The Central Nervous System
advertisement

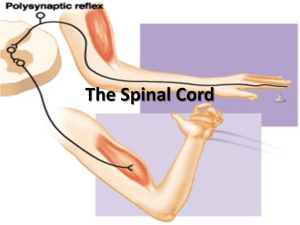
Ch. 5 The Central Nervous System Objectives • Understand how the nervous system is organized • Know the various cell types that are found in nervous tissue and their function • Identify and understand the function of the various parts of the central nervous system • Define and know what memory is • Understand how a reflex arc works Organization and Cells faculty.clintoncc.suny.edu Neurons and Glial Cells • Three functional classes of neurons – Afferent • Four types of glial cells – Astrocytes • Spatial orientation and support • Synapse formation • sensory – Thrombospondin – Interneurons – Efferent • • • • Repair and barrier formation Nourish Degradation of neurotransmitters K+ regulation • motor – Oligodendrocytes • myelination – Microglia • Immune protection • Nerve growth factor – Ependymal cells • Internal lining of CNS • Production of CSF • Neural stem cells yachigusaryu.com Protection and Nourishment • Skull • Oxygen • Meninges – neuroglobin – Dura mater – Arachnoid mater – Pia mater • Cerebral Spinal fluid • Glucose – Secreted by choroid plexus – Rich in Na+ • Blood-brain barrier – Anatomical and physiological barrier csuchico.edu Overview of CNS • Brain and spinal cord • Brain organization – Forebrain • Cerebrum – Cerebral cortex – Basal nuclei • Diencephalon – Thalamus – Hypothalamus – Cerebellum – Brain stem • Midebrain • Pons • medulla open-source-cranio.com Cerebrum • Composed of two hemispheres divided into four lobes – Frontal • Voluntary motor skills, speaking, though – Parietal • Somatosensory processing – Temporal • Auditory processing – Occipital • Visual processing – Hemispherical specialization • Left – logical and analytic • Right – creative and artisitic islamicmiracles.net Motor and Sensory Humunculi • Use-dependent competition – Modifications based on use • Plasticity – Ability to be functionally remodeled structural-communication.com Electroencephalogram (EEG) • Record of postsynaptic activity in cortical neurons – EPSPs or IPSPs • Uses – Brain dysfunction – Brain death – Sleep stages Basal Nuclei and Diencephalon • Basal Nuclei – Regulatory inhibition of motor control – Divided into four regions of grey matter • • • • Caudate nucleus Putamen Globus pallidus Claustrum – Associated with Parkinson’s disease • Diencephalon – Thalamus • Relay station for sensory input • Also involved in motor control – Hypothalamus • Integrates and regulates important homeostatic functions – Body temp – Thirst – Adenohypophysis control The Limbic System • Associated with learning and emotions • Controls basic behavioral patterns – Reward and punishment centers – Motivation – ability to direct behavior to toward specific goals • Norepinephrine, dopamine, and seratonine Learning and Memory • The acquisition of knowledge or skills as a consequence of experience or instruction • The storage of acuired knowledge for later recall • Memory traces – Neural changes responsible for storage of knowledge Short-term Memory • Involve temporary modifications in the function of preexisting synapses • Two types – Habituation • Decreased responsiveness to a repetitive indifferent stimulus • Ca2+ channels do not readily open – Sensitization • Increased responsiveness to mild stimuli following a strong stimulus • Ca2+ channel open and stay open longer – K+ influx prevented • Long term Potentiation – Modifications due to increased use, connection gets stronger the more it is used – Transition to long term memory Long-Term Memory • Involves formation of new, permanent synaptic connections • Immediate early genes – Play a role in memory consolidation – Genes may encode for proteins that are necessary for synapse formation, production of neurotransmitters, answer not clear yet Memory Traces in the Brain • Hippocampus – Declarative memory • The “what’ memories of specific people, places, objects, facts (semantic) and events (episodic) • Cerebellum – Procedural memories • “how to” memories involving repetitive motor skills • Prefrontal cortex – Working memory • Memory necessary to integrate information that is relevant now Cerebellum • Balance and coordination • Three regions – Vestibulocerebellum • Balance and controls eye movements – Spinocerebellum yourbrainetc.tumblr.com • Enhances muscle tone and coordinates voluntary movements – Cerebrocerebellum • Plans and initiates voluntary activity by providing input to cortical motor areas – Procedural memory Brain Stem • Link between spinal cord and high brain – Medulla, pons, midbrain • 12 cranial nerves arise from brain stem • Cardiac, respiratory, and digestive control centers • Reticular formation (RAS) • Regulates muscle reflexes involved with euilibrium and posture • House the sleep center Spinal Cord • Slender tube that extends from the brain stem and goes through vertebral column • Gives rise to 31 pairs of spinal nerves – Cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, coccygeal • Grey matter core, white matter on the periphery – White matter organized into tracts • Begin and end in specific brain regions and transmit specific information Spinal Tracts • Ascending tracts – Carry sensory information up • Descending tracts – Carry motor input down • Horns of spinal cord – Dorsal • Synapse with sensory neurons – Ventral • Cell bodies of motor neurons – Lateral • Fibers supplying cardiac and smooth muscle, glands people.eku.edu Reflexes • Response that occurs automatically without conscious effort – Basic reflexes – Acquired reflexes • Reflex arc – – – – – Sensory receptor Afferent pathway Integrating center Efferent pathway Effector • Please know reflexes described