Jacksonian America, 1824-45
advertisement

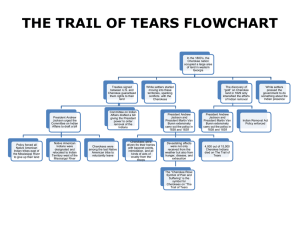
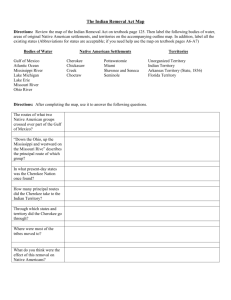
Jacksonian America, 1824-45 I). Democratizing America? II). Religious Fervor III). Rise of Andrew Jackson IV). Indian Policy V). Political Parties Things to consider Expansion & reduction of democracy Deepening of slavery Role of government in economic, social, cultural, national life Mass political movements Religion and politics Indian sovereignty & U.S. democracy Democratizing America? -No property -Popular election of officials -Non-farming groups -Voters chose electors & Pres -All white male political equality Reducing Democracy -Citizen defined practically as white and male -Women lacked voting rights: treated as male property, no legal status -Increased oppression of blacks *Growth of slave codes *Punishment against free blacks *Racial inferiorities “biological” *Slave rebellions The Rise of Andrew Jackson -b.1767: humble birth -Western lawyer -Scots-Irish, farmer -War hero -Indian fighter “Jacksonian Democrats” The Politics of Image -Vote for the party, the policies, the person, or the perception? -“Populist” image -Emotionalism -Mass politics/parties -Communication & organization Election of 1828 Jackson’s Inauguration Party Jackson Presidency, 1828-1836 -Image of antielitism, big gov’t, North East -Rejected Nat’l Bank & “American Plan” -Spoils System -Pay back supporters Religious Democracy, 1839 Second Great Awakening I). Methodists & Baptists A. Rural & West B. “Choose salvation” C. Pop culture D. Reformist 1830s Lorenzo Dow Democratizing religion -Outlet for women -Church attendance -African Americans -Emotionalism and evangelicalism -American Political System -Slavery & women’s rights African American Religion J.L. Kimmel, 1935 Jackson and the Indians I). Eastern Indians after IV). Indian Removal Act 1812 V). Resistance II). “Five Civilized Tribes” VI). Trail of Tears III). Georgia Indian Nations after 1812 -British eliminated -Tecumseh defeated -Treaties and land -125,000 Natives -Conflict with states -Assimilation? -Extermination? -Removal? “Five Civilized Tribes” Cherokee Choctaw Chickasaw Creek Seminole William McIntosh Cherokee Nation Constitution Dictionary Cherokee Phoenix Bilingual Schools & churches Sequoyah Georgia and the Cherokee GA ignored 1827 constitution Jurisdiction over tribe Farm land Barred from court Gold, 1829 Indian Removal Act, 1830 Jackson disliked federal-Indian relations Did not want to void treaties “Save” the Indians from harm East of the Mississippi River Open land for white farmers Resistance to Removal, 1831-2 Cherokee v. Georgia Worcester v. Georgia -Tribe sued Georgia -Are Cherokees a foreign nation? -Rev. Samuel Worcester -GA arrested him -Sued GA, won in Court -“Domestic dependent nations” -Indians and federal gov’t -States lack power on res. Chief Justice John Marshall “…one of the great constitutional crises in the history of the nation.” Jackson Ignored Marshall Cherokee Removal Chief John Ross Opposed removal 16,000 signatures Wife died on Trail of Tears Chief until 1860s Trail of Tears 1838: ¼ Died on trip No compensation for property Cold, hunger, disease Some refused to go, remain in GA, NC, TN Indian Removal More Removal to Indian Territory Conclusions re: Indian affairs 1840s Indian Affairs shift to Plains Most Natives relocated east of Miss. Seminole Wars in Florida Indian Nations above states Direct relations with federal gov’t. Conclusions for Jacksonian America Mass politics Growth and decline of democracy Religious revivalism Importance of Race Indian removal and resistance