PPT 2 - Teach.Chem
advertisement

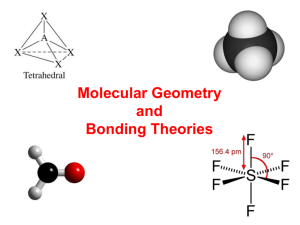
.. .. .. [ – ] .. Cl .. .. .. 36 e– .. ICl4– Cl .. .. Cl– .. I –Cl .. EDG: octahedral MG: sq. planar For molecules with more than one central atom, simply apply the VSEPR model to each part. Predict the EDG and MG around the three interior atoms of ethanoic (acetic) acid. CH3COOH PORTION EDG MG H O .. H–C–C–O–H .. H –CH3 tetra. tetra. C=O trig. plan. trig. plan. .. tetra. bent –OH .. Nonbonding domains are attracted to only one nucleus; therefore, they are more spread out than are bonding domains. The effect is that nonbonding domains (i.e., “lone pairs”) compress bond angles. Domains for multiple bonds have a similar effect. e.g., the ideal bond angle for the tetrahedral EDG is 109.5o H H H2O N O .. C H 109.5o H H H H COCl2 124.3o H O=C 124.3o 107.0o 104.5o .. Cl .. ..111.4 Cl .. .. NH3 o .. CH4 H EDG = trig. plan. ideal = 120o Polarity of Molecules A molecule’s polarity is determined by its overall dipole, which is the vector sum of the dipoles of each of the molecule’s bonds. Consider CO2 v. H2S... bond dipoles O=C=O bond dipoles S H H overall dipole = zero overall dipole = (NONPOLAR) (POLAR) Classify as polar or nonpolar: BCl3 .. .. .. Cl B .. .. 26 e– .. PCl3 .. .. .. Cl– .. P–Cl .. Cl .. .. 24 e– Boron can be extracted by the electrolysis of molten boron trichloride. Boron is an essential nutrient for plants, and is also a primary component of control rods in nuclear reactors. polar nonpolar Valence-Bond Theory: merges Lewis structures w/the idea of atomic orbitals (2s, 3p, etc.) Lewis theory says… covalent bonding occurs when atoms share electrons V-B theory says… covalent bonding occurs when valence orbitals of adjacent atoms overlap; then, two e–s of opposite spin (one from each atom) combine to form a bond V-B theory is like Velcro: “No overlap, no bond.” Consider H2, Cl2, and HCl... (unpaired e– is in 1s orb.) H Cl [Ne] H2 (unpaired e– is in 3p orb.) Cl2 HCl = orbital overlap region (responsible for bond) There is always an optimum distance between two bonded nuclei. At this optimum distance, attractive (+/–) and repulsive (+/+ and –/–) forces balance. Energy 0 H2 molecule optimum dist. (min. PE) H–H distance