Chem_10_Resources_files/Writing Formulasppt
advertisement

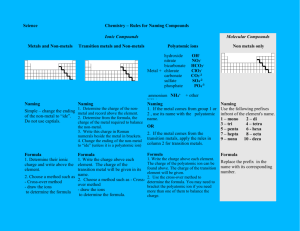
Writing Formulas Chapter 6 (Chapter 9) Rules for Writing Chemical Formulas Name does NOT begin with a metal Name begins with a metal (Ammonium acts like a metal) Ends with -IDE Ends with –ATE/-ITE ‘ACID’ in the name 1) Write the metal symbol/charge 1) Write the metal symbol/charge 2) Write the non metal symbol/charge 2) Write the polyatomic ion/charge 3) Add subscripts if necessary to make it neutral (criss-cross) 3) Add subscripts/parenthesis if necessary to make it neutral (criss-cross) *These metals use a Roman Numeral after their name to indicate it’s charge Copper (I) – Cu+1 Iron(II) – Fe+2 Lead(II) – Pb+2 +2 +3 Copper (II)- Cu Iron (III) – Fe Lead(IV) – Pb+4 Mercury(I) – Hg2+2 Chromium (II) – Cr+2 Tin(II) – Sn+2 Mercury(II) – Hg+2 Chromium(III) – Cr+3 Tin(IV) – Sn+4 Manganese(II) – Mn+2 Manganese(III) – Mn+3 Cobalt(II) – Co+2 Cobalt(III) – Co+3 Classic Names: add –OUS for lower charge/ -IC for higher charge to these roots Cupr Mercur - Ferr Chrom Mangan Cobalt - Plumb Stann - No ACID in Name 1) Write each element symbol [NO CHARGES USED HERE] [NO Polyatomic IONS HERE] 2) The Prefix IS the subscript (mono, di, tri, tetra, penta, hexa, hepta, octa, nona, deca) ‘HYDRO’ in front No ‘HYDRO’ in front Name ends with -IC 1) Write H+1 Name ends with - OUS 2) Write non metal symbol/charge 3) Add subscripts if necessary to make it neutral (criss-cross) 1) Write H+1 1) Write H+1 2)Write Polyatomic ion that ends with -ATE 2)Write Polyatomic ion that ends with -ITE 3) Add subscripts if needed to make it neutral 3) Add subscripts if needed to make it neutral Rules for Writing Chemical Formulas 1. All molecules have a neutral charge 2. Subscripts are used when individual charges are not the same 3. Parenthesis are used ONLY WITH POLYATOMIC IONS that need a subscript to make it neutral 4. Two non metals have prefixes to indicate their subscripts 5. The charges of representative elements are known to be: Charges for metals and non metals Potassium sulfate K2SO4 Barium oxalate BaC2O4 Chlorous acid HClO2 Ammonium sulfite (NH4)2SO3 Magnesium carbonate MgCO3 Carbon tetrabromide CBr4 Diphosphorous pentoxide P2O5 Nitric Acid HNO3 Sodium hydrogen sulfite NaHSO3 Oxalic acid H2C2O4 Aluminum acetate Al(C2H3O2) 3 Magnesium hydroxide Mg(OH)2 Phosphorous Acid H3PO3 Hydrofluoric Acid HF Zinc hypochlorite Zn(ClO)2 Lithium hydride LiH Chloric acid HClO3 Rubidium sulfide Rb2S Strontium chromate SrCrO4 Potassium permanganate KMnO4 Sodium cyanide NaCN Calcium hydrogen sulfite Ca(HSO3)2 Barium nitrate Ba(NO3)2 Phosphorous acid H3PO3 Silver chromate Ag2CrO4 Zinc carbonate ZnCO3 stop SO3 Sulfur trioxide BeSe Beryllium selenide AlN Aluminum nitride NH4C2H3O2 Ammonium acetate PCl3 Phosphorous trichloride K2HPO3 Potassium hydrogen phosphite H2SO4 Sulfuric acid H2S Hydrosulfuric acid (NH4)2C2O4 Ammonium oxalate HNO2 Nitrous acid Al2(SO4)3 Aluminum sulfate LiClO2 Lithium chlorite Ag2Cr2O7 Silver dichromate Hl Hydroiodic acid NaClO Sodium hypochlorite NI3 Nitrogen triodide H2CrO4 Chromic acid