12.1 The PPF, Economic Growth, and Productivity
advertisement

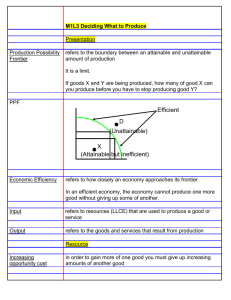
2.1 The PPF, Economic Growth, and Productivity SLIDE 1 12 Economic Growth 12.1 The PPF, Economic Growth, and Productivity 12.2 Living Standards and Labor Productivity Growth 12.3 Issues of Technological Change CONTEMPORARY ECONOMICS © Thomson South-Western 2.1 The PPF, Economic Growth, and Productivity SLIDE 2 CONSIDER Why is the standard of living so much higher in some countries than in others? How can a nation boost its standard of living? Why is the economy’s long-term growth rate more important than short-term fluctuations in economic activity? What is labor productivity, and why has it grown faster in recent years? Are firms or are governments better positioned to identify the growth industries of the future? CONTEMPORARY ECONOMICS © Thomson South-Western 12.1 The PPF, Economic Growth, and Productivity Objectives Use the production possibilities frontier to analyze economic growth. Define labor productivity, and discuss what can increase it. CONTEMPORARY ECONOMICS © Thomson South-Western 12.1 The PPF, Economic Growth, and Productivity Key Terms standard of living productivity labor productivity human capital physical capital capital deepening rules of the game CONTEMPORARY ECONOMICS © Thomson South-Western 2.1 The PPF, Economic Growth, and Productivity SLIDE 5 The PPF and Economic Growth The production possibilities frontier shows alternative combinations of goods that the economy can produce if available resources are used efficiently. An outward shift of the production possibilities frontier reflects economic growth. CONTEMPORARY ECONOMICS © Thomson South-Western 2.1 The PPF, Economic Growth, and Productivity SLIDE 6 Economic Growth What can generate economic growth? Greater availability of resources An improvement in the quality of resources Technological breakthroughs that make better use of resources Improvements in the rules of the game that enhance production incentives CONTEMPORARY ECONOMICS © Thomson South-Western 2.1 The PPF, Economic Growth, and Productivity SLIDE 7 Capital and Growth The amount of capital produced this year will affect the location of the PPF next year. Economies that save more can invest and grow more. CONTEMPORARY ECONOMICS © Thomson South-Western 2.1 The PPF, Economic Growth, and Productivity SLIDE 8 Economic Growth Shown by Outward Shifts of the Production Possibilities Frontier Figure 12.1 CONTEMPORARY ECONOMICS © Thomson South-Western 2.1 The PPF, Economic Growth, and Productivity SLIDE 9 Productivity The standard of living is an economy’s level of economic prosperity, best measured by the value of goods and services produced per person. CONTEMPORARY ECONOMICS © Thomson South-Western 2.1 The PPF, Economic Growth, and Productivity SLIDE 10 Labor Productivity Productivity compares total output to a specific measure of input. Labor productivity is the output per unit of labor. CONTEMPORARY ECONOMICS © Thomson South-Western 2.1 The PPF, Economic Growth, and Productivity SLIDE 11 Human and Physical Capital Human capital is the accumulated knowledge, skill, and experience of the labor force. Physical capital, or capital goods, includes the machines, building, roads, airports, communications networks, and other manufactured creations used to produce goods and services. CONTEMPORARY ECONOMICS © Thomson South-Western 2.1 The PPF, Economic Growth, and Productivity SLIDE 12 Capital Deepening An increase in the quantity and quality of capital per worker is called capital deepening. Capital deepening contributes to labor productivity and to economic growth. CONTEMPORARY ECONOMICS © Thomson South-Western 2.1 The PPF, Economic Growth, and Productivity SLIDE 13 Rules of the Game Rules of the game are the formal and informal institutions that provide production incentives and promote economic activity. Rules of the game include laws, customs, and conventions that encourage people to undertake productive activity. CONTEMPORARY ECONOMICS © Thomson South-Western