Description
advertisement

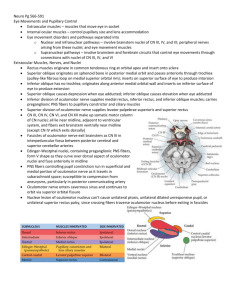
Pupil & Systemic diseases Abnormally shaped pupils: Acquired Congenital Abnormalities Description Aniridia Iris is hypoplastic, creating a large pupillary opening Ectopia lentis et pupillae lens dislocations associated with oval, ellipsoid, or slitlike displaced pupils Iris coloboma notch inferiorly or infranasally in the iris Ocular associations cataracts, glaucoma, and macular or optic nerve hypoplasia Systemic associations Wilms' tumor Marfan syndrome Hyper-homocysinuria Weil Machesani syndrome chorioretinal or optic nerve colobomas - AC cleavage anomalies Ectopic "corectopia" Persistent pupillary membrane Iritis Trauma Neurologic abnormal adhesions between the cornea and iris Misplaced pupil Chromosomal anomalies: Patau, Edward, Cat eye Goldenhar, Dandy Walker, CHARGE syndromes Peters anomaly Rieger syndrome spoke-like opacities across the pupil Posterior synechia Iris tear, rupture sphincter Irregular pupil (ARP) Neuro-syphilis Abnormal reactivity: A) Diseases affecting the afferent pathway: 1- Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect (RAPD): Optic neuropathy Asymmetric chiasmal syndromes Isolated optic tract lesions "contralateral RAPD" Retro-geniculate lesions Lesions in the midbrain pretectum Large macular lesion 2- Absolute Afferent Pupillary Defect (APD): The eye is completely blind Pupils can also react during attempted gaze at near targets, and thus exhibit light-near dissociation - B) Diseases affecting the efferent pathway: 1- Sympathetic: Central Pre-ganglionic Brainstem disease (stroke, - Pancoast tumor tumor…) - Neck lesion (trauma, Syringomyelia surgery…) Lateral medullary syndrome - Carotid & aortic Spinal cord tumors aneurysm, dissection DM autonomic neuropathy Isolated optic tract lesions may have a contralateral RAPD, despite normal visual acuities, because the defective temporal field in the contralateral eye is 61–71% larger than the nasal field of the ipsilateral eye, the nasal retina has a greater photoreceptor density, and the ratio of crossed to uncrossed fibers in the chiasm is 53:47. The magnitude of the RAPD in this setting may reflect the relative light sensitivity of the intact temporal versus nasal field - Post-ganglionic Cluster headache Internal carotid dissection Nasopharyngeal tumors Cavernous sinus lesion Orbital apex syndrome 2- Parasympathetic: - Holmes Adie syndrome tonic pupil(s) and absent deep tendon reflexes concurrent involvement of the ciliary and dorsal root ganglia C) Light-Near Dissociation: Abnormal size (Anisocoria): "Tonic pupil" Local ocular process affecting the ciliary ganglion or short ciliary nerves, e.g. eye or orbital trauma, sarcoidosis viral illnesses (e.g., varicella) ischemia (e.g., GCA) strabismus surgery Orbital tumors - Autonomic dysfunction neuro-syphilis advanced DM dys-autonomias e.g. Riley Day amyloidosis Guillian Barre syndrome