Chapter 12 & 13 Quiz Topics: CNS & PNS
advertisement

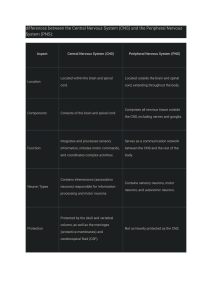
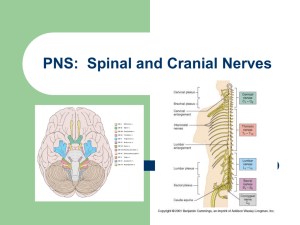
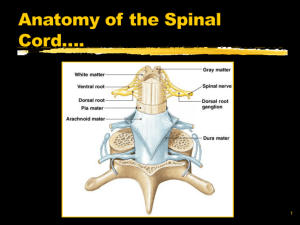
A&P Chapter 12 & 13 Quiz Topics: CNS & PNS Chapter 12: The CNS Major regions of the adult brain White matter v. gray matter Visible structures: sulcus, gyrus, fissure Be able to label major structures & lobes on a diagram of a sagittal section the brain o Cerebrum o Thalamus o Hypothalamus o Cerebellum o Midbrain o Pons o Medulla Overall function of the cerebrum & functional areas of the cerebral cortex o Frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, insula – Know general location and function o Motor areas, sensory areas, association areas o Broca’s Area, Wernicke’s Area, prefrontal cortex, somatosensory cortex, motor cortex Commissures v. association fibers v. projection fibers Location and subdivisions of the diencephalon; Be able to describe the general role of each o Thalamus o Hypothalamus o Epithalamus Three regions of the brain stem and their functions o Midbrain o Pons o Medulla Oblongata Structure & function of the cerebellum How the CNS is protected – Explain how each of the following provides protection o CSF Where is it made? Where is it found? How is it circulated? o Blood-brain barrier o Meninges Dura mater v. Arachnoid Mater v. Pia mater Epidural space v. Subdural space v. Subarachnoid space Structure of the spinal cord: o white matter v . gray matter o lateral (anterior (ventral) horn, posterior (dorsal) horn, interneuron Spinal nerves: broad categories, dorsal root v. ventral root Injuries to spinal cord – paraplegia v. quadriplegia Chapter 13: The PNS Sub- Divisions of the PNS o Sensory v. Motor Sub-Divisions of the Motor System: Autonomic v. Somatic Sub-Divisions of Autonomic System: Classification of sensory receptors: type of stimuli, location, complexity Be able to describe examples of each category of sensory receptor o Mechanoreceptor, thermoreceptor, chemoreceptor, photoreceptor, nociceptor Rods v. Cones for photoreceptors o Exteroceptor, interoceptor, propioceptor Cranial nerves v. spinal nerves – what regions of the body do they serve? Be able to describe functions of the following cranial nerves: o Facial o Oculomotor, Trochlear, Abducens o Olfactory o Optic o Vagus o Vestibulocochlear Reflexes – What are they? Components of a reflex arc (be able to follow the 5 steps of a reflex pathway)