Cash in Bank
advertisement

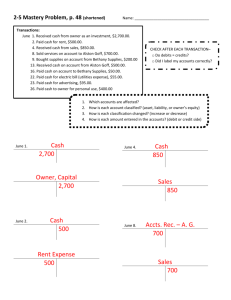
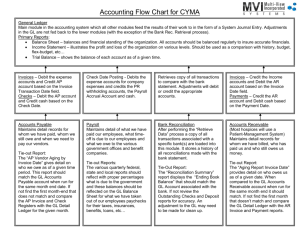
Chapter 7 Cash Learning Objectives 1. Cash and Cash Controls 2. Internal Control of Cash Receipts 3. Internal Control of Cash Payments 4. Bank Accounts: A Cash Control 5. Bank Reconciliation 6. Petty Cash 7. Balance Sheet Cash Presentation 8. Financial Analysis and Interpretation C7 - 1 Cash Accounts and Internal Controls Many companies need several cash accounts to account for different cash categories and funds. Most companies have multiple bank accounts. The title for each bank account should be: Cash in Bank – (Name of Bank) Preventive controls protect cash from theft and misuse of cash. Detective controls are designed to detect theft or misuse of cash and are also preventive in nature. C7 - 2 Internal Control of Cash Receipts p.281 Cash is normally received from two sources: 1. Over the counter from cash customers. Use of a cash register is an important control. 2. Received in the mail from credit customers. Cash is in the form of checks. All cash is sent to the Cashier’s Department. An employee prepares a bank deposit ticket and makes a bank deposit. The bank deposit record is sent to the Accounting Department where it is recorded. C7 - 3 Cash Short and Over Date Description May 08 Cash Cash Short and Over Sales Debit Credit 3,142.00 8.00 3,150.00 To record day’s cash sales. Actual cash received is less than cash register receipts. Cash Short and Over account is included in the income statement: •Miscellaneous Administrative Expenses •Other Income C7 - 4 Cash Short and Over Date Description May 08 Cash in Bank Cash Short and Over Sales Debit Credit 3,142.00 8.00 3,150.00 To record day’s cash sales. Actual cash received is less than cash register receipts. A debit in the Cash Short and Over account represents an expense. C7 - 5 Cash Receipts From Credit Customers Sales Accts. Receivable Cash PURCHASE ORDER 1 1 SALES ORDER A purchase order is received and a sales order is prepared. C7 - 6 Cash Receipts From Credit Customers Sales Accts. Receivable Cash in Bank PURCHASE ORDER 1 SALES ORDER 2 SHIPPING REPORT 1 A purchase order is received and a sales order is prepared. 2 Merchandise is shipped and a shipping report is prepared. C7 - 7 Cash Receipts From Credit Customers Sales Accts. Receivable Credit SALES ORDER Debit SALES INVOICE PURCHASE ORDER 1 Cash 3 2 SHIPPING REPORT 1 A purchase order is received and a sales order is prepared. 2 Merchandise is shipped and a shipping report is prepared. 3 A sales invoice is prepared and sent to customer. C7 - 8 Cash Receipts From Credit Customers Sales Accts. Receivable Credit SALES INVOICE PURCHASE ORDER 1 SALES ORDER Debit Credit 4 Cash Debit DEPOSIT RECORD 3 2 SHIPPING REPORT 1 A purchase order is received and a sales order is prepared. 2 Merchandise is shipped and a shipping report is prepared. 3 A sales invoice is prepared and sent to customer. 4 Cash is received from customer, deposited, and recorded. C7 - 9 Internal Control of Cash Payments 1. Cash controls must provide assurance that payments are made for only authorized transactions. 2. Cash controls should ensure that cash is used efficiently. 3. A voucher system provides assurance that what is being paid for was properly ordered, received, and billed by the supplier. C7 - 10 Cash Payments to Suppliers Cash Accts. Payable Merchandise PURCHASE ORDER 1 1 A purchase order is sent to a supplier. C7 - 11 Cash Payments to Suppliers Cash Accts. Payable Merchandise PURCHASE ORDER RECEIVING REPORT 1 2 1 A purchase order is sent to a supplier. 2 Merchandise is received and a receiving report is prepared. C7 - 12 Cash Payments to Suppliers Cash Accts. Payable Merchandise Credit Debit VOUCHER 3 PURCHASE ORDER PURCHASE RECEIVING INVOICE REPORT 1 2 1 A purchase order is sent to a supplier. 2 Merchandise is received and a receiving report is prepared. 3 A purchase invoice is received and a voucher is prepared. C7 - 13 Cash Payments to Suppliers Cash Credit Accts. Payable Debit CHECK Merchandise Credit Debit VOUCHER 4 3 PURCHASE ORDER PURCHASE RECEIVING INVOICE REPORT 1 2 1 A purchase order is sent to a supplier. 2 Merchandise is received and a receiving report is prepared. 3 A purchase invoice is received and a voucher is prepared. 4 Cash is paid to the supplier and recorded. C7 - 14 Cash Receipts and Payments Selling Side of Business Accts. Receivable Credit 1 1 Buying Side of Business Cash Debit Accts. Payable Credit DEPOSIT RECORD Cash received on account from customers. Debit CHECK 2 2 Cash paid on account to suppliers. C7 - 15 Bank Reconciliation Special terms: 1. Signature 2. Deposit ticket 3. A check 4. Drawer 5. Drawee 6. Payee 7. Bank reconciliation C7 - 16 Bank Reconciliation • Exhibit 4 Bank statement • Exhibit 5 recordings • To prepare the bank reconciliation – The reconciling items (p.290) C7 - 17 Total Bank 3,359.78 816.20 Company 2,549.99 408.00 -1,061.00 -435.39 -48.60 2,630.99 -300.00 -18.00 -9.00 2,630.99 C7 - 18 Power Networking Bank Reconciliation July 31, 2003 Balance per bank statement Add deposit of July 31, not recorded by bank Deduct outstanding checks: No. 812 No. 878 No. 883 Adjusted balance Balance per depositor’s records Add note and interest collected by bank $1,061.00 435.39 48.60 $3,359.78 816.20 $4,175.98 1,544.99 $2,630.99 $2,549.99 408.00 $2,957.99 Deduct: Check NSF check returned $300.00 Bank service charges 18.00 Error in recording Check No. 879 9.00 Adjusted balance $2,630.99 C7 - 19 Power Networking Bank Reconciliation July 31, 2003 Balance per bank statement Add deposit in transit Deduct outstanding checks: No. 812 No. 878 No. 883 Adjusted balance $3,359.78 816.20 $4,175.98 $1,061.00 435.39 48.60 Balance per depositor’s records A Add note and interest collected by bank B Deduct: Customer NSF check Bank service charges Error in recording Check No. 879 Adjusted balance 1,544.99 $2,630.99 $2,549.99 408.00 $2,957.99 $ 300.00 18.00 9.00 327.00 $2,630.99 C7 - 20 p.291 Bank Reconciliation Journal Entries Date Description Jul. 31 Cash A Debit Credit 408 Notes Receivable Interest Revenue 400 8 To record note collected by bank. Jul. 31 Accounts Receivable - T. Ivey B Miscellaneous Expense Accounts Payable - Taylor Co. Cash 300 18 9 327 To record customer’s NSF check, bank service charges, and error in recording Check No. 879. C7 - 21 Bank Reconciliation - Journal and Ledger General Journal Date A 7/31 7/31 B Page 1 Description P.R. Cash Notes Receivable Interest Revenue Accts. Receivable - T. Ivey Miscellaneous Expense Accts. Payable - Taylor Co. Cash 11 Debit Credit 408.00 400.00 8.00 300.00 18.00 9.00 11 327.00 General Ledger Account: Cash Date 7/31 7/31 7/31 Item Account No. 11 P.R. Debit Credit Balance J1 J1 408.00 327.00 Balance Debit Credit 2,549.99 2,957.99 2,630.99 C7 - 22 Petty Cash Accounting • Petty Cash – A special cash fund is called a petty cash fund • Example: – Travel expenses for salesperson • Set up the fund for $100 • Total the expenses $88 • Refund C7 - 23 Petty Cash Accounting Date Aug. 1 Description Petty Cash Cash Debit Credit 100.00 100.00 To establish a petty cash fund. Aug. 31 Office Supplies Store Supplies Misc. Admin. Expense Cash 50.00 35.00 3.00 88.00 To replenish the petty cash fund. Note: No entry in Petty Cash account when the fund is replenished. C7 - 24 Solvency Analysis Solvency is the ability of a business to meet its financial obligations (debts) as they are due. Solvency analysis focuses on the ability of a business to pay or otherwise satisfy its current and noncurrent liabilities. This ability is normally assessed by examining balance sheet relationships. C7 - 25 Solvency Measures — The Short-Term Creditor Doomsday Ratio Laettner Co. Oakley Co. A. Cash and equivalents B. Current liabilities Doomsday ratio A / B $100,000 400,000 0.25 $ 120,000 1,500,000 0.08 How are these ratios used? C7 - 26 Solvency Measures — The Short-Term Creditor Doomsday Ratio Laettner Co. Oakley Co. A. Cash and equivalents B. Current liabilities Doomsday ratio A / B $100,000 400,000 0.25 $ 120,000 1,500,000 0.08 Use: To indicate the worst case assumption that should the business cease to exist, only the cash on hand is available to meet creditor obligations. C7 - 27 HOME WORK READING: 1. Illustrative problem 2. Self- examination questions 3. Multiple choice Writing: 1. Exercise: 2. Problem : 7-3A Discussion: Activity 7-5 C7 - 28 This is the end of Chapter 7. C7 - 29