Poster template
advertisement
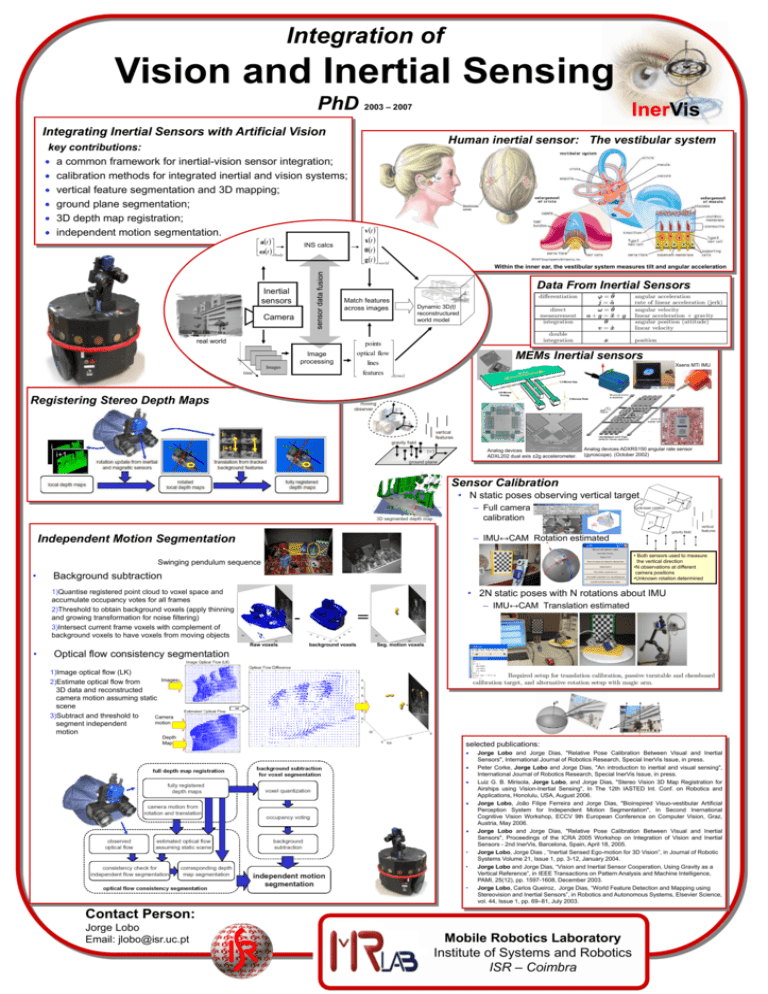
Integration of Vision and Inertial Sensing PhD 2003 – 2007 InerVis Integrating Inertial Sensors with Artificial Vision Human inertial sensor: The vestibular system key contributions: a common framework for inertial-vision sensor integration; calibration methods for integrated inertial and vision systems; vertical feature segmentation and 3D mapping; ground plane segmentation; 3D depth map registration; independent motion segmentation. at ωt body v t xt θt g t world INS calcs Within the inner ear, the vestibular system measures tilt and angular acceleration Data From Inertial Sensors Inertial sensors Match features across images Camera real world Image processing Images time Dynamic 3D(t) reconstructured world model points optical flow lines features time MEMs Inertial sensors Xsens MTi IMU Registering Stereo Depth Maps Analog devices ADXL202 dual axis ±2g accelerometer. Analog devices ADXRS150 angular rate sensor (gyroscope). (October 2002) Sensor Calibration • N static poses observing vertical target – Full camera calibration – IMU↔CAM Rotation estimated Independent Motion Segmentation • Both sensors used to measure the vertical direction •N observations at different camera positions •Unknown rotation determined Swinging pendulum sequence • Background subtraction • 2N static poses with N rotations about IMU 1)Quantise registered point cloud to voxel space and accumulate occupancy votes for all frames 2)Threshold to obtain background voxels (apply thinning and growing transformation for noise filtering) 3)Intersect current frame voxels with complement of background voxels to have voxels from moving objects – IMU↔CAM Translation estimated Raw voxels • = background voxels Seg. motion voxels Optical flow consistency segmentation 1)Image optical flow (LK) Images 2)Estimate optical flow from 3D data and reconstructed camera motion assuming static scene 3)Subtract and threshold to Camera motion segment independent motion Depth Map selected publications: • • • Jorge Lobo and Jorge Dias, "Relative Pose Calibration Between Visual and Inertial Sensors", International Journal of Robotics Research, Special InerVis Issue, in press. Peter Corke, Jorge Lobo and Jorge Dias, "An introduction to inertial and visual sensing", International Journal of Robotics Research, Special InerVis Issue, in press. Luiz G. B. Mirisola, Jorge Lobo, and Jorge Dias, "Stereo Vision 3D Map Registration for Airships using Vision-Inertial Sensing", In The 12th IASTED Int. Conf. on Robotics and Applications, Honolulu, USA, August 2006. Jorge Lobo, João Filipe Ferreira and Jorge Dias, "Bioinspired Visuo-vestibular Artificial Perception System for Independent Motion Segmentation", In Second Inernational Cognitive Vision Workshop, ECCV 9th European Conference on Computer Vision, Graz, Austria, May 2006. Jorge Lobo and Jorge Dias, "Relative Pose Calibration Between Visual and Inertial Sensors", Proceedings of the ICRA 2005 Workshop on Integration of Vision and Inertial Sensors - 2nd InerVis, Barcelona, Spain, April 18, 2005. Jorge Lobo, Jorge Dias , “Inertial Sensed Ego-motion for 3D Vision”, in Journal of Robotic Systems Volume 21, Issue 1, pp. 3-12, January 2004. Jorge Lobo and Jorge Dias, “Vision and Inertial Sensor Cooperation, Using Gravity as a Vertical Reference”, in IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, PAMI, 25(12), pp. 1597-1608, December 2003. Jorge Lobo, Carlos Queiroz, Jorge Dias, “World Feature Detection and Mapping using Stereovision and Inertial Sensors”, in Robotics and Autonomous Systems, Elsevier Science, vol. 44, Issue 1, pp. 69–81, July 2003. Contact Person: Jorge Lobo Email: jlobo@isr.uc.pt Mobile Robotics Laboratory Institute of Systems and Robotics ISR – Coimbra