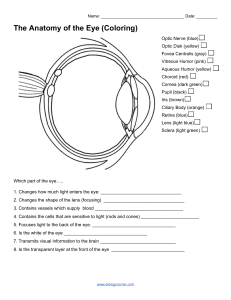
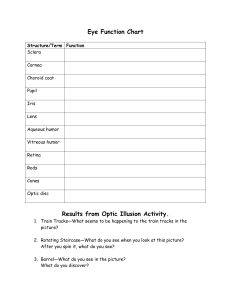
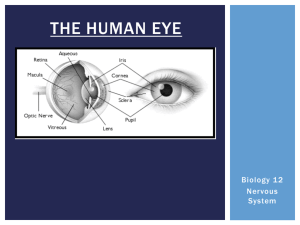
Eye dissection post-lab Structure Location Function Sclera Cornea
advertisement

SCCS Anatomy/Physiology Name: Eye dissection post-lab Structure Sclera Cornea Pupil Lens Iris Ciliary Body Humor Choroid & Retina Optic Nerve Location Function Observe the eye model. Examine the extrinsic muscles: Match the functions. Use the word bank: a. superior oblique b. inferior oblique c. superior rectus d. inferior rectus e. medial rectus ab. lateral rectus 21. Moves the eye up and out to the side 22. Moves the eye straight up 23. Moves the eye down and in toward the nose MATCHING: Use the Key Terms below. Terms may be used more than once. aqueous humor cornea vitreous humor ciliary body/muscle conjunctiva fovea centralis lens retina sclera suspensory ligament choroid Optic nerve Tapetum lucidum radial iris circular iris .Extrinsic eye muscles. pupil optic disk (if term is not listed here, you may write in your own term) 1. Aims the eye. 2. Contains muscle that controls the shape of the lens. 3. Nutritive (vascular) layer / wall of the eye 4. The blind spot. 5. Layer/wall of the eye containing the neuron receptors. 6. Gel-like substance filling the posterior cavity of the eyeball. 7. Helps to maintain the placement of the retina as well as the eyeball shape. 8. Intrinsic muscle of the eye. 9. Attaches the lens to the ciliary body/muscle. 10. Fluid that fills the anterior chamber of the eye. 11. Layer/wall of the eye composed of tough, white fibrous collagen connective tissue. 12. An area of the retina that lacks photoreceptors 13. Area of acute or discriminatory/sharpestvision 14. Refractory mediums of the eye. (name all) 15. Most anterior and transparent part of the outer wall of the eyeball. 16. Rich in mucous membranes and glands to lubricate the eye 17. Operates to dilate the iris to enlarge the pupil size 18. Transmits the action potential from the retina to the optic tract. 19. Area where the largest number of cones can be found 20. Increases night vision in animals