Air-Pressure-and-Wind-2013
advertisement

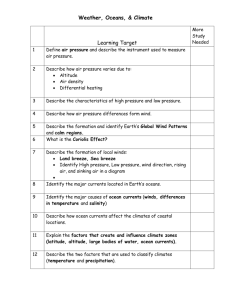
Air Pressure and Wind Name ____________________Period_____ P. 398-402 and 418-424 1. What is air pressure? 2. What is a barometer? 3. What are the two main reasons air pressure changes?_________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 4. Warm air is ____________ than cold air because __________________________ ____________________________________________________________ 5. Warm air contains more water vapor, and the more water vapor the air contains the more _____________ it is. 6. What will the weather be like when air pressure is falling? ___________________ 7. What will the weather be like when air pressure is rising? ____________________ 8. Wind moves from _____ to _____ pressure. 9. A north wind means it is blowing from the north. What does a southwesterly wind mean? ______________________________________________________________ 10. When does a sea breeze occur? Time of Day: __________________ Temperature Land warmer/colder: ___________________ Temperature Water warmer/colder: ___________________ Pressure Land high/low: __________________ Pressure Water high/low: __________________ Sketch a sea breeze 11. When does a land breeze occur? ___________________ Time of Day: day / night: ______________ Temperature Land warmer/colder: ___________________ Temperature Water warmer/colder: ___________________ Pressure Land high/low: __________________ Pressure water high/low: __________________ Sketch a land breeze (The arrows show how air moves during the day. Cool night temperatures affect air pressure. Air moves in the opposite direction at night. Draw arrows on the bottom diagrams to show how the air moves at night.) 12. What is the coriolis effect?____________________________ 13. What does the Coriolis Effect do to a wind in the Northern Hemisphere? GLOBAL WINDS Name __________________ Period____________ DIRECTIONS: 1) Label the names of the global winds on the map below. 2) Finish drawing the direction of winds that are missing on the map. 3) Provide three facts about each of the wind patterns below. POLAREASTERLIES: ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ WESTERLIES: ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ TRADEWINDS: ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ DOLDRUMS: _____________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Answer the following questions. 1. What causes the wind patterns to turn to the right in the northern hemisphere and to the left in the southern hemisphere? _______________________________________________________________________________ 2. In which direction do the polar easterlies move? _____________________ 3. What winds did sailors rely on to move their cargos from Europe to the West Indies and South America? __________________ 4. Which winds play an important part in the weather here in the U.S.? ________________________________ 5. Name the winds near the equator with little or no wind? _______________