Solutions
advertisement

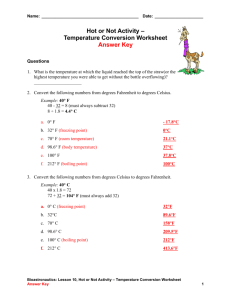
Effects of Solutes in Solution Define: boiling point, freezing point and electrolytes. Explore the effect of solutes on the boiling point and freezing point of solutions (colligative properties). Describe the behavior of electrolytes in a solution. Essential Questions 1. What effects do solutes have on the boiling and freezing points of solvents? Aim How do solutes affect the properties of the solution? Key Words 2. What forces are responsible for these effects? 3. How does the presence of electrolytes affect a solution? boiling point, freezing point, elevation, depression, ions, electrolytes, conductivity What is the Boiling Point of Water at STP? B.P. (Boiling Point) = __________ H2O F.P. (Freezing Point = _________ Predict what happens to the B.P. and the F.P. of water when NaCl is added? F.P. _______ B.P. _________ Boiling Point Elevation Recall Boiling is transition between two states of matter Recall the following concept covered last semester: what attractions/forces are responsible for states of matter. Intermolecular Forces! Examples of Intermolecular forces What kind of intermolecular forces are at play between NaCl and H2O? ___________________________________ ____ Molecule-Ion Attraction The intermolecular force between NaCl and water are very strong and therefore, very hard to break. How is this related to the boiling point elevation of the solution? _____________________________ __ Freezing Point Depression Hint: Solids Consist of a Rigid Crystalline Structure Why does the presence of solutes lower the freezing points of solvents? Solutes Get in the Way! When solutes are present, it becomes more difficult for water molecules to connect with each other in order to form a rigid solid shape. Also, solutes interact with solids to dissolve the solid. In the same way that water dissolves solutes, solutes dissolve ice (example: NaCl). Complete the Following Dissolving “Reactions” A. C12H22O11(s) + H2O(l) __________________________ 1. How many different particles will be “floating” in water? Which one(s)? _____________________________________________ Deduction Question A. NaCl(s) + H2O(l) __________________________________________ 1. How many different particles are “floating” in solution? Which one(s)? _____________________________________________________________________________________ B. CaCl2(s) + H2O(l) _________________________________________ 1. In how many parts does CaCl2 break up? Which one(s)? _____________________________________________________________________________________ C. From NaCl and CaCl2, which salt do you predict will be more effective in melting the snow? Explain? ________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ Hypothesize! According to your answers to the previous question, what conclusion can be drawn? Explain. _______________________________________________ _____ _______________________________________________ Hypothesize! What conclusion can be drawn from the diagram? _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ Notes IV. Effects of Solute on Solvent Properties A. Boiling Point Elevation – a rise in boiling point of a solution caused by the presence of solutes (ex. addition of antifreeze to car radiators to prevent the water from boiling). B. Freezing Point Depression – a lowering of the freezing point of a solution caused by the presence of solutes (ex. using salt to melt ice). C. Colligative Properties – Properties that depend on the number of solutes and the nature of the solvent but NOT on the identity of the solute. i. Boiling point elevation and freezing point depression are colligative properties. ii. The more particles of solute a solution contains, the more the affect on boiling & melting points. Number of solute : B.P. of Solvent : F.P. of Solvent Does Water Conduct Electricity? Can we add something to the water to make it conduct electricity? If so, what can we add? NaCl v.s. Sugar Does solid NaCl Conduct Electricity by itself, without water? What happens in the dissolving of sodium that allows it to conduct electricity in solution? Notes D. Conductivity – conductivity of electrical current by a solution caused by the presence of electrolytic solutes. 1. Electrolytes – are solutes that dissociate/ionize (separate into ions) in water and are therefore, able to conduct electricity in solution form (Ex: Salts). 2. Electricity - the flow of charges (such as ions in solution or electrons in metallic bonds). Video Electrolytes Animation http://youtu.be/aELPrWzixeU Learning Check 1. When ethylene glycol (an antifreeze) is added to water, the boiling point of the water a. decreases, and the freezing point decreases b. decreases, and the freezing point increases c. increases, and the freezing point decreases d. increases, and the freezing point increases 2. Which solution will freeze at the lowest temperature? a. 1 mol of sugar in 500 g of water b. 1 mol of sugar in 1000 g of water c. 2 mol of sugar in 500 g of water d. 2 mol of sugar in 1000 g of water Learning Check 3. A 1-Kilogram sample of water will have the highest freezing point when it contains 3. 1 x 1017 dissolved particles 4. 1 x 1019 dissolved particles c. 1 x 1021 dissolved particles d. 1 x 1023 dissolved particles 4. At standard pressure, an aqueous solution of sugar has a boiling point a. b. c. d. greater than 100°C and freezing point greater than 0°C greater than 100°C and freezing point less than 0°C less than 100°C and a freezing point greater than 0°C less than 100°C and a freezing point less than 0°C 5. Which solution containing 1 mole of solute dissolved in 1000 grams of water has the lowest freezing point? a. KOH(aq) b. C6H12O6(aa) c. C2H5OH(aq) d. C12H22O11(aq) Notes Effects of Solutes on the Properties of Solvents Notes IV. Effects of Solute on Solvent Properties A. Boiling Point Elevation – a rise in boiling point of a solution caused by the presence of solutes (ex. addition of antifreeze to car radiators to prevent the water from boiling). B. Freezing Point Depression – a lowering of the freezing point of a solution caused by the presence of solutes (ex. using salt to melt ice). C. Colligative Properties – Properties that depend on the number of solutes and the nature of the solvent but NOT on the identity of the solute. i. Boiling point elevation and freezing point depression are colligative properties. ii. The more particles of solute a solution contains, the more the affect on boiling & melting points. Number of solute : B.P. of Solvent : F.P. of Solvent Notes D. Conductivity – conductivity of electrical current by a solution caused by the presence of electrolytic solutes. 1. Electrolytes – are solutes that dissociate/ionize (separate into ions) an aqueous solution and as a result, the solution is able to conduct electricity (Ex: salts such as NaCl or CaCl2). 2. Electricity - the flow of charges (such as ions in solution or electrons in metallic bonds). 3. The higher the concentration of ions within a solution, the greater the degree of conductivity of a solution.