File
advertisement

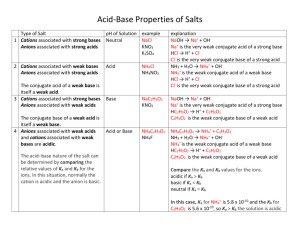
CJ Bianconi Chem102 Spring 2015 Acids & Bases Worksheet Key Acids 1. What two things in the formula of a neutral molecule will indicate that it is acidic? Starts with H or ends with COOH 2. What are the strong acids? HI, HBr, HCl, HNO3, HClO4, H2SO4 3. What is the Arrhenius definition of an acid? It produces H+/H3O+ when added to water 4. What is the Bronsted-Lowry definition of an acid? It is a proton donor 5. How can you take an acid and turn it into its conjugate base? Remove one H+ from the molecule 6. What is the relative strength of the conjugate base of a strong acid? The conjugate base of a strong acid is neutral 7. What type of ion can potentially be acidic? What can we see about this type of ion to confirm if it is acidic, rather than neutral? Cations can be acidic, specifically high charge density metal cations and substituted ammonium cations 8. List 10 different cations ranging from +1 to +3. Include one complex cation. Na+, Co3+, Al3+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Be2+, Cs+, Ni2+, NH4+, Ga3+ 9. From this list, circle the acidic cations. 10. Take one of the acidic cations and write the balanced equation for the reaction that would take place between it and water. Al3+(aq) + 3 H2O(l) ⇋ Al(OH)3(aq) + 3 H3O+(aq) 11. Does the reaction make sense? What is being produced in the reaction? How would Bronsted-Lowry define such a product? The reaction does make sense because Bronsted-Lowry defines an acid as something that produces H+ when added to water, and the balanced reaction shows an acidic cation producing H+ when added to water. CJ Bianconi Chem102 Spring 2015 Bases 1. What things in the formula of a neutral molecule will indicate that it is basic? OH at end, lone pair on N 2. What are the rules for strong bases? Group 1A & heavy Group 2A hydroxides 3. What is the Arrhenius definition of a base? It produces OH- when added to water 4. What is the Bronsted-Lowry definition of a base? It is a proton acceptor 5. How can you take a base and turn it into its conjugate acid? Add one H+ to the molecule 6. What is the relative strength of the conjugate acid of a strong base? The conjugate acid of a strong base is neutral 7. What type of ion can potentially be basic? What can we see about this type of ion to confirm that it is basic, rather than neutral? Anions can be basic, and all anions are basic that are not the conjugate bases of strong acids 8. List 10 anions ranging from -1 to -3. Include one complex anion. F-, I-, Cl-, P3-, Se2-, SO42-, NO3-, S2-, As3-, O29. From this list, circle the basic anions. 10. Take one of the basic anions and write the balanced equation for the reaction that would take place between it and water. F-(aq) + H2O(l) ⇋ HF(aq) + OH-(aq) 11. Does the reaction make sense? What is being produced in the reaction? How would Bronsted-Lowry define such a product? The reaction makes sense because Bronsted-Lowry defines a base as something that produces OH- when added to water, and the balanced reaction shows a basic anion producing OH-. Arrhenius asks us if a molecule is _______________an acid or a base____________________. Bronsted-Lowry asks us if a molecule is ____behaving like an acid or a base_______________.