:1 Example: Polonium (Po) has 84 protons and 125 neutrons Radioactive Oxygen has 8 protons and 8 neutrons Not Radioactive Nuclear Reaction • Reaction that affects the nucleus of an atom. • Radioactive decay: Spontaneous disintegration of a nucleus into a slight lighter nucleus. • Particles and energy can be emitted. • This is called nuclear radiation 92-Uranium-238 • 92 protons and 146 neutrons • Radioactive nuclide • Undergoes a series of radioactive decay 3 Main types of radioactive decay • Alpha • Beta • Gamma Alpha Particle • Nucleus of a Helium atom • 2 p+ and 2 no • Mass = 4, Atomic number = 2 Beta Particle • neutron to proton ratio that is too high • Mass = 0, number -1 Gamma Radiation • High energy electromagnetic waves (light) • No mass • Pure energy g Radiation Exposure Balancing Nuclear Equations 212-4 = 208 mass of new element 84-2 = 82 atomic number of new element Balancing Nuclear Equations Uses for Nuclear Radiation Uses for Nuclear Radiation Uses for Nuclear Radiation Nuclear Fission • Heavy nuclei splits into more stable nuclei • Releases enormous amount of energy Nuclear Reactors Nuclear Fusion 2 small nuclei form a larger nuclei, producing a crazy amount of energy. Warm Up What is the difference between nuclear fission and fusion? Nuclear Reactors Nuclear Fusion 2 small nuclei form a larger nuclei, producing a crazy amount of energy. Questions on Vegium? Check your calculations… do you have the right number of SF? Check your Isotope WS Do you have any questions on these calculations? Work I’m Collecting Vegium Unit 2 Review Atomic Structure WS- (3 worksheets on 1 sheet) Isotope WS