Chapter 17
advertisement

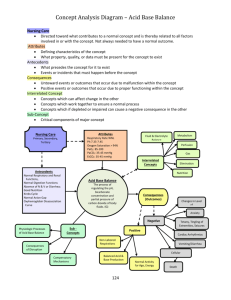
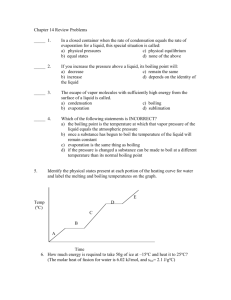
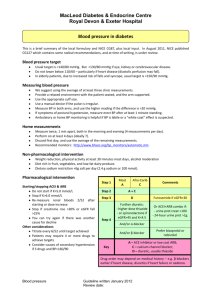
Chapter 17 Part 4 Solid-Vapor Equilibrium • Sublimation is a process in which molecules go directly from the solid into the vapor phase (deposition is the reverse process). Sublimation Iodine and dry ice are substances that commonly undergo sublimation. Which of these can reach equilibrium? Deposition • The formation of frost. Boiling • A substance boils when the vapor pressure of the liquid is equal to the atmospheric pressure. How could I boil this water? A A A What is temperature of the water? A A A Why does water boil at 100°C? Water Vapor Pressure Table Temperature (°C) 0.0 5.0 10.0 12.5 15.0 15.5 16.0 16.5 17.0 17.5 18.0 18.5 19.9 Pressure (mmHg) 4.6 6.5 9.2 10.9 12.8 13.2 13.6 14.1 14.5 15.0 15.5 16.0 16.5 Temperature (°C) 19.5 20.0 20.5 21.0 21.5 22.0 22.5 23.0 23.5 24.0 24.5 25.0 26.0 Pressure (mmHg) 17.0 17.5 18.1 18.6 19.2 19.8 20.4 21.1 21.7 22.4 23.1 23.8 25.2 Temperature (°C) 27.0 28.0 29.0 30.0 35.0 40.0 50.0 60.0 70.0 80.0 90.0 95.0 100.0 Pressure (mmHg) 26.7 28.3 30.0 31.8 42.2 55.3 92.5 149.4 233.7 355.1 525.8 633.9 760.0 Is there another way to boil the water? Is there another way to boil the water? Is there another way to boil the water? What is the pressure inside the bell jar if the water is boiling at 20°C? Water Vapor Pressure Table Temperature (°C) 0.0 5.0 10.0 12.5 15.0 15.5 16.0 16.5 17.0 17.5 18.0 18.5 19.9 Pressure (mmHg) 4.6 6.5 9.2 10.9 12.8 13.2 13.6 14.1 14.5 15.0 15.5 16.0 16.5 Temperature (°C) 19.5 20.0 20.5 21.0 21.5 22.0 22.5 23.0 23.5 24.0 24.5 25.0 26.0 Pressure (mmHg) 17.0 17.5 18.1 18.6 19.2 19.8 20.4 21.1 21.7 22.4 23.1 23.8 25.2 Temperature (°C) 27.0 28.0 29.0 30.0 35.0 40.0 50.0 60.0 70.0 80.0 90.0 95.0 100.0 Pressure (mmHg) 26.7 28.3 30.0 31.8 42.2 55.3 92.5 149.4 233.7 355.1 525.8 633.9 760.0 We can make water boil at “any” temperature. Water Vapor Pressure Table Temperature (°C) 0.0 5.0 10.0 12.5 15.0 15.5 16.0 16.5 17.0 17.5 18.0 18.5 19.9 Pressure (mmHg) 4.6 6.5 9.2 10.9 12.8 13.2 13.6 14.1 14.5 15.0 15.5 16.0 16.5 Temperature (°C) 19.5 20.0 20.5 21.0 21.5 22.0 22.5 23.0 23.5 24.0 24.5 25.0 26.0 Pressure (mmHg) 17.0 17.5 18.1 18.6 19.2 19.8 20.4 21.1 21.7 22.4 23.1 23.8 25.2 Temperature (°C) 27.0 28.0 29.0 30.0 35.0 40.0 50.0 60.0 70.0 80.0 90.0 95.0 100.0 Pressure (mmHg) 26.7 28.3 30.0 31.8 42.2 55.3 92.5 149.4 233.7 355.1 525.8 633.9 760.0 234 Elevation = 29,035 ft. What would happen to this water as it boiled? It gets colder How can we continue to boil the water as it cools? Water Vapor Pressure Table Temperature (°C) 0.0 5.0 10.0 12.5 15.0 15.5 16.0 16.5 17.0 17.5 18.0 18.5 19.9 Pressure (mmHg) 4.6 6.5 9.2 10.9 12.8 13.2 13.6 14.1 14.5 15.0 15.5 16.0 16.5 Temperature (°C) 19.5 20.0 20.5 21.0 21.5 22.0 22.5 23.0 23.5 24.0 24.5 25.0 26.0 Pressure (mmHg) 17.0 17.5 18.1 18.6 19.2 19.8 20.4 21.1 21.7 22.4 23.1 23.8 25.2 Temperature (°C) 27.0 28.0 29.0 30.0 35.0 40.0 50.0 60.0 70.0 80.0 90.0 95.0 100.0 Pressure (mmHg) 26.7 28.3 30.0 31.8 42.2 55.3 92.5 149.4 233.7 355.1 525.8 633.9 760.0 And then when the vapor pressure of water reaches 4.6 mm Hg. Water Vapor Pressure Table Temperature (°C) 0.0 5.0 10.0 12.5 15.0 15.5 16.0 16.5 17.0 17.5 18.0 18.5 19.9 Pressure (mmHg) 4.6 6.5 9.2 10.9 12.8 13.2 13.6 14.1 14.5 15.0 15.5 16.0 16.5 Temperature (°C) 19.5 20.0 20.5 21.0 21.5 22.0 22.5 23.0 23.5 24.0 24.5 25.0 26.0 Pressure (mmHg) 17.0 17.5 18.1 18.6 19.2 19.8 20.4 21.1 21.7 22.4 23.1 23.8 25.2 Temperature (°C) 27.0 28.0 29.0 30.0 35.0 40.0 50.0 60.0 70.0 80.0 90.0 95.0 100.0 Pressure (mmHg) 26.7 28.3 30.0 31.8 42.2 55.3 92.5 149.4 233.7 355.1 525.8 633.9 760.0 What is the boiling point of ethanol at normal air pressure? What is the boiling point of water at an air pressure of 400 torr? At what air pressure will Diethyl ether boil at 20°C? How do these substances compare in terms of Van der Waals forces, rate of evaporation, vapor pressure, and volatility ? How do these substances compare in terms of Van der Waals forces, rate of evaporation, vapor pressure, and volatility ? “Which would you expect to have the higher boiling point? “Which would you expect to have the higher boiling point? He = -269˚C Rn = -62˚C Homework Worksheet 2 Chapter 17 Illustrate the relationship between ∆H and exo/endo reactions. ↑Temp shifts reactions in the endothermic direction