Stakeholder Engagement
advertisement

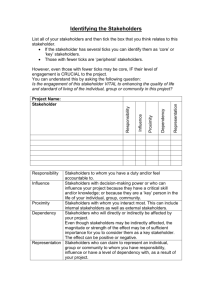
Welcome to the Effective Stakeholder Engagement Briefing 26th February 2009 1 Agenda 8.00am 8.30am 8.35am 8.50am 8.55am 9.10am 9.15am 9.30am 9.35am 10.00am Arrival & Registration Welcome address : Anthony Hyde British American Tobacco : Verity Lawson - Stakeholder Engagement as it relates to Sustainability Reporting Q&A England Marketing : Fiona Tarpey & Jan England - Stakeholder Engagement - why bother and how to do it Q&A Bureau Veritas : Murray Sayce - Stakeholders & Assurance Q&A Summary and close : Anthony Hyde Departure 2 British American Tobacco Verity Lawson Stakeholder Engagement as it relates to Sustainability Reporting 3 Stakeholder Engagement at British American Tobacco Verity Lawson Sustainability Reporting Manager British American Tobacco at a glance World’s most international tobacco group business in 180 countries, over 300 brands global market share approx.17% only international tobacco group with a significant interest in tobacco leaf growing over 53,000 employees 2007 financial performance £ 26bn gross turnover £ 2.9bn profit from operations £ 17bn tax contribution WHY Does BAT carry out Dialogue? Engagement is linked to our Strategy “ To achieve leadership of the tobacco industry through strategies focused on growth, productivity and responsibility ”. Responsibility is fundamental to our strategy for building long term shareholder value We cannot be responsible unless we listen and act on the concerns of our stakeholders. Group Strategy Engagement – HOW we do it Identifying our stakeholders • Persons or organisations who are impacted by our actions • Persons or organisations who’s actions can impact us. • The bigger the potential impact, the more important the stakeholder. Some of BAT’s key stakeholders are: Employees Investors Anti-tobacco lobby Governments Farmers Suppliers Retailers Scientists …but we often have different global and local stakeholders Engagement – HOW we do it Engaging stakeholders is often a challenge for a tobacco company Rigorous approach External expert guidance Stakeholder and issues mapping Independently facilitated dialogue AA1000 Series GRI Guidelines Independent assurance Engagement – HOW we do it Engagement requires a fundamental shift in the way we conduct our business Traditional Decide Deliver Defend Social Reporting Listen Decide Deliver The impact of dialogue on BAT CSI GUIDELINES Youth Smoking Prevention Snus launch May 2005 Social Responsibility in Tobacco Production Social reporting & dialogue allowed us to… Engage constructively with our stakeholders Understand their expectations in depth Ensure these expectations are given due consideration in our decision making Demonstrate with actions that we are responsive to stakeholders’ concerns and thereby gain their trust Provide a powerful incentive for stakeholders to support BAT initiatives Gain recognition that we are a responsible tobacco company So why did we need to change? We made good progress, but: Plc reporting risked lagging behind best practice Reporting on process not performance Comprehensive approach to issues coverage no longer meets stakeholder needs Social reporting adding limited value to the business group-wide 2007-2008 Used stakeholder dialogue to redefine our reporting & issues… Defining materiality Stage one: Mapping dialogue issues level of interest to stakeholders and; current or potential impact on company Stage two: Internal consultation Management board Function’ champions’ Stage three: External consultation CSR experts Issue experts Stakeholder dialogue to review our conclusions Have we included the right issues? Is there anything missing? Feedback on the targets and plans HIGH MEDIUM LOW Level of interest to stakeholders Low impact, high concern issues Medium impact, high concern issues High impact, high concern issues Low impact, medium concern issues Medium impact, medium concern issues High impact, medium concern issues Low impact, low concern issues Medium impact, low concern issues High impact, low concern issues LOW MEDIUM Current or potential impact on Company HIGH BAT’s Sustainability Agenda Harm reduction We will strive to bring commercially viable, consumer acceptable reduced-risk products to market Marketplace We will take a lead in upholding high standards of corporate conduct in our marketplace Supply chain We will work for positive social, environmental and economic impacts in our supply chain Environment We will actively address the impacts of our business on the natural environment People & culture We will work to ensure we have the right people in the right environment to deliver our vision Stakeholder dialogue Dialogue has provided a huge amount of benefit to the business New ideas Opening doors Helping us listen and learn Highly valued across the Group …but it wasn’t perfect Stakeholder fatigue Dialogue for reporting’s sake Asking the same questions and getting the same answers Stakeholder dialogue Dialogue is our unique selling point! Independent facilitation Fully assured Demonstrating responsiveness What we need to do differently Based on business need, not reporting need Balance stakeholder expectations with business impact No more ‘shopping lists’ of expectations Use to guide reporting and inform activity, not dictate it Objectives for dialogue… Creating a vision Gather expectations Still valid if an issue hasn’t been the subject of dialogue in the past How to achieve the vision? Develop targets and measures of success Get stakeholder feedback on a new approach Review strategies and activities To get advice and opinion in areas where we aren’t the experts ‘Sense check’ Are we still heading in the right direction? 2007-2008 Dialogue Topics 2007 Marketplace Supply chain People & culture CSR/Sustainability 2008 Human rights Environment Illicit trade of tobacco products CSR/Sustainability England Marketing Fiona Tarpey & Jan England Stakeholder Engagement why bother and how to do it 21 Stakeholder Engagement – Why bother? And how to do it. 26th February 2009 Who we are Fiona Tarpey – Operations Director Jan England – Managing Director Independent Market Research Agency Established in 1994 Based in Cambridgeshire Extensive experience in agriculture, environment and leisure sectors Team of 11 very experienced researchers MRS Company Partner Investors in People www.englandmarketing.co.uk Why we can talk to you » » » 15 years of experience in helping many companies undertake stakeholder research Knowledgeable and experienced team who share their learning and understand CSR Use tried and tested market research techniques to achieve effective results www.englandmarketing.co.uk Stakeholder Engagement » What is it? » A flamboyant term to describe talking to, listening to, meeting with and reporting back to stakeholders » Who are stakeholders? » Stakeholders are those who have an interest in what you as a company are doing typically they are customers, employees, investors and neighbours www.englandmarketing.co.uk Why engage with Stakeholders? » To understand the perceptions of your company » To confirm how well you are regarded » Gain feedback on how you are performing » Benchmark performance year on year » To build trust – especially in the current economic climate! » To give value and meaning to your CSR activity » To give you a better understanding of the future » To elevate your organisation above the competition to ensure long term sustainability of your activities www.englandmarketing.co.uk Why engage with stakeholders? www.englandmarketing.co.uk The process 1. Stakeholder mapping 2. Define a materiality index 3. Create a matrix 4. Undertake the engagement process 5. Analyse the results 6. Report back 7. Create a benchmark for future years www.englandmarketing.co.uk Stakeholder Mapping Employees Investors Customers Suppliers Media NGOs Academics Government www.englandmarketing.co.uk Stakeholder Mapping » What is their relative importance? » How important are they to you? » How important are your activities to them? » Devise a scale…….. 1 Low www.englandmarketing.co.uk 5 Medium 10 High Stakeholders » Consider your approach......... » What do you ask them? » Do you ask their opinions ahead of developing your strategy or after? » Do you use their opinions to help inform your strategy? www.englandmarketing.co.uk Materiality – what are the issues? Climate Change Food Security Water Supply CO2 Flooding Giving Biodiversity Poverty www.englandmarketing.co.uk Materiality Index » What is their relative importance? » Devise a scale…….. 1 Low www.englandmarketing.co.uk 5 10 medium high Ranking by Importance » Use a matrix to score importance of stakeholder group and importance of material issues » Highest score suggests the areas on which to focus www.englandmarketing.co.uk Matrix of Importance Current Issue Stakeholder Group Customers Employees Climate Change Water Supply CO2 Food Security Flooding Biodiversity Poverty Giving www.englandmarketing.co.uk Suppliers Investors Government NGOs Media Academics Matrix of Importance Current Issue Stakeholder Group Customers Employees Suppliers Climate Change 18 18 16 18 19 15 15 15 Water Supply 14 7 8 12 12 4 6 7 CO2 20 18 16 18 19 16 16 16 Food Security 2 4 2 8 2 3 2 2 Flooding 4 8 6 4 3 8 6 2 Biodiversity 10 9 8 6 4 4 8 10 Poverty 16 9 8 7 15 4 2 4 Giving 10 16 5 6 8 8 6 5 www.englandmarketing.co.uk Investors Government NGOs Media Academics How to talk to Stakeholders Use conventional market research techniques Methodology based on characteristics of stakeholder group » » » » » Face-to-face interviews Telephone interviews Online/postal/touch screen surveys Focus groups and workshops Stakeholder panels Results » Analysed using market research software » Can be linked to a stakeholder management system » Conventional statistical analysis combined with qualitative analysis www.englandmarketing.co.uk Who should do the stakeholder engagement? INTERNAL TEAM VS • Knowledge of the company • Knowledge of the issues • Knowledge of the stakeholders • Could be biased • Lack interviewing skills • Lack experience of analysis of qualitative data www.englandmarketing.co.uk EXTERNAL RESEARCH TEAM • Skills in questionnaire design • Independent and unbiased • Respondents open and honest with third party •Trained interviewers •Familiarity with capture and analysis of data •Understanding of CSR issues •Can benchmark against other organisations •Less knowledge of the company Why bother? In summary………. » Clearer picture of who your stakeholders are » How important they are and why » Focus for developing your strategy www.englandmarketing.co.uk Bureau Veritas Murray Sayce Stakeholders & Assurance 40 26th February 2009 Stakeholders & Assurance London CR reporting – stakeholder engagement • Getting involved in stakeholder engagement can appear as tricky as hooking up with someone who has just been through a messy divorce. • The … baggage that is carried in those two words is … enough to persuade most sustainability managers to take up a monasticEngagement life. is a pretentious catchall phrase that covers: “talking with”, “meeting with”, “listening to”, and “informing” … wrapped up in the notion of transparency 42 CR reporting - best practice in assurance ► Challenge CR strategy and performance Governance and risk Doing the ‘right things’ and in the right way ► Focus on understanding / response to material issues Sector specific issues and ‘Hot topics’ Confidence in robustness of systems and data ► Greater reassurance to stakeholders on management of priority issues and enhanced credibility How stakeholder engagement/feedback is used Stakeholder panels/stakeholder perspectives ► Value protection to value creation From business and CR perspective Assurance process to promote performance improvement ► Strategic / forward looking Overview of CR strategy and reporting Identification of future vision and challenges 43 CR reporting – stakeholder engagement ► Key to building trust and external credibility ► Stakeholders increasingly included in identifying issues ► Identifying and prioritising stakeholders + transparency over who is engaged Of the G250 of which 65% ‘better understand s/holder expectations’ 70 60 40 % 30 20 10 s/holder feedback IN reporting s/holder feedback for reporting s/holder feedback informs strategy identify s/holders 0 structured s/holder engagement % 50 Stage further..: 44 CR reporting – stakeholder engagement • a principles-based, open source framework for quality stakeholder engagement • a robust basis for designing, implementing, evaluating and assuring the quality of stakeholder engagement Stage further..: 45 External Review Committees & Expert Panels ….review, evaluate, scrutinise and recommend • 3rd successive year to assess Sustainability Report and process • express views as individuals, not on behalf of respective organisations • 3 main questions: • has the company selected the most important topics ? • how well has report dealt with these topics / responded to stakeholders ? • did Shell give sufficient information and access to do this ? • to encourage innovation and leadership on sustainable development & CR : • advising on key areas of strategy and performance (objectives, targets, performance, policy, stakeholder relationships & governance) • independent scrutiny of BT’s understanding of critical societal issues; and • advising on new or significantly altered report content. Stage further..: 46 assurance – stakeholder inclusion An approach used for assurance of GSK, 2007/8 – Access to Medicines • Interviews with external stakeholders to evaluate Materiality and Responsiveness • Has material information (around subject matter) been included ? • Does the information help with informed opinions and decisions ? • Is the Company responding to issues / concerns & adequately communicating this ? • Is information clear, understandable, timely and accessible ? • Stakeholder selection based on: • Nature, activities & objectives of stakeholder (PPP, investor, NGO, research…) • Area of concern (R&D, preferential pricing, voluntary licensing…) • openness to collaboration / practicality of engagement. • Standing and credibility Preference also given to groups/ bodies quoted in the Report, to include in the process elements of text verification. 47 assurance – stakeholder inclusion • Private-Public Partnerships • Responsible investors • Governmental Organisations • Non Governmental Organisations And other groups were approached: • Research bodies • Industry groups and associations • Patients’ and consumers’ groups / associations • Others 48 GSK Case study – “what they said…” • ‘GSK a leading organisation on vaccines…’ • ‘PPPs can be very positive if set up well…’ • ‘GSK understands relevance of business model in LDCs’ • ‘compares favourably to peers…’ • ‘[GSK] is at the frontline of R&D for DDW…’ • ‘positive response to tiered vaccine model…’ • ‘Tearing Down the Barriers is good approach…like idea of dual branding…’ • ‘[GSK] keeps us well informed…’ • ‘There is no global access policy or strategy obviously in place’ • ‘Would like to see KPIs on % invested in R&D on DDW’ • ‘What is [GSK’s] real contribution to PPPs?’ • ‘Cheapest prices still may be very high’ • ‘Need to negotiate a model where …increased transparency over price’ • ‘Need innovative approach to IP. Is tighter IP always necessary?’ • ‘Need increased transparency on lobbying’ • ‘Feel aggressively marketed to as a buyer of product’ 49 assurance – outcomes Issues to manage together Statement Opinion: Feedback from indicates that GSK is performing well in relation to vaccines; differential pricing; PPPs…. illustrates a partnership approach to healthcare and… Provides information on direct impacts Main benefits include: • increased visibility amongst important and sometimes ‘difficult’ audiences • enhanced and ‘unfiltered’ evaluation against AA1000 Principles • direct sampling of external perceptions / feedback on subject specific CR activities • through corroboration can accelerate the verification of factual information • helps to form assurance conclusions AND to inform future reporting approach / content • more robust forum to discuss issues of concern independently / anonymously • enhanced process credibility, transparency and reputation recognition 50 assurance – learnings Issues to manage together • Willing participation and positive feedback • Importance of cross-representation • Independence of the process enables greater inclusivity • Confidentiality and the offer of unanimity to gain buy-in • Can build relationships with key s/holder groups • Demonstrate commitment and alignment with the AA1000AS • Need for ongoing communication to maintain levels of trust • Planning time / adequate information to optimise interview process Other considerations • Can be done a scale to suit the assurance engagement • Consider informal /confidential feedback process to reporting organisation 51 52 Thank you for attending Have a safe journey 53