Chapter 4. The Chemistry of Carbon
advertisement

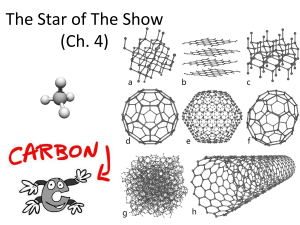
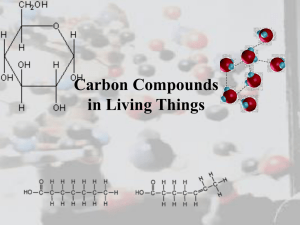
Chapter 4. The Chemistry of Carbon Why study Carbon? All living things are made of cells Cells ◦ ~72% H2O ◦ ~3% salts (Na, Cl, K…) ◦ ~25% carbon compounds ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ carbohydrates lipids proteins nucleic acids 2003-2004 Chemistry of Life Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds C atoms are versatile building blocks ◦ bonding properties ◦ 4 stable covalent bonds pair of electrons are shared 2003-2004 Complex molecules assembled like – candy & toothpicks 2003-2004 Hydrocarbons Simplest Carbon molecules = hydrocarbons ◦ A compound with a combination of Carbon & Hydrogen Simplest HC molecule = methane ◦ 1 carbon bound to 4 H atoms ◦ stable ◦ a gas at room temperature Hydrocarbons can grow methane adding C-C bonds ethane ◦ straight line ethane hexane ◦ branching isohexane hexane ◦ ring cyclohexane isohexane 2003-2004 cyclohexane Diversity of organic molecules 2003-2004 Isomers Molecules with same molecular formula but different structures ◦ different chemical properties – C6H14 Various kinds of isomers Molecules differ in structural arrangement of atoms Around a double bond – alkenes Isomers of ethene Most macromolecules are polymers Three of the four classes of macromolecules form chainlike molecules called polymers. ◦ Polymers consist of many similar or identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds. The repeated units are small molecules called monomers. (like links of a chain) 4 MAIN MACROMOLECULES MOLECULE Proteins Lipids MONOMER USES support/motion (amino acids) (glycerol & fatty acids) energy storage/insulation Carbohydrates (monosaccharides) Nucleic acids (nucleotides) • quick energy store information They all contain CARBON and are called ORGANIC molecules (Also hydrogen, oxygen are in all of them) Diversity of molecules Substitute other atoms or groups around the C ◦ ethane vs. ethanol H replaced by an hydroxyl group (–OH) ethane ethanol What element is the blue one above? How many bonds does it form? Hydroxyl –OH ◦ organic compounds with OH = alcohols ◦ names typically end in -ol ethanol More on Functional Groups 2003-2004 Types of functional groups 6 functional groups most important to chemistry of life: ◦ hydroxyl ◦ carbonyl ◦ carboxyl amino sulfhydryl phosphate Affect reactivity ◦ hydrophilic ◦ increase solubility in water ◦ Change all kinds of properties 2003-2004 Carboxyl –COOH ◦ C double bonded to O & single bonded to OH group compounds with COOH = acids ◦ fatty acids ◦ amino acids 2003-2004 Amino -NH2 ◦ N attached to 2 H compounds with NH2 = amines ◦ amnio acids NH2 acts as base ◦ ammonia picks up H+ from solution 2003-2004 Viva la difference! Basic structure of male & female hormones is identical ◦ identical C skeleton ◦ attachment of different functional groups ◦ interact with different targets in the body 2003-2004