Diode Applications
advertisement

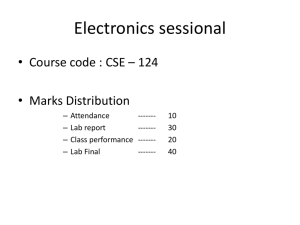
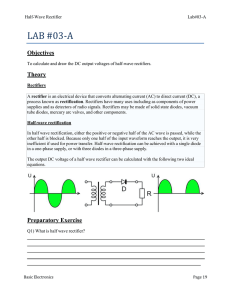
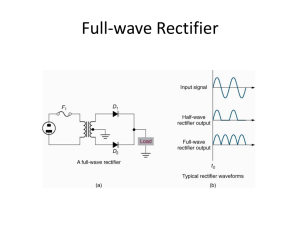
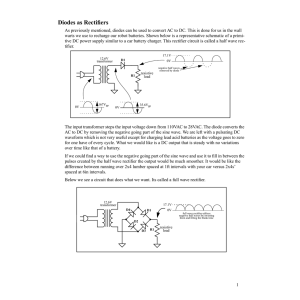
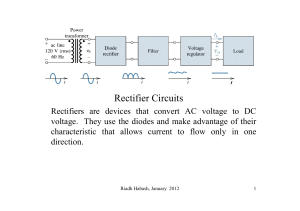
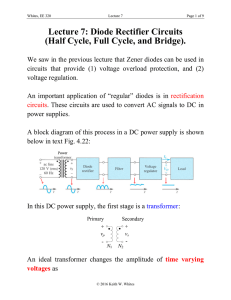
Diode Applications LOAD-LINE ANALYSIS The operating point (Q point) The operating point or Q point of the diode is the quiescent or no-signal condition. The Q point is obtained graphically and is really only needed when the applied voltage is very close to the diode’s barrier potential voltage. 3/28 Example Solution Series diode configurations with DC inputs Example 1 Example 2 Example 3 EXAMPLE 4 Vo 0.7 VR E VD I1 R R 10 V 0.7 V 0.33KΩ 28.18mA EXAMPLE 5 V0 12 0.3 11 .7 V EXAMPLE 6 V 0.7V T 2 I1 0.212 mA R 1 3.3KΩ By KVL : - V2 E VT1 VT2 0 V2 E VT1 VT2 20V 0.7V 0.7V 18.6V V 18.6V I2 2 3.32mA R 5.6KΩ 2 I D 2 I 2 I1 3.32mA 0.212mA 3.108 mA Diode Applications • Rectifier a device for converting alternating AC current into direct current DC • Half-Wave Rectifier • Full-Wave Rectifier SINUSODIAL INPUT HALF-WAVE RECTIFICATION Half-Wave Rectifier Vdc 0.318Vm Vdc 0.318(Vm VT ) Effect of VT on half-wave rectified signal The peak Inverse voltage PIV for half wave rectifier Determining the required PIV ratting for the half wave rectifier PIVrating Vm Bridge Rectifier Full – wave rectification Bridge Rectifier Vdc (average voltage): for ideal diodes and for silicon diodes Determining the required PIV ratting for the bridge configuration PIV Vm Full – wave rectification Center tapped transformer Full – wave rectification Center tapped transformer Full – wave rectification Center tapped transformer • Determine PIV (PRV) for each diode: Inserting the maximum voltage for the secondary voltage and Vm as established by the adjoining loop will result in PIV = Vsecondary + VR = Vm PIV ≥ 2 Vm + Vm