Week 1 Slides
advertisement

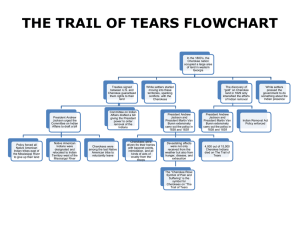
Forced Removal Murder is murder and somebody must answer Private John G. Burnett 1802 Thomas Jefferson promised to Delaware and others to respect all treaties but, Also planning to move them 2 ways Trade Might Trade Bring civilization to “savages” “we shall push our trading houses, and be glad to see the good and influential individuals run into debt” “because we observe that when these debts get beyond what the individuals can pay, they become willing to lop them off by cession of land” Might No regulation on frontier Leads to warfare Army steps in to make peace, dictate peace terms and You guessed it! land cession part of peace 200,000 square miles in nine states during presidency Next big push in 1830 with the Indian removal Act Andrew Jackson “What good man would prefer a country covered with forests and ranged by a few thousand savages to our extensive republic studied with cities, towns, and prosperous farms embellished with all the improvements that art can devise or industry execute by more than 12 million happy people and filled with the blessings of civilization, liberty and religion” – State of the Union 1830 Jackson new this but needed the Cherokee and others to be “Savage” in order to disposes them Jefferson –Culturally inferior but capable of improvement Jackson –Racially inferior and incapable of change Cherokee most well known movement “trail of tears” But many others also forced to move west Video Clip Two factors arise from removal that will affect Native Americans post 1840 1. White conceptions and action cause friction within and abuse of Native American communities 2. Explanation of importance of court cases – A. Cherokee Nation V Georgia – B. Worcester V Georgia QUESTIONS FOR CONSIDERATION 1. What do the following Marshall and Ross documents reveal about the status of Indian nations in the United States? Identify key passages and consider their bearing on the standing and sovereignty of Indian tribes. 2. How does John Marshall define the place of Indian tribes in the federal constitutional system? Which of his statements about Indian rights and sovereignty seem to be most important—and most relevant to the political aspirations of Indian peoples today? 3. What does John Ross identify as the "strong shield" of Cherokee rights, and what does he see as the threat to those rights? John Marshall Supreme Court lacked original jurisdiction over Native Americans “Domestic, dependent nations” – Retain some aspect of sovereignty from treaties Marshalls opinion was a feeble gesture compared with Georgia’s dramatic assertion of state power when it hung Corn Tassel – Legal Scholar Sidney Harring Cherokee Nation V. Georgia Worcester V Georgia Established the legal doctrine in American Law of American law of United States Native American Relations Marshall Cherokee Nation “a distinct community occupying its own territory . . .in which the law of Georgia can have no right to enter without the consent of the Cherokee” Federal – Native American relationship stronger than State –Native American relation ship 19th C focus on Domestic and Dependent 20th C focus on Nation “Tribes are sovereign nations with broad inherent powers that, almost without exception, exist by dint of inherent right not by delegation” “one cannot really understand the field (Indian law) without understanding Worcester” – Charles F. Wilkinson