Culture influence Leadership
advertisement

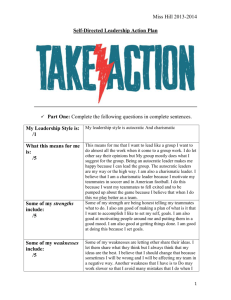
Doing Business in France By: Ying, Jessica, and Harriet Background Capital: Paris Government: Republic President: François Hollande Good temperate climate Language: 88% French Generous space for agriculture and a fortunate population distribution 80% of Texas Population: 65,820,916 people (2013) Ethic Make-Up: Celtic and Latin with Teutonic , Slavic, North African, Indochinese, Basque minorities Religion: Roman Catholic 83-88% Protestant 2% Jewish 1% Muslim 5-10% Background to business in France France remains 5th largest economy in the World Leading in banking, finance, aeronautics, and many hi tech fields The cold economic climate post- 2008 challenges the viability of the country’s traditional social models Unemployment running around 10% Two elements that play a great role in business (Second World War) : Government In shaping the direction of French businesses Education- Higher Elite Institutions (Grandes Ecoles) Background to business in France Co-operations between the government and industry has been aided by the influence of the French educational system Brightest pupils – System of elite schools (Grandes Ecoles) Graduates of these institutions: enter large commercial organizations & civil service Brotherhood- CEO path Cross-Cultural Business Things to Know: • • • • • Leading economic players in E.U. Second largest trading nation in Western Europe Many opportunities Learn French etiquette Punctuality: strive to be punctual – 10 mins is okay – 20 mins: Call to say you will be late – 30mins: reschedule Cross-Cultural Business • Low corruption rate • Language: try to speak the language – Do not get offended – They do not disapprove of our efforts • Strong national culture – Melting pot – Respect their culture Cross-Cultural Business Work/life balance Intellectually Superior to any other nationality Mission to teach and civilize other- due to their length magnificence/historical achievements Americans perceive French as too picky, detailed, and they do not focus on end result Cross-Cultural Business • French perceive Americans as too focused on the end result and that they do not provide answers with much justification. • Plans can be detailed – Americans Proposals versus French Proposals • Negatively affects Negotiations Cross-Cultural Business 1. Express thoughts and feelings Show intent Be genuine Disagreements are acceptable Go to dinner 2. Develop a relationship Slow down Get to know Business is personal 3. Contact is important 4. Give them TIME Be understanding Leadership Style 1. Autocratic Managers tend to work in isolation 2. Paternalistic The group is considered more of a family than an instrument. 3. Participative Depending on various mixes of directiveness and participation in decision making Leadership Style Characteristics Supervise the situation Use knowledge to make decisions Technical details Analyze the work Encourage the employees Manager is the main person Strict Comment/ advise Determined to win Self-confident Congratulate the team Leadership in France France leadership style is autocratic Compared to the US, France has a charismatic style of leadership (the US has a transformative leadership style) Charismatic leadership involves creating a self-image so powerful that people are naturally drawn to you Charismatic leaders are perceived as having an extraordinary type of influence on their followers—charismatic leaders gather followers through dint of personality and charm rather than any form of external power or authority Culture Influence on Leadership French culture display behaviors full power of decision making and control less need for group decision making autonomy-delegation behaviors Heavy emphasis on written rules and rigid procedures French leadership philosophy are their personal style being outgoing, operating with a good deal of energy, intensity, emotional and their tendency to use instincts Audio Culture Influence on Leadership French managers allow less participation of their subordinates in decision making Less emphasis on cooperation, group work Less active in giving information to subordinates Management Influence on Leadership A strong hierarchy is characteristic of the French working environment, and an autocratic leadership style is applicable. A highly educated management population which approaches leadership with an unusual degree of academic precision. French business behavior emphasizes courtesy and a degree of formality. Leadership and Organization The organization is based on respect for authority. A clear connection between the intellectual manager and the organizational centralization. Management as an intellectual activity The emphasis is on intellect rather than action. Managers must be able to grasp complex issues, analyze problems, manipulate ideas and evaluate solutions. The French Political System France is a republic France is a semi-presidential representative democratic republic, in which the President of France is head of state, and the Prime minister (PM) of France is head of government The president appoints the PM who forms the government (in theory, ministers are chosen by the PM) France has a multiparty system. French Politics (Cont.) The French business world follows specific business etiquette – the executive is expected to show interest and involvement in the task of others Opinions of experienced middle managers and technical staff may be dismissed. The French are generally collective people, their communication culture is high context. Politics Influence on Leadership Note that different cultures can have radically different leadership styles, and international organizations would do well to understand them to be able to do business in France In literature, leadership is typified as a trait, a role set, an adjective, the exercise of power, or even a process Also underscored in literature is the existence of three power sources, 1) Position, 2) Personal and 3) Political Political power – the ability to influence or control the behavior of others References Business Culture on the world stage. (n.d.). Retrieved November 05, 2014, from http://worldbusinessculture.com/ Doing Business in France - World Bank Group. (n.d.). Retrieved November 05, 2014, from http://www.doingbusiness.org/data/exploreeconomies/france/ France Business School. (n.d.). Retrieved November 13, 2014, from http://www.francebs.com/en# Suutari, V. (1996). Variation in the average leadership behavior of managers across countries: Finnish expatriates experiences from Germany, Sweden, France and Great Britain. The international Journal of Human Resource Management, 7(2), 677-707. Schramm-Nielsen, J. (2000). How to interpret uncertainty avoidance scores: A comparative study of Danish and French firms. Cross Cultural Management-An International Journal, 7, 3-11. Taleghani, G., Salmani, D., & Taatian, A. (2011). Survey of leadership styles in different cultures. Iranian Journal Management Studies, 3(3), 91-111.