Designing Products and Processes Chapter 6
advertisement

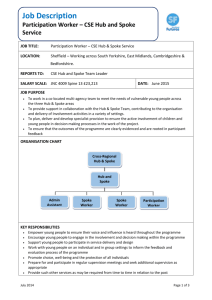
Hub and Spoke System Cameron Stevens Brigham Young University Things to consider • • • • • • • What is it? Processes that can use a hub and spoke model How it works Benefits: Why use hub and spoke? Drawbacks Example: Lowes Application What is a “Hub and Spoke” model? •Logistics term used to describe a transportation network of routes connecting origins to destinations •Its name is derived from the hub and spoke model of a wheel What is a “Hub and Spoke” model? • Companies centralize large distribution centers which essentially do three things – receive goods/information coming from many suppliers – consolidate goods/information according to the location where they are to be shipped – ship them individually to their final destination. Processes that use Hub and Spoke • Manufactured goods: – e.g. Retail • Services: – e.g. Airlines Processes that use Hub and Spoke • Information: – e.g. Financial Services • Technology: – e.g. Business Software systems How it Works • Pure Hub and Spoke vs. Hybrid Hub and Spoke How it Works • Hub and Spoke vs. Point to Point – One model consists of centralized transportation while the other model consists of many routes that are decentralized – Hub and spoke design simplifies the network of routes How it Works • Inter-hub (primary routes) • Spokes (secondary routes) How it Works • Design methods – various models – – – – weighted factor analysis centroid method linear models single and multiple allocation p-hub median problems Benefits: Why use a Hub and Spoke System • A hub and spoke distribution has several advantages that fall under these general areas – efficiency/ effectiveness – economies of scale – cost reduction Benefits: Why us a Hub and Spoke System • Efficiency and effectiveness • ensures that most routes are full or close to full • reduces the amount of deliveries lost in transit Benefits: Why use a Hub and Spoke System • Economies of scale – By having larger loads, you take advantage of lower per unit costs Benefits: Why use a Hub and Spoke System? • Transportation cost reduced • There is less time spent in transport which directly reduces the cost of the activity • Management costs • Management specialists generally focus on one location for distribution logistics Drawbacks • Disruption at the hub • Bound by hub capacity • Increased bureaucracy Example: Lowes • How to create competitive advantage in distribution logistics • Goals – – gain market share – higher profit margins Example: Lowes • Logistics and transportation costs take up a large portion of the cost of goods sold • Implementing the Hub and Spoke reduced transportation and distribution costs Example: Lowes • The longer your assets are in transit, the higher your acquisition costs • The key was reducing cycle time so that goods were being delivered at a quicker rate Example: Lowes • Idle inventory can create problems with turnover and lower return on assets • The key was decreasing the days in inventory by – reducing inventory levels – saving on holding costs Application • Finding an efficient method for designing a hub and spoke network – You have a situation where you have operation around a geographic area and you want to know where to locate a hub with respect to two factors• relative distances? • importance (load amount) of routes? Application • Designing a hub and spoke model is only an advantage if designed properly • To illustrate a design method, we will use the centroid method • This is a method used to find the best location for a distribution center Application • You are a sporting goods retail chain and are seeking to build a distribution center to serve your local operations around the intermountain west rather than having vendors deliver directly to local stores. • 8 spokes or local branches exist within the geographic range you are looking to serve. Application • Their respective coordinates are – (100,165), (205, 300), (296,267), (371, 400), (445, 457), (526, 500), (600, 185), (634, 616) • Their respective volume loads in tons per month are (000,000) – 25, 100, 560, 320, 1200, 420, 1520, 690 – Where do we locate a new distribution center? Summary • What a Hub and Spoke model is and how it works • Identified benefits and drawbacks to implementing the system • Real world example • Ideas on how to design one Suggested Readings • Hudson, Scott, “Success with Hub and Spoke distribution”, Supply Chain Cooperative – NC State University. March 14, 2003. • Pirkul, “An Efficient Procedure for Designing Single Allocation Hub and Spoke Systems”, Management Science, 44:12 (1998) -Part-2 pg:S235 -S242 • Elhedhli, Samir . "Hub-And-Spoke Network Design With Congestion ." Computers and Operations Research 32.6 (2005): 1615-1632. Suggested Readings • Yaman, Hande . "Allocation strategies in hub networks."European Journal of Operational Research16 June 2011, Pages 442-451 211.3 (2011): 442-451. • Horner, Mark W. . "Embedding economies of scale concepts for hub network design."Journal of Transport Geography 9.4 (2001): 255-265.