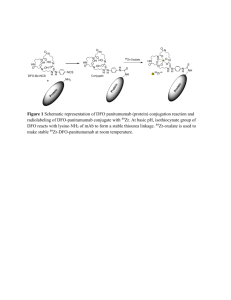
Acid Base Properties of Salts 2013
advertisement
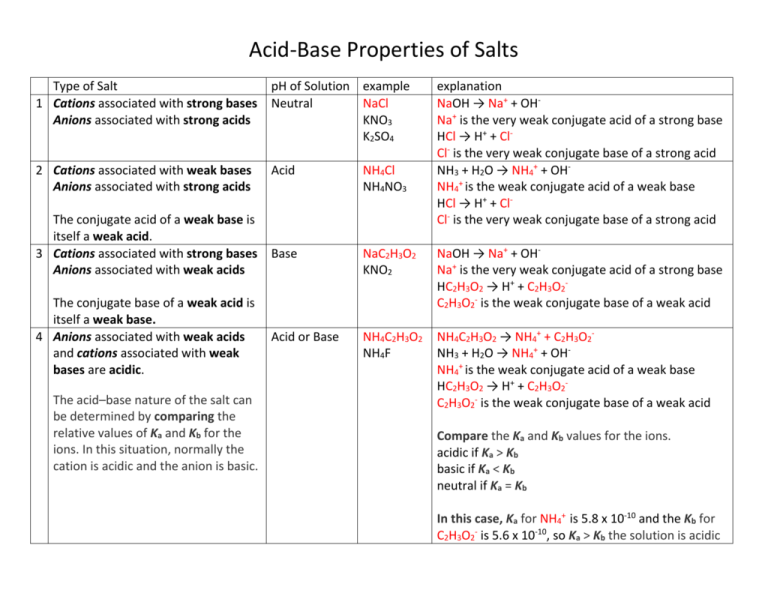
Acid-Base Properties of Salts Type of Salt 1 Cations associated with strong bases Anions associated with strong acids pH of Solution example Neutral NaCl KNO3 K2SO4 2 Cations associated with weak bases Anions associated with strong acids Acid NH4Cl NH4NO3 Base NaC2H3O2 KNO2 NaOH → Na+ + OHNa+ is the very weak conjugate acid of a strong base HC2H3O2 → H+ + C2H3O2C2H3O2- is the weak conjugate base of a weak acid Acid or Base NH4C2H3O2 NH4F NH4C2H3O2 → NH4+ + C2H3O2NH3 + H2O → NH4+ + OHNH4+ is the weak conjugate acid of a weak base HC2H3O2 → H+ + C2H3O2C2H3O2- is the weak conjugate base of a weak acid The conjugate acid of a weak base is itself a weak acid. 3 Cations associated with strong bases Anions associated with weak acids The conjugate base of a weak acid is itself a weak base. 4 Anions associated with weak acids and cations associated with weak bases are acidic. The acid–base nature of the salt can be determined by comparing the relative values of Ka and Kb for the ions. In this situation, normally the cation is acidic and the anion is basic. explanation NaOH → Na+ + OHNa+ is the very weak conjugate acid of a strong base HCl → H+ + ClCl- is the very weak conjugate base of a strong acid NH3 + H2O → NH4+ + OHNH4+ is the weak conjugate acid of a weak base HCl → H+ + ClCl- is the very weak conjugate base of a strong acid Compare the Ka and Kb values for the ions. acidic if Ka > Kb basic if Ka < Kb neutral if Ka = Kb In this case, Ka for NH4+ is 5.8 x 10-10 and the Kb for C2H3O2- is 5.6 x 10-10, so Ka > Kb the solution is acidic 5 Cations are small, highly charged (+2 Acid or +3) metal cations Anions associated with strong acids highly charged (+2 or +3) metal cations are hydrated in water and act as acidic cations. 6 Metal Oxides Basic 7 Non-metal Oxides Acidic AlCl3 CuSO4 AlCl3 → Al3+ + 3 ClAl3+ + 6 H2O → Al(H2O)63+ Al(H2O)63+→ Al(H2O)5(OH)2+ + H+ and a weak acid forms HCl → H+ + ClCl- is the very weak conjugate base of a strong acid CuO Fe2O3 SO2 CO2 CuO + H2O → Cu2+ + 2 OHCopper (II) oxide reacts to form a basic solution. H2O + SO2 → H2SO3 Sulfur dioxide gas reacts with water to form sulfurous acid Problems: Identifying Salt Solutions as Acid, Neutral or Basic: 1. 2. 3. 4. KCl K2CO3 NH4NO3 NaF Find the pH of the following solutions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 0.250 mol/L KCl 0.100 mol/L K2CO3 0.0100 mol/L NH4NO3 0.050 mol/L NaF 0.200 mol/L AlCl3 0.500 mol/L NaC2H3O2 5. 6. 7. 8. Na2SO3 NH4Cl AlCl3 N2O 9. NaClO4 10.NH4Cl 11.NaC2H3O2 12.PbO