Action potential synapses
advertisement

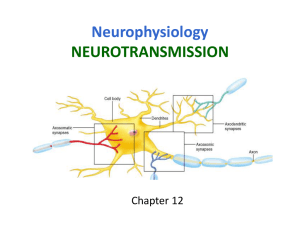
Action Potential revisited When a stimulus reaches threshold level, Sodium channels open up and Sodium rushes into the axon along the concentration gradient. depolarization Once a membrane potential of 40mV is reached, the sodium channels close, and Potassium channels open. This causes a rush of Potassium ions to the outside of the cell, and the cell is repolarized. The potassium gates close relatively slowly, therefore, hyperpolarization occurs, and the cell is said to be in a refractory period (toilet flushing) The Sodium-Potassium pump moves ions back across the membrane against the concentration gradient, and resting potential is restored. The refractory period helps to ensure that stimulus only flows in one direction. Neurotransmitters Neurotransmitters are chemicals that alter the membrane potentials of postsynaptic neurons. Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter found in the end plates of many nerve cells. It acts as an excitatory neurotransmitter on many postsynaptic neurons by opening Sodium ion channels. What would happen if the sodium channels remained open? The presynaptic neuron releases the enzyme cholinesterase which breaks down acetylcholine, allowing the sodium channels to close, and repolarization to take place. Why is this important to neuron function? Some neurotransmitters act on the postsynaptic membrane by making the membrane more permeable to Potassium. This causes the cell to go through a state of hyperpolarization. What effect do you think this has on the neuron? These are called inhibitory neurotransmitters. The inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA is the most abundant neurotransmitter in the brain. Summation refers to multiple presynaptic neurons acting at one time on a postsynaptic neuron. When do you think summation would be necessary? Now, lets look at how different drugs act on the synapse.