Metamorphic Rocks
Section 3.4
Metamorphic rocks form when existing rocks are changed by heat and pressure
Metamorphism means “to change form”
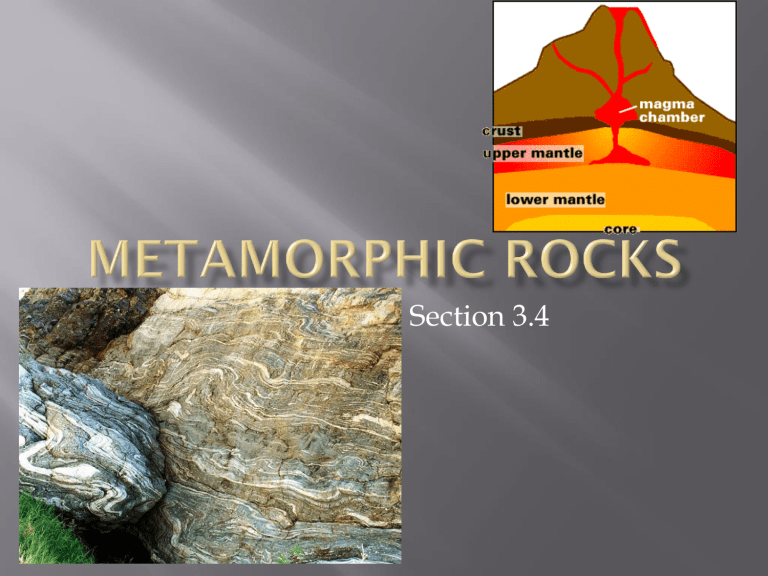
Most of the changes occur at elevated
temperatures and pressures. These conditions are found a few kilometers below
Earth’s surface and extend into the upper mantle
Metamorphism occurs in two ways: contact and regional
Changes caused by heat from nearby magma
Produces low-grade metamorphism
Marble often forms when magma intrudes limestone
During mountain building, large areas of rock are subjected to extreme pressure & temperatures
Regional metamorphism: large-scale deformation and high-grade metamorphism
There are three agents of metamorphism
Heat
Pressure
Hydrothermal solutions
During metamorphism, rocks are subjected to all 3 agents
Heat provides the energy needed to drive chemical reactions
The heat comes from magma & the change in temperature with depth
Pressure on rocks within Earth is applied in all directions
Pressure causes the space between the mineral grains to close, creating a more compact rock with a greater density
The mineral grains tend to flatten and elongate
Pressure can cause minerals to recrystallize into a new mineral
Water solutions that surround mineral grains aid in recrystallization making it easier for ions to move
Hydrothermal Solutions: Hot, watery solution that escapes from a mass of magma during the later stages of crystallization
A change in a rocks overall composition may occur
Metamorphic rocks can be classified by texture and composition
Types of Texture:
Foliated – a rock with layered or banded appearance
Non-foliated – a rock without a banded texture
When rocks are exposed to greater temperature and pressure, the minerals will become compacted and may recrystallize with a preferred orientation
A metamorphic rock that does not have a banded texture
Most non-foliated rocks contain only one mineral
Most metamorphic changes occur at elevated temperature and pressure
During contact metamorphism, hot magma moves into rock
Regional metamorphism results in large-scale deformation and high-grade metamorphism
The agents of metamorphism are heat, pressure and hydrothermal solutions
Classified by texture as foliated or non-foliated








