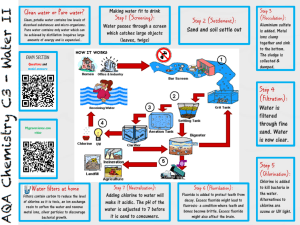
Halogens - singhscience
advertisement

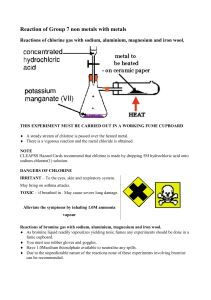
Halogens Elements in the Halogen Group Group 7 Elements • Similar reactions to with other elements because they all gain one electron. • All react with metals to form compounds called halides. • Fluorine is the most reactive halogen, and the reactivity decreases as you go down the group. • They are diatomic (Cl2 Fl2, they always exist in pairs) Properties of Halogens Need to learn! Element Symbol State at Colour room temperature Fluorine F Gas Pale Yellow Chlorine Cl Gas Bromine Br Liquid YellowGreen Red-Brown Iodine I Solid Grey Equations for Reactions of Halogens with Metals You just saw iron reacting with chlorine, can you write a word equation for this reaction? What might the symbol equation for this reaction be? Some More Examples (Ide at the end when combined) 1. Potassium + Chlorine Potassium Chloride 2. Calcium + Bromine Calcium Chloride Halogens and hydrogen (Used to make acids) • The halogens react with hydrogen gas to form halogen halides. These form acids when they dissolve in water. • For example: hydrogen (g) +fluorine (g) → hydrogen fluoride (g) H2 + F2 → 2HF When hydrogen fluoride dissolves in water it makes hydrofluoric acid, HF(aq) (aq) means aqueous – Latin for dissolved in water Your turn 1. Write word and balanced symbol equations for the reactions of hydrogen with a) chlorine b) bromine 2. Which acids are formed from a) and b)? Answers 1. a) hydrogen (g) + chlorine(g) → hydrogen chloride (g) H2 + Cl2 → 2HCl b) hydrogen (g) + bromine(g) → hydrogen bromide (g) H2 + Br2 → 2HBr 2. Hydrochloric acid, hydrobromic acid Hydrofluoric acid All the acids just named are extremely hazardous. Hydrofluoric acid is used in etching glass. It has the following hazard symbols. What do they mean? When we say wear goggles, we really mean it. Example of burns from HF acid, from a home glass polisher kit. Toxic and corrosive. It is absorbed through the skin and bonds to calcium in your bones! Displacement reactions Some elements are more reactive than others. A reactive metal will displace (take the place of) a less reactive one to form a compound. For example: Iron + copper sulphate → iron sulphate + copper Which is the more reactive metal, iron or copper? Iron!! Displacement Reactions of Halogens • These can be used to work out how reactive the different halogens are. • A more reactive halogen will displace a less reactive halogen from its compounds. • In the example below chlorine is more reactive than bromine, so chlorine displaces bromine from a bromide. Potassium Iodide + Chlorine Potassium Chloride + Iodine The order of reactivity of the halogens is: Reactivity decreases Fluorine Chlorine Bromine Iodine Astatine Balanced symbol Equations NB, remember the halogens are diatomic molecules this means that in their natural state they are so reactive that they exist as two atoms joined together. Chlorine + potassium bromide → potassium chloride + bromine (red-brown) Cl2 + 2KBr → 2KCl + Br2 Chlorine + potassium iodide → potassium chloride + iodine (brown/purple) Cl2 + 2KI → 2KCl + I2 Bromine + potassium iodide → potassium bromide + iodine Br2 + 2KI → 2KBr + I2 Exam question (c) When chlorine is added to a solution of potassium bromide, a colour change is seen. When chlorine is added to a solution of potassium fluoride, no colour change is seen. Explain how these observations provide evidence for the order of reactivity of bromine, chlorine and fluorine. (6 marks) *(c) A explanation to include some of the following points • colour change shows reaction occurs • chlorine reacts with potassium bromide solution • bromine is formed • colour is red brown • chlorine displaces bromide ions • chlorine is more reactive than bromine • no colour change shows no reaction / chlorine does not react with potassium fluoride solution • chlorine does not displace fluoride ions • chlorine is less reactive than fluorine • order of reactivity from most reactive halogen is fluorine, chlorine, bromine Level 1 1-2 2 3-4 • a limited description of at least two relevant points either from one reaction or from both reactions • the answer communicates ideas using simple language and uses limited scientific terminology • spelling, punctuation and grammar are used with limited accuracy • a detailed description of one reaction (one minor omission may be ignored) / a limited description of some aspects of both reactions • a detailed description of one reaction (one minor omission may be ignored) / a limited description of some aspects of both reactions • spelling, punctuation and grammar are used with some accuracy 3 5-6 • a detailed description of both reactions (one minor ommision may be ignored) • the answer communicates ideas clearly and coherently uses a range of scientific


![[1] - Boswellsgmt](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006603407_1-fadfbce8d94050a9fb3c38a07d86e8ee-300x300.png)