Wind - Science!
advertisement

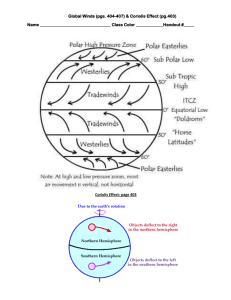
Wind Wind • Wind: the horizontal movement of air • Wind is caused by the uneven heating of Earth’s surface Wind • Wind speed is measured using an anemometer • Wind direction is measured using a weathervane The Coriolis Effect • The Coriolis effect: a shift in the path of a moving object caused by the rotation of the earth on its axis • Animation • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=i2mec3v geaI • Video • hank Coriolis effect • airplane Coriolis Effect • As wind blows, earth rotates underneath it, making the wind appear to curve • Northern Hemisphere: wind is deflected to the right • Southern Hemisphere: wind is deflected to the left Local Winds • Land and Sea Breezes: Land heats up and cools down faster than water • Daytime: low pressure air rises , wind comes from the sea and is called a sea breeze • Nighttime: high pressure air sinks, wind blows out to sea and is called a land breeze Local Winds • Mountain and Valley Breezes • Daytime: warm air from the valley moves up and is called a valley breeze • Nighttime: mountains cool down more quickly than valleys • Cool air sinks down the mountain and is called a mountain breeze Global Winds global winds • Each hemisphere has three looping patterns called convection cells (Hadley cells) • Each cell corresponds to a wind belt, characterized by winds that blow in one main direction (prevailing winds) • Winds are named according to the direction they came from (winds blowing west to east are called “westerly”) Global Winds • Winds are named for the direction they come from • Hadley Convection Cells: Vertical convection currents in the atmosphere (Brown) • global winds Global Winds • Trade winds: between the equator and 30⁰ North or South latitude (green) • Westerlies: between 30⁰ and 60⁰ N or S latitude (red) • (Polar) Easterlies: between 60⁰ and 90⁰ N or S latitude (blue) Global Winds • Doldrums: areas along the equator where there is little wind (orange) • Horse Latitudes: areas near 30⁰ N or S latitude where there is little wind (Yellow) Global winds • Jet Stream: narrow bands of high speed winds in the stratosphere (purple) • Jet streams can affect airline routes and the paths of storms Weather • Weather: the current conditions of the atmosphere • All weather takes place in the troposphere • Included in a weather report: Air temperature, air pressure, cloud type, wind speed and direction, the amount and type of precipitation, moon phase Weather • Weather changes every day because the air in the atmosphere is always moving • Weather also changes because the energy from the sun is constantly being redistributed after it reaches earth’s surface Weather • Meteorology: the study of atmospheric changes (weather) • Climate: the long term weather patterns of a certain area • Climatology: the study of the climate and climate change • Weather can change rapidly, climate changes slowly over time