What is radioactivity? Nuclear radiation
advertisement

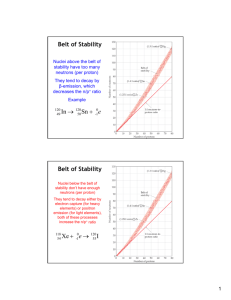
I. What is radioactivity? A. Nuclear radiation – charged particles or energy emitted by an unstable nucleus. 1. Radioactivity – unstable nucleus emits one or more particles or energy in the form of electromagnetic pulse. 2. 4 types of radiation: a) Alpha particle: α 1) Has +2 charge. 2) Consists of 2 protons and 2 neutrons. 3) Resembles a helium nuclei.42He (top # = mass #, bottom # = atomic #) 4) Does not travel far through matter b/c it is so massive. 1 b)Beta particle: β 1)Has –1 charge. 2)Fast moving electrons. 3)Symbol: 0-1e 4)Travel farther and faster through matter b/c not as massive as α. 5)Most stopped by 3 mm of Aluminum or 10 mm or wood. c)Gamma particle: γ 1)Not matter and has no charge => electromagnetic energy. 2)High energy radiation. 3)Penetrates up to 60 cm of Al or 7 cm of lead. 2 d)Neutron emission: 1)Has no charge. 2)Symbol: 10n. 3)Can travel farther than α or β particles. 4)Need 15 cm thick block of lead to stop neutrons. 5)Very dangerous to organisms. B. Nuclear decay: 1. Alpha decay: a)An alpha particle is released from an atom. b) 22688Ra -> 22286Rn + 42He c)226 = 222 + 4 3 88 = 86 + 2 2. Beta decay: a)A nucleus gains a proton and loses a neutron. b) 146C -> 147N + 0-1e c)14 = 14 + 0 6 = 7 + -1 d)Mass number does not change. C. Radioactive Decay Rates 1. Half-life – time required for half a sample of radioactive nuclei to decay. a) Varies with each radioactive isotope. 4 2. Problems: 1.Radium-226 has ½-life = 1599 years How long did it take for 7/8 to disappear? 1)How much is remaining? 1 – 7/8 = 1/8 remaining 2)How many ½-lives did it take? ½ x ½ x ½ = 1/8, so 3 ½-lives 3)Total time: 3 ½-lives x 1599 yrs. = 4797 yrs 1 ½-life • Practice p. 228 (1-5) 5 II. Nuclear Fission and Fusion A. Nuclear Fission – nucleus SPLITS into two or more smaller fragments, releasing neutrons and energy. 1. Release of energy is expressed as: E = mc2 E = energy (Einstein) m = mass c = speed of light 2. Nuclear chain reaction – series of fission reactions in which the neutrons emitted by a dividing nucleus cause the division of other nuclei. (Figure 7-8) a) Critical mass – minimum mass needed to sustain a chain reaction. 6 B. Fusion – light nuclei combine at high temperatures, forming heavier nuclei and releasing energy. 1. Occurs in stars. 2. 4 H -> 42He + γ (gamma ray) III. Dangers and Benefits of Nuclear Radiation A. Dangers: 1. Health concerns: a) Change hemoglobin b) Lung cancer (radon in buildings) c) Radiation sickness (cancer, sterility, hair loss, etc.) d) Genetic mutations 7 B. Benefits: 1. Used to treat cancers (brain, etc.) 2. Radioactive tracer 3. Nuclear power: a)Advantages: 1)No gaseous pollutants 2)More known energy reserves than fossil fuels. b)Disadvantages: 1)Radioactive products => nuclear waste 2)Public safety => nuclear meltdown (Chernobyl and Three-mile island). 3)Very expensive 8