Ancient Rome
advertisement

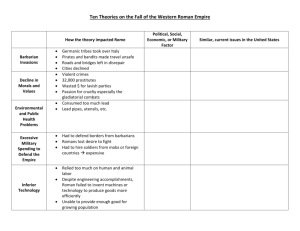
The Birth of the Roman Empire I. A Weakening Republic A. Tiberius and Gaius Gracchus saw need for reform 1. Known as Gracchi 2. Tiberius named Tribune in 133 B.C. a. Instituted land reforms i. Popular with people ii. Senators were threatened by his popularity iii. Senators murdered Tiberius 3. Gaius named Tribune in 123 B.C. a. b. Bought grain with public funds Sold it to poor at low price i. Angered senators and was killed 4. Violence became a key political tool B. The Social War 1. Italian allies rebelled against Romans a. Wanted Roman citizenship for help in Punic Wars 2. 3. One of the bloodiest wars in Roman History Were finally granted citizenship a. All Italians became Roman 4. Gaius Marius was elected consul in 107 B.C. a. Brought major changes b. Created army of volunteers i. Rewarded with money, land, and war loot 5. Sula was elected Consul a. b. c. d. e. Marched on Rome after his term was over Brought civil war to Rome Sulla won Tried to increase power of senate However, military power ruled Rome II. Caesar in Power A. Julius Caesar 1. 2. 3. 4. Popular general Used money to gain influence Good public speaker Won right to rule through military success B. The First Triumvirate – Rule by Three 1. Caesar joined with other popular generals a. Crassus & Pompey 2. Caesar took command of army in Gaul (France) a. Took control of all of Gaul 3. Pompey, elected Consul in 52 B.C. a. He was jealous of Caesar and called him home from Gaul b. Told him to leave his army C. Caesar declared war on the republic, defeated Pompey D. Made himself Consul for life, but was killed in the Senate III. The Roman Empire A. The Second Triumvirate 1. Octavian – Caesars grandnephew a. b. c. Forced Lepidus to resign Divided Empire with Antony Built power in Italy 2. Antony – Drove the conspirators out a. b. Defeated Brutus and Cassius in Asia Minor and Syria Controlled Eastern half of empire 3. Lepidus – Caesar’s right hand man B. Octavian: the first Augustus 1. Called himself the first Citizen or princeps 2. People gave Octavian the title Augustus a. Revered One 3. 63 B.C. – 14 B.C. 4. Captured Alexandria 5. Rome reached its height under Octavian C. The Pax Romana (Roman Peace) emperors 1. Julio-Claudian Emperors a. Tiberius – adequate but disliked b. Caligula – insane and brutal, murdered c. Claudius – intelligent and managed wisely, poisoned by wife d. Nero i. Brutal to Christians ii. Thought to have been responsible for great fire that burned Rome iii. Killed himself 2. Army Emperors a. Four different emperors ruled in 69 because the army wouldn’t accept any of them 3. Flavian Emperors a. Vespasian Last of the Army and first of the Flavian b. Titus put down rebellions in Germania and Jerusalem c. Domitian 4. The Five Good Emperors a. Nerva b. Trajan c. Hadrian i. ii. Built Hadrian’s Wall Protected the frontier d. Antoninus Pius e. Marcus Aurelius Roman Society and Culture I. Building a Strong Empire A. Government and laws 1. Changed Twelve Tables a. b. Made laws as necessary Made Twelve Tables applicable to current needs B. Trade and transportation 1. Most trade centered around: a. Exports: – – – – – – – Grain Wine Oil (olive) Food stuffs Linen Pottery Glassware b. Imports: Ivory Spices Silk Sand C. Romans built many roads wherever they went D. The Roman Army 1. Citizens soldiers served for 16 – 20 years 2. Stationed in large fortified camps a. Towns were often built around these 3. Most men living on the border enlisted a. Would become Romans Citizens II. Life in the Empire A. Daily life 1. Wealthy had a city home and country home 2. Running water and exotic food for rich a. Many dinner parties 3. Crowded apartments 4. Simple meals for most Romans B. Slaves and slavery 1. Gladiators – conquered warriors 2. Household slaves 3. Entertainment a. b. Catamites- Young boys sold to men for perversity Prostitutes C. The roles of the family 1. Men – father held power 2. Women – mother managed household 3. Children – education at home D. Religion – state religion E. Fun and games 1. Roman Bath 2. Theater a. 3. Comedies and Satire Arena a. b. c. Chariot Races – Circus Maximus Gladiators Lions F. Science and the Arts 1. Science, engineering, and architecture a. b. c. d. e. Galen – wrote several volumes on medicine Ptolemy – taught that the world was geocentric Roman built many roads, coliseums, and bridges Aqueducts – carried water from mountains to cities Used arch and vaulted dome 2. Literature a. b. c. d. e. Virgil – Aeneid tells about the prince of Troy, poetry Horace – odes, satires and epistles Ovid – wrote lyrics and Metamorphoses Tacitus – Annals, history of Rome Plutarch – Greek, wrote Parallel Lives, a collection of bios 3. Language a. Latin is the parent of modern Romance languages The Rise of Christianity I. The Beginning of Christianity A. Jews revolted and were banned from Jerusalem B. The teachings of Jesus 1. Grounded in Jewish traditions 2. Claimed to be Messiah (Savior) C. The death of Jesus 1. Crucifixion 2. Resurrection D. The Spread of Christianity 1. Spread through his apostles E. Christianity was for everyone 1. Paul’s letter to the Romans said, “call upon the name of the Lord and be saved” F. Martyrs were put to death for beliefs in Christianity 1. Roman efforts could not stop the spread of the religion G. Roman law accepted Christianity as a religion 1. Constantine was tolerant, converted before he died 2. Theodosius made it official Roman Religion 3. Church became organized with Bishops, Priests and Congregations 4. Bishops of Empirical Cities were called Patriarchal Bishops 5. Council of Mycenae a. Gave us the Bible 6. Council of Nicaea a. Canonized the main religion beliefs The Fall of the Western Empire I. Troubled Times Arise A. Rising inflation 1. Citizenship granted to all free people in the empire a. Done to increase tax base 2. Silver coin was in shortage a. Similar to the gold standard of U.S. economy 3. Used less silver to make coin a. Result was inflation B. Increasing insecurity A. B. C. D. Attacks from invaders continued Costs of defense went up Small business were forced to sell to large ones Less jobs available for common man C. Two Able Emperors Attempt Reform 1. Diocletian a. appointed a co-emperor and two caesars (assistants) b. Diocletian ruled the eastern empire c. Tried to control prices and wages 2. Constantine – supported Christianity a. Not supported by Diocletian i. Civil war broke out b. Received a vision before he defeated Diocletian i. Supported Christianity after the vision c. Created a new capital in the East called Constantinople d. Empire remained strong for 50 years after his death i. ii. Empire divided Eastern half became the Byzantine Empire II. The Final Invasions A. The Goths and the Vandals 1. Eastern Germanic tribes a. Treated poorly by Rome b. Goths with a large heavy army won the battle at Adrianople c. Rome allowed them to settle in Roman borders under own leadership d. The Goths sacked Rome after a short peace B. The Huns 1. Followed the Goths into Rome 2. Defeated by a Roman / Goth Army 3. Too late to save Western Half of Empire 4. Overthrown in A.D. 476 C. Results of the invasions 1. People were displaced 2. Instability 3. Destruction of cities D. Causes of the decline 1. Political and military weaknesses a. Empire grew to fast and too large to manage and protect 2. Economic decline a. Heavy taxes took cash flow out of the economy 3. Social change a. Most early Romans believed in “Rome” b. New generations care more about self than country c. People were no longer concerned with morals and politics