Ecology Intro
advertisement

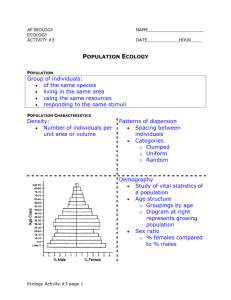
Introduction to Ecology Notes Ecology The scientific study of interactions between organisms and their environments. Ecologist A scientist who studies these interactions in order to understand the abundance and diversity of life within Earth's ecosystems. What is ecology about, anyway? • Ecology is the study of the relationships of living things to each other and to what’s around them. So, if you are learning about what kinds of relationships fish have with other animals (including us!) and plants in their neighborhood, then you are learning about ecology. • The word ECOLOGY comes from Greek words meaning “study of the household.” That means that ecology is the study of the “household” of living things: their neighbors and neighborhood. • Ecology includes not only how living things interact with each other, but how they interact with their physical environment: things such as climate, water, and soil. • Ecologists are the scientists who study ecology. They are curious and like to learn about living things by observing them, seeing what happens, and recording what they find. This is all part of the scientific method. What does Ecology look like? Organization of Life Biosphere Biomes Ecosystems Communities Populations Organisms Biosphere The regions of the surface and atmosphere of the earth or other planet occupied by living organisms. Ecosystems Ecosystems are dynamic interactions between plants, animals, and microorganisms and their environment working together as a functional unit. Ecosystems will fail if they do not remain in balance. Communities a group of actually or potentially interacting species living in the same place. A community is bound together by the network of influences that species have on one another. Population a group of individuals of the same species living in a particular geographic area. Organism/Species Individual members that form a population. Environment Is everything that surrounds a living thing and acts upon it. The environment is where all living things get the materials they need for survival. Interact The process of organisms acting upon one another or on the nonliving parts of their environment. Biotic Factors Biotic factors – all living organisms in a biosphere Biosphere – life-supporting layer of Earth Abiotic Factors Nonliving factors in an environment Examples: Air currents Temperature Moisture Light Soil Three Basic Approaches to Modern Ecological Research Observing – Ecologist observe interactions between living things and their environment. Observing these interactions and phenomena is often difficult because they occur over long periods of time Experimenting – Ecologists experiment with setting up artificial environments in laboratories because this enable them to better control factors in the environment Modeling – Ecologist use models to represent both small and large geographical areas. Models often include mathematical formulas. HW: What is Ecology? Complete the “What is Ecology?” Worksheet A Periwinkle could be either a snail or type of flower. In the lesson we assume that it is a snail. A Gull is a long-winged, web-footed seabird with a raucous call, typically having white plumage with a gray or black mantle. Cordgrass, also called marsh grass, or salt grass, any of 16 species of grasses constituting the genus Spartina (family Poaceae). The erect, tough, longleaved plants range from 0.3 to 3 metres (1 to 10 feet) in height and are found on marshes and tidal mud flats of North America, Europe, and Africa. Exit Ticket Complete the Ecology 4square or Frayer Model Define, Connect, Illustrate, Write a Sentence