PPT 1 - Teach.Chem
advertisement

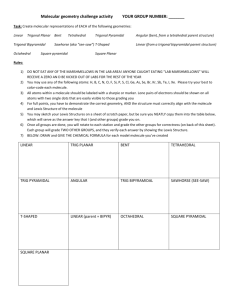
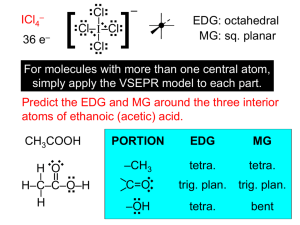
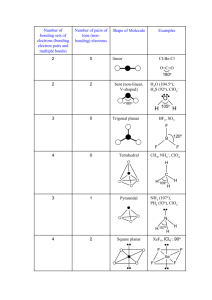
Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories The properties of a molecule depend on its shape and and the nature of its bonds. In this unit, we will discuss three models. (1) a model for the geometry of molecules -- valence-shell electron-pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory (2) a model about WHY molecules form bonds and WHY they have the shape they do -- valence-bond theory (3) a model of chemical bonding that deals with the electronic structure of molecules -- molecular orbital (MO) theory bond angles: the angles made by the lines joining the nuclei of a molecule’s atoms carbon dioxide CO2 180o methane CH4 109.5o formaldehyde CH2O 120o VSEPR electron domain: a region in which at least two electrons are found -- they repel each other because… they are all (–) bonding domain: 2-to-6 e– that are shared by two atoms; they form a… covalent bond nonbonding domain: 2 e– that are located on a single atom; also called a… lone pair For ammonia, there are NH3 .. three bonding domains and H– N –H one nonbonding domain. .. H N H Domains arrange themselves so H H as to minimize their repulsions. .. The electron-domain geometry is one of five basic arrangements of domains. N H H H -- it depends only on the total # of e– domains, NOT the kind of each domain The molecular geometry describes the orientation of the atoms in space. -- it depends on how many of each kind of e– domain .. Total # of Electron-Domain Domains Geometry 2 3 4 5 6 linear Possible Molecular Geometries linear (CO2) trigonal planar trigonal planar (BF3), bent (NO2) tetrahedral tetrahedral (CH4), trigonal pyramidal (NH3), bent (H2O) trigonal bipyramidal trig. bipyramidal (PCl5), linear (XeF2) seesaw (SF4), T-shaped (ClF3) octahedral octahedral (SF6), sq. pyr. (BrF5), square planar (XeF4) “atoms – axial” To find the electron-domain geometry (EDG) and/or molecular geometry (MG), draw the Lewis structure. Multiple bonds count as a single domain. Predict the EDG and MG of each of the following. SeCl2 20 e– .. .. .. .. .. Cl–Se–Cl .. .. .. .. .. 18 e– ] – .. O3 [ .. .. 26 e– .. SnCl3 – .. .. .. Cl– .. Sn–Cl .. Cl .. .. O– .. EDG: tetrahedral MG: trig. pyramidal EDG: trig. planar MG: bent EDG: tetrahedral MG: bent IF5 EDG: trig. planar MG: trig. planar .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. 34 e– 2– ] F .. .. SF4 [ .. 24 e– (res.) CO32– .. O– C= O .. O .. .. .. F .. ..F– S –F .. ..F .. EDG: octahedral MG: sq. pyramidal I 42 e– EDG: trig. bipyr. MG: seesaw 28 e– .. .. .. ClF3 .. .. .. ..F .. .. .. ..F– Cl –F .. ..F EDG: trig. bipyr. MG: T-shaped