Cell Membrane Just Passing Through Worksheet
advertisement

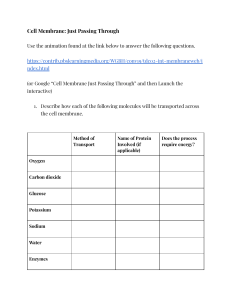
Cell Membrane: Just Passing Through Use the animation found at the link below to answer the following questions. http://www.pbslearningmedia.org/asset/tdc02_int_membraneweb/ 1. Describe how each of the following molecules will be transported across the cell membrane. Method of Transport Name of Protein Involved Does the process (if applicable) require energy? Oxygen Carbon Dioxide Glucose Potassium Sodium Water Enzyme 2. Explain why glucose continues to enter a cell, even when the concentration inside the cell might be higher than outside. 3. How many ions can move through a protein channel per second (on average)? 4. Do protein channels have specificity? (i.e. Are they specific about what they let cross the membrane or can any molecule go through any channel?) 5. Explain how the sodium/potassium pump works. Why does this process require ATP? 6. Correctly color code and identify the name for each part of the cell membrane. Letter Name/Color Letter Name/Color Phospholipid bilayer (no color) Receptor protein (red) Protein channel (pink) Cholesterol (blue) Fatty acid tails (orange) Glycoprotein (green) Phosphate heads (yellow) Carbohydrate markers (purple) Match the cell membrane function with the correct letter from the cell membrane diagram. Letter Function Letter Function Attracts water Repels water Helps maintain flexibility Make up the bilayer Involved in cell-to-cell recognition Help transport certain materials across the membrane 7. Use arrows to show the direction of water movement into or out of each cell below. 8. Label the tonicity for each solution below (isotonic, hypotonic, or hypertonic): ___________________ ___________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________