What is statistics
advertisement

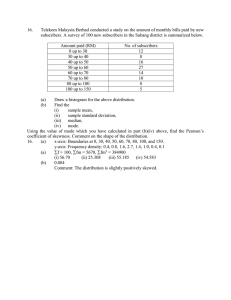
1. Introduction What is statistics? • Statistics as a subject provides a body of principles and methodology for : - (1) designing the process of data collection, - (2) summarizing and interpreting the data, - (3) and drawing conclusions or generalities. Three branches of Statistics • (1) designing the process of data collection = Experimental Design. • (2) summarizing and interpreting the data = Descriptive Statistics. • (3) and drawing conclusions or generalities = Inferential Statistics. Population vs. Sample • A (statistical) population includes each element from the set of observations that can be made. • A sample consists only of observations drawn from the population. Population vs. Sample • The population for a study of how long an infant might be all children born in the UK in the 1980's. • The sample might be lengths of all babies born on 7th May in any of the years. Population vs. Sample • We want to know things about populations. • But we do not have the data of population. Because: • Collecting the population data often impractical or impossible. • Instead, we collect a sample data. • Example: If a company's customer service division wanted to learn whether its customers were satisfied, it would not be practical (or perhaps even possible) to contact every individual who purchased a product. Instead, the company might select a sample of the population. Population vs. Sample • Example: • You want to know the mean income of the subscribers to a particular magazine—a parameter of a population. • You draw a random sample of 100 subscribers. • The sample mean income is $27,500 (a statistic). You conclude that the population mean income is likely to be close to $27,500 as well. Sample Size • The number of observations in a sample is its sample size. • Usually, a sample has sample size less than or equal 30 is a small sample, otherwise it is a large sample. Group work - Collecting a sample 1) Determine the number of hours per day OU student plan to study. 2) Determine the number of hours per day this year freshman in OU plan to study. - Collect a large sample from the population. - Describe how you collect your sample data. - Present your sample data. - Write some comments, or draw some conclusion, hypothesis about the data. - Work in group of 2 and turn in a typed-in solution. - Due: August, 31st.