The Constitution
advertisement

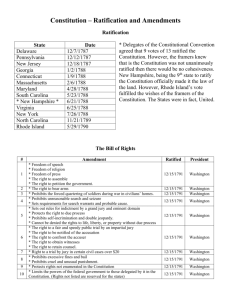
The Constitution Annapolis Convention (1786) o Failure Constitutional Convention / The Philadelphia Convention of 1787 o Delegates from all states Except Rhode Island “The Demigods” Fifty-Five o May 25, 1787 o Washington o Franklin o James Madison – “Father of the Constitution” o Alexander Hamilton The Legislative Branch o The Virginia Plan Representation by population o The New Jersey Plan Representation by State o The Great Compromise / The Connecticut Compromise The Lower House - House of Representatives Population Taxation The Upper House – The Senate Two senators from each state Approve treaties and appointments o Three-Fifths Compromise Slaves count as 3/5 of a person for taxation and representation The Executive Branch o The Presidency o Commander in Chief o Appointment of domestic offices Including judges o Veto o Must be Natural born citizen 35 or older Living in US for a14 years Checks & Balances o “Mobocracy” safeguards Judicial o Chief Justices appointed for life Indirect Election o Electoral college o Senators & State Legislatures Federalists o Pro constitution o Strong Central Government Anti-Federalists o Anti-Constitution o Strong Local Governments o Anti-Federalist Complaints No Bill of Rights No annual elections New Standing Army Ratification o December 1787 Delaware Pennsylvania New Jersey o January 1788 Georgia Connecticut o February 1788 Massachusetts Bill of Rights o April 1788 Maryland o May 1788 South Carolina o June 1788 New Hampshire Virginia Debates in Virginia o Official ratification June 21, 1788 The Federalist Papers o Alexander Hamilton o John Jay o James Madison Late Ratifications o July 1788 New York o November 1789 North Carolina o May 1790 Rhode Island President George Washington o The First Cabinet Secretary of State: Thomas Jefferson Secretary of the Treasury: Alexander Hamilton Secretary of War: Henry Knox The Bill of Rights o Amendment 1 - Freedom of religion, speech, press, right to peaceful assemble and petition. o Amendment 2 - Right to bear arms. o Amendment 3 - Protection from quartering soldiers in homes. o Amendment 4 - Protection from searches or seizures without a warrant. o Amendment 5 - Right to not testify against one's self and protection from double jeopardy. o Amendment 6 - Guarantee of a proper trial. o Amendment 7 - Guarantee of a jury trial. o Amendment 8 - Protection from excessive bail or fines. o Amendment 9 - Statement that people have rights that are not even listed here. (The People's Rights Amendment). o Amendment 10 - Statement that any power not granted in the Constitution is left to the states. (The State's Rights Amendment). The Judicial Branch o The Judiciary Act of 1789 Supreme Court Federal Courts Circuit Courts Attorney General o John Jay First Chief Justice