GENETICS Ch. 12 *Definition: the study of heredity
advertisement
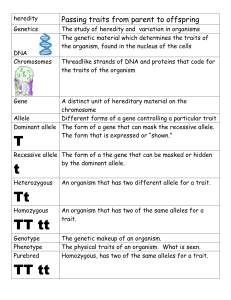
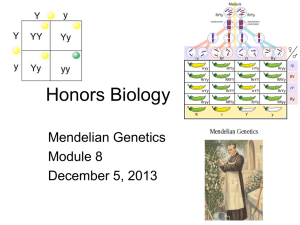
GENETICS Ch. 12 *Definition: the study of heredity ~heredity: the passing of traits from parent to offspring. Gregor Mendel the “Father of Modern Genetics” • Austrian monk • 1860’s • used garden pea plants why? 3 reasons: 1. the structure of the pea flowers (usually self-pollinates). 2. the presence of contrasting traits. 3. rapid reproductive cycle (~90 days). http://www.flinnsci.com/introgenetics • *Mendel studied 7 distinct characters (physical features that are inherited; ex. flower color)…pg. 268 – *YOU ARE RESPONSIBLE FOR KNOWING THESE! • Trait: one of several possible forms of a character; ex. purple or white • Mendel’s experiments used monohybrid crosses (a 4 box Punnett square) in order to study one pair of contrasting traits (ex. purple vs. white for flower color). • P generation F1 (true-breeding parents) (1st filial) F2 (2nd filial) -VOCAB• ~purebred: an organism that receives the same genetic traits from both of its parents (*self-pollination in plants). • ~hybrid: an organism that receives different forms of a genetic trait from each parent (purple X white). Mendel and Modern Genetics 12.2 • gene: sections of a chromosome that code for a trait. *most organisms have 2 copies (homologous chromosomes) of every gene and chromosome…1 from each parent. • allele: versions of a gene (ex. tall vs. short for plant height)…T and t • dominant allele: the expressed form of a gene when 2 different alleles are present. *ex. Tt (T is dominant; the plant is tall) • recessive allele: a form of a gene that is not expressed when the dominant allele is present (masked). • genotype: the set of alleles an individual has for a character. *genetic makeup -includes both genes in a homologous pair of chromosomes. -ex. Rr, rr, RR • phenotype: the trait that results from a set of alleles. – *-ex. tall, short, purple, white. • Genotype determines phenotype! • homozygous: 2 alleles in a gene pair are identical. • heterozygous: 2 alleles in a gene pair are different. • Punnett square: shows the expected outcomes of a genetic cross. *shows all possible combinations of gametes. (ch.12.3) • Probability: the likelihood that a specific event will occur. – can be written as a %, fraction, ratio, or in words • EXAMPLES • Test Cross: used to determine an organism’s genotype. -done by breeding the organism whose genotype is unknown with a homozygous recessive organism (known genotype). -ex. G = green (dominant) g = yellow (recessive) -Question: what is the genotype of a plant with green peas?...to find the answer, we can perform a test cross. Mono vs. Dihybrid Crosses • Monohybrid Cross: predicts the offspring of a cross for one trait (ex. plant height). • Dihybrid Cross: predicts the offspring of a cross for two traits (ex. plant height and seed shape). EXAMPLES (dihybrid) • coin toss with 2 pennies the outcome of 1 flip doesn’t influence the outcome of the other b/c the coins are not attached in any way (independent of one another).