Chapter Fourteen
Leadership
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Copyright © 2010 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
After reading the material in this chapter,
you should be able to:
• Review trait theory research, and discuss the
takeaways from both the trait and behavioral
theories of leadership.
• Explain, according to Fiedler’s contingency
model, how leadership style interacts with
situational control.
• Discuss House’s revised path-goal theory and
Hersey and Blanchard’s situational leadership
theory.
14-2
After reading the material in this chapter,
you should be able to:
• Describe the difference between transactional and
transformational leadership and discuss how
transformational leadership transforms followers and
work groups.
• Explain the leader-member exchange (LMX) model
of leadership and the concept of shared leadership.
• Review the principles of servant leadership and
discuss Level 5 leadership.
• Describe the follower’s role in the leadership process
14-3
What Does Leadership Involve?
• Leadership
- influencing employees to voluntarily pursue
organizational goals
14-4
Trait Theory
• Leader trait
- personal characteristics that differentiate
leaders from followers.
• Leadership prototype
- mental representations of the traits and
behaviors possessed by leaders.
14-5
Gender and Leadership
• Men and women were seen as displaying
more task and social leadership,
respectively
• Women used a more democratic or
participative style than men and men used
a more autocratic and directive style than
women
14-6
Behavioral Styles Theory
• The Ohio State Studies identified two
critical dimensions of leader behavior.
- Consideration: creating mutual respect and
trust with followers.
- Initiating structure: organizing and defining
what group members should be doing.
14-7
Question?
Allen thrives on organizing and defining
what group members should be doing to
maximize output. According to the Ohio
State researchers, Allen is exhibiting which
of these behaviors?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Initiating structure
Concern for people
Relationship-motivated
Consideration
14-8
Takeaways from Behavioral Styles Theory
• Leader behaviors can be systematically
improved and developed.
• There is no one best style of leadership.
• It is important to consider the difference
between how frequently and how
effectively managers exhibit various leader
behaviors.
14-9
Situational Theories
• Situational theories
- propose that leader styles should match the
situation at hand.
14-10
Fiedler’s Contingency Model
The performance of a leader depends on
two interrelated factors:
1.The degree to which the situation gives
the leader control and influence
2.The leader’s basic motivation
14-11
Fiedler’s Contingency Model
• Situational control
- refers to the amount of control and influence
the leader has in his immediate work
environment
14-12
Three Dimensions of Situational Control
• Leader-member relations
- the extent to which the leader has the support, loyalty,
and trust of the work group
• Task structure
- concerned with the amount of structure contained
within tasks performed by the work group
• Position power
- the degree to which the leader has formal power to
reward, punish, or otherwise obtain compliance from
employees
14-13
Representation of
Fiedler’s Contingency Model
Figure 14-1
14-14
Question?
Kimberly is a task-motivated leader.
According to Fiedler's work, Kimberly
would not be effective under which
conditions?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Situations of high control
Conditions of low control
Conditions of achievement-orientation
Conditions of moderate control
14-15
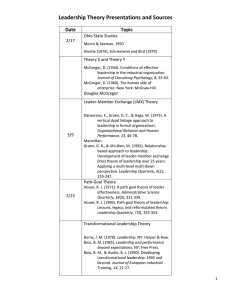
Path-Goal Theory
• Describes how leadership effectiveness is
influenced by the interaction between four
leadership styles – directive, supportive,
participative, achievement-oriented
• Contingency factors
- variables that influence the appropriateness of
a leadership style
14-16
Path-Goal Theory Reformulated
Three key changes:
1. Leadership is more complex and
involves a greater variety of leader
behavior.
2. The role of intrinsic motivation and
empowerment in influencing leadership
effectiveness
3. Shared leadership
14-17
A General Representation of
House’s Revised Path-Goal Theory
Figure 14-2
14-18
Categories of Leader Behavior
14-19
Hershey and Blanchard’s
Situational Leadership Model
• Effective leader behavior depends on the
readiness level of a leader’s followers.
• Readiness
- follower’s ability and willingness to complete a
task
14-20
Situational
Leadership Model
Figure 14-3
14-21
Question?
Cathy is providing guidance to employees about
what should be done and how to do it, scheduling
work, and maintaining standards of performance.
She is exhibiting the _________ leadership style,
according to the Path-Goal Theory?
A. Achievement-oriented
B. Directive
C. Supportive
D. Middle-of-the-road
14-22
Transactional Leadership
• Transactional leadership
- focuses on the clarifying employees’ roles and
providing rewards contingent on performance.
• Transformational leadership
- transforms employees to pursue
organizational goals over self-interests.
14-23
Transformational Leader Behaviors
• Inspirational motivation
• Idealized influence
• Individualized consideration
• Intellectual stimulation
14-24
Question?
Coach Bryant gave many great halftime
speeches. Which transformational behavior
was this?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Inspirational motivation
Idealized influence
Individualized consideration
Intellectual stimulation
14-25
A Transformational Model of
Leadership
Insert Figure 14-4
14-26
Managerial Implications
1. The best leaders are both transformational and
transactional
2. Transformational leadership influences group
dynamics and group-level outcomes
3. Employees can be trained to be more
transactional and transformational
4. Transformational leaders can be ethical or
unethical
14-27
Maintaining Ethical Transformational
Leadership
1. Create and enforce a clearly stated code of
ethics.
2. Recruiting, selecting, and promoting people
who display ethical behavior.
3. Develop performance expectations around the
treatment of employees.
4. Train employees to value diversity.
5. Identify, reward, and publicly praise employees
who exemplify high moral conduct.
14-28
The Leader-Member Exchange (LMX)
Model of Leadership
• Focuses on the quality of relationships
between managers and subordinates as
opposed to the behaviors or traits of either
leaders or followers.
• Assumes that leaders develop unique oneon-one relationships with direct reports.
14-29
The Leader-Member Exchange (LMX)
Model of Leadership
• In-group exchange
- a partnership characterized by
mutual trust, respect and liking
• Out-group exchange
- a partnership characterized by
a lack of mutual trust, respect and liking
14-30
Managerial Implications
• Leaders are encouraged to establish highperformance expectations for all of their
direct reports.
• Managers should be careful that they don’t
create a homogeneous work environment.
14-31
Shared Leadership
• Shared leadership
- simultaneous, ongoing, mutual influence
process in which people share responsibility
for leading
14-32
Considerations When Developing
Shared Leadership
Table 14-3
14-33
Question?
Jimmy’s team is working on the new
GrannySmith computer project. ________
leadership is most likely to be needed.
A.
B.
C.
D.
Servant
Shared
Concurrent
Contributory
14-34
Servant Leadership
• Servant leadership
- focuses on increasing services to others
rather than oneself
- less likely to engage in self-serving behaviors
that hurt others
Read the Servant
Leader newsletter
14-35
Characteristics of the Servant-Leader
14-36
Question?
Rhonda tries to put herself in her
subordinates shoes and will listen to their
feelings and emotions. This is the servantleader characteristic of _________.
A.
B.
C.
D.
Healing
Awareness
Persuasion
Empathy
14-37
The Level 5 Hierarchy
Figure 14-5
14-38
Role of Followers in the Leadership
Process
• Critical for followers to understand their
boss
• Followers need to understand their own
strengths and weaknesses
• Followers should build on mutual
strengths to accommodate the leader’s
expectations
14-39
Supplemental Slides
• Slides 41-45 contain extra non-text
examples to integrate and enhance
instructor lectures
-
Slide 41-42: Leadership Development
Slide 43: Succession Planning
Slide 44: Transformational Leaders
Slide 45: Video discussion slide
14-40
Leadership Development
1. Develop a comprehensive strategy for
integrated leadership development
2. Connect leadership development to
organization’s environmental challenges
3. Use the leadership story to se the context
for development
4. Balance global enterprise-wide needs
with local individual needs
14-41
Leadership Development
5. Employ emergent design and
implementation
6. Ensure that development options fit the
culture
7. Focus on critical moments of the
leadership lifecycle
8. Apply a blended methodology
14-42
Succession Planning
1. Visible support from the CEO and top
management
2. Clearly defined leadership criteria
3. A defined plan to find, retain, and
motivate future leaders
4. A simple, easy-to-follow, measurable
process
14-43
Vision Statements of
Transformational Leaders
• Walt Disney, Walt Disney, Co.
- Provide wholesome, high-quality entertainment
to families throughout the world
• Herb Kelleher, Southwest Airlines
- To provide excellent service and great value to
the flying public
• Mary Kay Ash, Mary Kay Cosmetics
- To enhance the self-esteem of women by
building their financial independence while
providing quality cosmetics.
14-44
Video: Women Leading in the
Workplace
• Space Shuttle Commander Eileen Collins hopes to serve
as a role model for other women. How has life in the
USAF changed for women over the past several decades
to allow her to be Shuttle Commander?
• Commander Collins cites cultural issues as a potential
cause of women not pursuing math and engineering
oriented training and careers as frequently as men. Why
do you think this is?
• Based on what you saw in the video, do you think that
family responsibilities prevent women from growing in
their careers?
14-45