Electronics sessional 1 half wave rectifier
advertisement

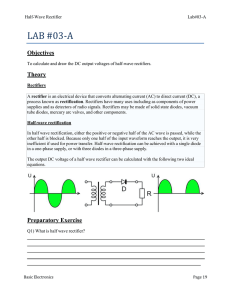
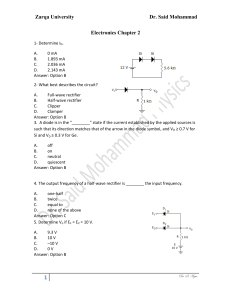
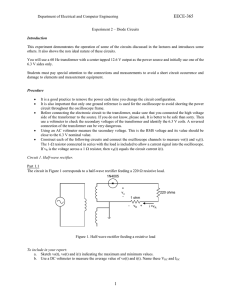
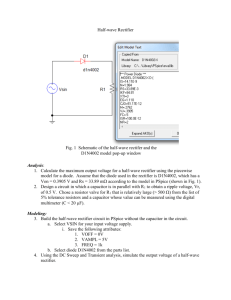
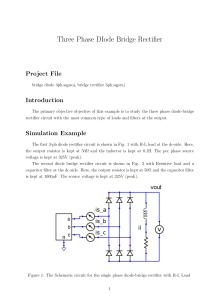
Electronics sessional • Course code : CSE – 124 • Marks Distribution – – – – Attendance Lab report Class performance Lab Final ------------------------- 10 30 20 40 Details of Lab Final • • • • Multiple choice ( MCQ ) Fill in the blanks True false Very short notes. Lab Experiment: 1 Name of the Experiment: Half Wave Rectifier Characteristics. • Objectives: • To understand the diode’s characteristics. • Construct the half wave bridge rectifier. • Explain it’s wave form. Theory • In analog electronics, a Diode is a component that restricts the direction of movement of Charge Carriers. It allows an Electric Current to conduct in one direction, but blocks the current in the opposite direction. One important application of Diodes is in the design of Rectifier Circuit, which is one of the important parts of a DC Power Adapter, Figure 1. Figure 1: Block Diagram of a DC Power Adapter • Rectification is the process of converting Alternating Current (AC) into Direct Current (DC). AC current and voltage change to positive and negative polarities alternately (bidirectional), while DC current and voltage only has either one polarity (unidirectional). The electrical devices used to perform rectification are called Rectifiers. Rectification is classified as Half-wave or Full-wave, with Half-wave being the simplest. Figure 2a: A Diode acts as a Halfwave Rectifier Figure 2b: The Diode is equivalent to a short circuit during positive half cycles Figure 2c: The Diode is equivalent to an open circuit during negative half cycles Circuit Construction • Half-wave Rectifiers allow either the positive or negative half cycles of the AC to pass and block the other one. It can be implemented by a Diode. An example of a positive Half-wave Rectifier is given in Figure 2a. The Diode conducts during positive half cycles; therefore it can be treated as a short circuit, Figure 2b. On the other hand, it blocks the current during the negative half cycles; therefore it can be treated as an open circuit, Figure 2c. Experimented Wave form: The input and output voltage Waveforms of a Positive Half-wave Rectifier are shown in Figure 3a and Figure 3b respectively. The output is unidirectional and has a finite average value, DC component. Figure 3a: AC Input Voltage Waveform Figure 3b: DC Output Voltage Waveform after Positive Half-wave Rectifier