File
advertisement

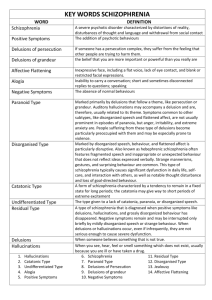
David Rude, MA, CPC Classifying mental disorders Psychotic disorders ◦ Schizophrenia Diagnostic and Statistical Manual for Mental Disorders ◦ First published in 1952 ◦ Updated every few years Reflects updated research and changing attitudes Term Neurosis removed Some disorders removed Some disorders added "Internet-Use Disorder" or IAD Being Added for further consideration to New Edition of DSM Some people who spend a lot of time on the Internet demonstrate similar symptoms to people diagnosed with other addiction disorders, and that the psychiatric community should study it and consider promoting it to a full-blown disorder. Are you Internet addicted…take this test or this test 1. Disruptive mood dysregulation disorder 2. Internet Gaming Addiction 3. Binge-eating Disorder – at least once a week for at least three months 4. Negative Altruism 5. Social Media Narcissism In the news: Can LSD cure alcoholism? Trials show 59 per cent of problem drinkers improve after a single dose of powerful hallucinogen http://www.dailymail.co.uk/sciencetech/article2111687/LSD-alcohol-Trials-59-problem-drinkersimprove-single-dose-hallucinogen.html Mental Disorder: ◦ Significant impairment in psychological functioning Psychotic Disorder ◦ Primary problem Loss of contact with reality ◦ Typical signs of trouble You hear or see things that others don’t; your mind has been playing tricks on you Watch Evaluating Patients with Brain Damage ◦ Primary problem Mania or depression ◦ Typical signs of trouble You feel sad and hopeless Your talk too loud and too fast You have a rush of ideas and feelings that others think are unreasonable. ◦ Primary problem High anxiety or anxiety-based distortions of behaviors ◦ Typical signs of trouble Anxiety attacks and feel like you are going to die Afraid to do things that most people can do Spend unusual amount of time doing things like washing your hands or counting your heartbeats. Somatoform disorders ◦ Primary problem Bodily complaints without an organic (physical) basis ◦ Typical signs of trouble Feel physically sick, but your doctor says nothing is wrong with you Suffer from pain that has no physical basis Preoccupied with thoughts about being sick ◦ Primary problem Amnesia, feelings of unreality, multiple identities ◦ Typical signs of trouble Major gaps in your memory of events Feel like you are a robot or a stranger to yourself Others say you have done things you don’t remember doing ◦ Primary problem Unhealthy personality patterns ◦ Typical signs of trouble Your behavior patterns repeatedly cause problems At work School In your relationships with others Watch Deep Brain Stimulation, parts 1 and 2 ◦ Primary problem Disturbed gender identity, deviant sexual behavior, problems in sexual adjustment Watch video on Transgender Professor ◦ Typical signs of trouble Feel that you are a man trapped in a woman’s body (or the reverse) Can only gain sexual satisfaction by engaging in highly atypical sexual behavior Have problems with sexual desire, arousal, or performance ◦ Primary problem Disturbances related to drug abuse or dependence ◦ Typical signs of trouble Drinking too much Using illegal drugs Taking prescription drugs more often than you should Watch video on Addiction Transfer & Teenage Prescription Drug Abuse Social Conditions ◦ Poverty, homelessness, overcrowding, stressful living conditions Family Factors ◦ Parents who are immature, mentally ill, abusive, or criminal ◦ Poor child discipline ◦ Severe marital or relationship problems ◦ Disordered family communications Psychological Factors ◦ Low intelligence, stress, learning disorders Biological Factors ◦ Genetic defects or inherited vulnerabilities ◦ Poor prenatal care ◦ Low birth weight Insanity ◦ A legal term ◦ Inability To manage one’s affairs To be unaware of the consequences of one’s actions Consequences of being judged insane (by a court of law) ◦ Not held legally accountable for their actions ◦ Can be involuntarily committed to a psychiatric hospital Many movements today are trying to abolish the insanity plea and defense ◦ Desire to make everyone accountable for their actions ◦ Guilty but insane/mentally ill How is a person declared to be insane? ◦ Established by testimony from expert witnesses ◦ A danger to themselves or to others, or severely mentally disabled ◦ Most often occurs when people are brought to emergency rooms ◦ If two doctors agree Person will either Commit suicide Or hurt someone else They are put into a hospital Two core features ◦ Hallucinations Imaginary sensations Seeing, hearing, or smelling things that do not exist in the real world ◦ Delusions Holds a false belief regardless of the facts Depressive delusions ◦ Feel they have committed horrible crimes or sinful deeds Somatic delusions ◦ Concern the body ◦ One’s body is “rotting away” or emitting foul odors Delusions of grandeur ◦ Thing they are an extremely important person Delusions of influence ◦ They feel they are being controlled or influenced by others or unseen forces Delusions of persecution ◦ Others are “out to get them” Delusions of reference ◦ Unrelated events are given personal significance ◦ A newspaper article or television program is giving a special personal message Most common ◦ Hearing voices Others ◦ Tactile Things crawling on skin ◦ Extreme sensitivity to heat, cold, pain, or touch ◦ Anesthesia - a loss of normal sensitivity Note: ◦ Olfactory hallucinations sometimes occur with seizure disorder (epilepsy) Disturbed emotions ◦ Mood Swings Elation to depression ◦ Flat Affect ◦ Lack of emotional responsiveness Flat affect Disturbed Verbal Communication ◦ Garbled and chaotic speech; word salad Problems with thought, memory, actions or attention Personality Disintegration ◦ When a person’s thoughts, actions and emotions are no longer coordinated ◦ “Lost touch with person, place or time.” Psychosis caused by brain injury or disease ◦ Toxic chemical poisoning (lead, mercury) ◦ Steroid psychosis Dementia ◦ Serious mental impairment in old age ◦ Caused by brain deterioration ◦ Circulatory problems, repeated strokes, general brain shrinkage or atrophy ◦ Results in disturbances in memory, reasoning, judgment, impulse control, and personality ◦ Alzheimer’s Disease is most common form Characterized by ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Hallucinations Delusions Apathy Thinking abnormalities “Split” between thoughts and emotions Symptoms ◦ Emotions may become blunted or very inappropriate ◦ Withdrawal from contact with others ◦ Loss of interest in external activities ◦ Breakdown of personal habits ◦ Inability to deal with daily events Does NOT refer to having split or multiple personalities Disorganized Schizophrenia ◦ Near complete personality disintegration ◦ Incoherence, grossly disorganized behavior, bizarre thinking, and flat or grossly inappropriate emotions ◦ Typically develops in adolescence or young adulthood ◦ Improvement is limited ◦ Impairment is extreme Catatonic Schizophrenia ◦ Marked by stupor where victim may hold same position for hours or days ◦ Period of rigidity resemble tendency to “freeze” at times of emergency or panic ◦ Mute and unresponsive ◦ may sometimes show agitated, purposeless behavior Paranoid Schizophrenia ◦ Preoccupation with delusions of persecution ◦ Also involves hallucinations that are related to a single theme, especially grandeur or persecution ◦ Most common Undifferentiated ◦ Prominent psychotic symptoms ◦ None of the specific features of catatonic, disorganized or paranoid types. Environment ◦ Exposure to influenza or rubella virus during pregnancy ◦ Malnutrition during pregnancy ◦ Complications during birth ◦ Early Psychological Trauma Some individuals inherit a potential for developing schizophrenia Makes them more vulnerable to the disorder Evidence from twin studies