2011 Ecosystems PPT (1) bio II
advertisement

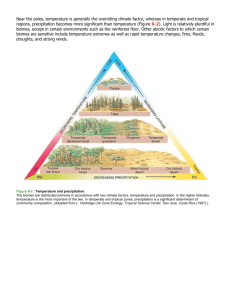
Biology Ecology Ecology Ecology is the study of the relationships among organisms and their environment. Studying organisms in their environment organism population community ecosystem AP Biology biosphere Components of Ecosystems Abiotic = nonliving chemical & physical factor Biotic= living factors Components of Ecosystems Population = group of individuals of the same species in a particular geographical area Community = assemblage of populations of different species Ecosystem = all abiotic factors and the community of species in an area A biome is a major regional or global community of organisms characterized by the climate conditions and plant communities that thrive there. Biome Ecosystem Ecosystem Community Community Population Population Organism Organism Terrestrial Biomes Biomes You Should Know Tundra Taiga Temperate Rainforest Tropical Rainforest Temperate Deciduous Forest Temperate Grassland Chaparral Desert Savanna Tundra Northernmost biome – Frozen layer of subsoil (permafrost) – Low-growing vegetation adapted to extreme cold/short growing season – Little Precipitation – Relative cold all year Taiga Cold winters short growing season acidic, mineral-poor soil Coniferous trees Temperate Rainforest – Large conifers – High precipitation – Relatively stable Cool temperatures Temperate Deciduous Forest – Precipitation relatively high – Soils rich in organic matter – Broad-leaf trees that lose their leaves seasonally dominate Temperate Grassland – Deep, mineral-rich soil – Moderate but uncertain precipitation – Well suited to growing grain crops Chaparral – Thickets of small-leaf evergreens – Climate of wet, mild winters and dry summers Desert – Cold deserts in temperate climates – Warm deserts in subtropical or tropical regions – Low levels of precipitation – Organisms with specialized water-conserving adaptations Savanna – Tropical grassland – Widely scattered trees interspersed with grassy areas – Occurs in topical areas with low or seasonal rainfall Tropical rain forest – Mineral-poor soil – Layers of vegetation (canopy, understory, ect) – High rainfall evenly distributed throughout the year – High species richness and high productivity Quiz Be ready for a possible quiz on these Biomes. Page 463 in your text will help. • Name of each major terrestrial biome • Area of the world where the biome is located • Climatic conditions (main abiotic factors) • Primary types of vegetation • Common animals found in each biome Aquatic Biomes Aquatic Biomes • Aquatic Biomes are those biomes located in bodies of water • All Aquatic Biomes are based upon the salinity (saltiness) of the water. • There are 3 Kinds of Aquatic Biomes: – Marine: High Salinity Level (Saltwater) – Estuary: Moderated Salinity Level (Mildly Salty) – Freshwater: Little to No Salinity Levels at all Freshwater • Ponds & Lakes –Deep and still water • Streams & Rivers –Moving water • Wetlands –Shallow and still water Marine •Oceans •Coral Reefs •Estuary –Where fresh and salt meet