Glandular Epithelia
advertisement
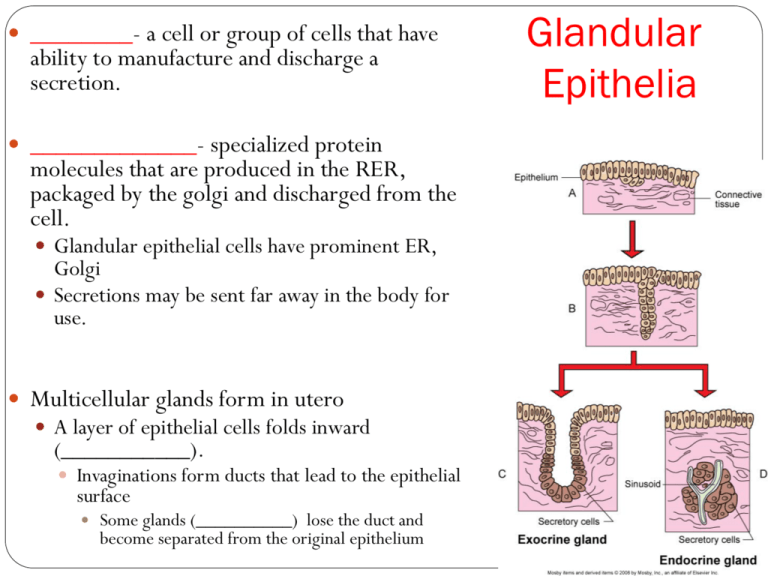
________- a cell or group of cells that have ability to manufacture and discharge a secretion. _____________- specialized protein molecules that are produced in the RER, packaged by the golgi and discharged from the cell. Glandular epithelial cells have prominent ER, Golgi Secretions may be sent far away in the body for use. Multicellular glands form in utero A layer of epithelial cells folds inward (___________). Invaginations form ducts that lead to the epithelial surface Some glands (__________) lose the duct and become separated from the original epithelium Glandular Epithelia Glands can be classified by the following factors: Presence or absence of _________ Endocrine vs. Exocrine __________ of cells that compose them Unicellular vs multicellular __________ of secreting ducts Simple or compound _____________ of glandular structure Tubular, acinar, tubuloacinar Type of ____________ made Mucoid or serous Manner in which secretion is _____________ and _____________ Merocrine, apocrine, or holocrine No ________ (cells die) Produce and Secrete _____________ Regulate body functions (growth, maturity, sex cycle) Blood stream delivers secretions to entire body ___________ within the gland bring secretions to the circulatory system Endocrine glands are part of the Endocrine System Endocrine Glands Contain ducts (except for ________ cells) Have _______ effect. Discharge secretions via ducts directly into nearby areas. Secretions act locally and do not enter into the circulatory system Examples of secretions: Egg/Sperm Saliva Bile Pancreatic and liver digestive enzymes Musk (scent) Sweat Anal (scent glands) Exocrine Glands Only unicellular exocrine gland _____less Opens into GI, respiratory tracts, conjunctiva Composed of a modified ___________ epithelial cell. Found interspersed among the columnar cells of the respiratory and digestive tracts and conjunctive of eye Secretes _______: (polysaccharides, proteins, and glycoproteins) when mixed with water → mucus Mucus functions to protect the apical surface of the epithelial cell and traps microorganisms and foreign particles Unicellular Exocrine Gland: Goblet Cell Multicellular Exocrine Glands Contain 2 distinct components: 1) ___________ Unit Secretory cells usually surrounded by connective tissue rich in blood vessels and nerve fibers. connective tissue provides nourishment to the secretory cells/unit and gives structural support 2) ________ carries secretion to its deposit site _____epithelial cells may be present that assist with the discharge of secretions into the glandular duct. Rate of secretion production is controlled by hormonal and nervous influences Classification of Multicellular Exocrine Glands: Shape Based on shape and number of tubes If main duct is unbranched, the gland is ________ If main duct is branched, gland is __________ If secretory cells form a long channel of even width, gland is _________ If cells form a rounded sac, it is _________ or acinar Glands with both tubular and alveolar qualities are tubuloalveolar or tubuloacinar Classification of Exocrine Glands: Manner of secretion How much of a cell is sacrificed in the act of secretion determines the classification: Merocrine Glands package their secretions and release them via exocytosis as they are manufactured Secretory cells remain intact Majority of glands (ex: pancreas, sweat glands, salivary glands) Apocrine Glands store their secretions in the apex of the secretory cell after they are manufactured. When apex is full, it is pinched off and released with the secretions into the duct system. Cell is repaired and process is repeated. (ex: mammary glands, some sweat glands) Holocrine Glands store their secretions until they are needed. The cell lyses, releasing its contents. Cell dies and is replaced via mitosis. (ex: sebaceous glands)