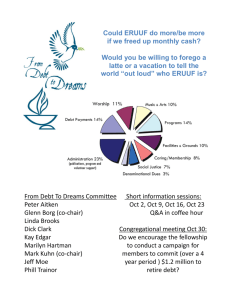
What are the main hardware components of a computer
advertisement

TABLE OF CONTENTS COMPUTER BASICS ................................................................................................................................................ 2 WHAT IS A COMPUTER? .................................................................................................................................................. 2 WHAT IS A PERIPHERAL? ................................................................................................................................................. 2 WHAT PERIPHERALS ARE COMMONLY USED, AND WHAT ARE THEY USED FOR? ........................................................................... 3 WHAT ARE THE MAIN HARDWARE COMPONENTS OF A COMPUTER? ......................................................................................... 3 CPU:...................................................................................................................................................................... 3 Main Memory: ..................................................................................................................................................... 4 Secondary Storage: .............................................................................................................................................. 4 WHAT IS A NETWORK? WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN A NETWORK AND A STAND-ALONE ENVIRONMENT? ........................... 4 WHAT IS AN OPERATING SYSTEM? WHAT IS ITS PURPOSE? ..................................................................................................... 5 At the most basic level, the operating system can do 2 things: ........................................................................... 5 There are also many types of operating systems. ................................................................................................ 5 WHAT IS HARDWARE? .................................................................................................................................................... 6 WHAT IS SOFTWARE? ..................................................................................................................................................... 6 GIVE SOME EXAMPLES OF SOFTWARE: SEE FIGURE 4 ............................................................................................................. 7 HOW SHOULD A COMPUTER WORKSTATION BE SET UP TO MAXIMIZE THE COMFORT OF THE USER? ................................................. 8 IDENTIFY COMMON USER INTERFACE ELEMENTS AND DESCRIBE THEIR FUNCTIONS ....................................................................... 9 REVOLUTIONS IN COMPUTING TIMELINE ............................................................................................................. 12 EVALUATION OF A WEBSITE ................................................................................................................................. 18 GLOSSARY ............................................................................................................................................................ 20 BIBLIOGRAPHY ..................................................................................................................................................... 22 INDEX ................................................................................................................................................................... 26 1 COMPUTER BASICS WHAT IS A COMPUTER? A computer is a device which can be used for various arithmetic and logic operations. In a conventional computer, there is at least one processing element, often a central processing unit and a memory. A modern computer is based on integrated circuits but it is much more likely than older computers, but old computers, invented between 1940 and 1945, were the size of a room and were very slow. WHAT IS A PERIPHERAL? A peripheral is a Device that is connected to a computer, but it is not part of it. Through a device the capabilities of the computer are large. It is often dependent on the computer. An example of this is a printer. See figure 1. Figure 1: Wireless printer 2 WHAT PERIPHERALS ARE COMMONLY USED, AND WHAT ARE THEY USED FOR? The peripherals commonly used are the Keyboard, the Mouse, the Screen and the Printer. See figure 2. The input peripherals are used to provide information to the computer. The output peripherals are used to get information from the computer system. The peripherals are used to transmit information from the people to the computer or vice-versa. Figure 2. Computer Peripherals WHAT ARE THE MAIN HARDWARE COMPONENTS OF A COMPUTER? These are Components that constitute the elements of laptops. They are often in a computer case, but they can also be connected to the computer with a cable, so they can be considered as peripherals. CPU: The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the brain of the computer. It carries out the instructions of a computer Program. The CPU is composed of the Central Unit (CU) and the Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU). CU: It is the part of the computer that carries out instructions ALU: It is the part of the computer that performs arithmetic and logical operations 3 MAIN MEMORY: The main memory is the primary storage. The CPU reads the instruction stored in the Main Memory and executes them. When your computer is powered off, the information stored in the Main Memory is lost. The information in the Main Memory is directly accessible by the CPU. SECONDARY STORAGE: The information stored in the Secondary Storage is NOT accessible by the CPU. The computer usually uses the input/output channels to get secondary storage. Secondary storage devices include USBs and hard drives. WHAT IS A NETWORK? WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN A NETWORK AND A STAND-ALONE ENVIRONMENT? A network is two or more computers linked to share resources (printers and CDs), exchange files and allow electronic communication. Computers in a network can be linked by cables, telephone lines, radio waves or satellites. The Internet is an example of a network; it connects millions of people around the world. A stand-alone environment is when a computer is not connected to any type of network or any other communication device. The computer is used independently. If you need to transfer data between two stand-alone computers, it will have to be done manually. Although a stand-alone computer and a network computer are relatively the same, there are differences in the setup and management in each type of computer. While a stand-alone computer works independently, a network computer is connected to several other computers and it can share resources. Also, stand-alone computers are more secure because it isn’t 4 communicating with other computers like a network. It limits the amount of hackers and spyware. Unfortunately, a stand-alone computer is not very useful in today’s technologies. WHAT IS AN OPERATING SYSTEM? WHAT IS ITS PURPOSE? An operating SYSTEM is a software system that allows the computer hardware to communicate with the computer software. The purpose of an operating system is to organize and control the software and the hardware. AT THE MOST BASIC LEVEL, THE OPERATING SYSTEM CAN DO 2 THINGS: 1. It controls the hardware and software resources in the computer. In a desktop computer, this can include disk space, the processor, memory and many more. In a computer, many applications fight for the attention of the central processing unit (CPU). With the operating system, everything is regulated. 2. It provides a stable way for applications to deal with the hardware without having to know all the information about the hardware. THERE ARE ALSO MANY TYPES OF OPERATING SYSTEMS. Real time operating system: This operating system is used to control machinery, scientific and industrial systems. This type of system generally has very few interface elements. Single user, single task: This system is for one person to do one single task very well and effectively. Single user, multi-tasking: This system is the one that most people use on their Desktop. This allows the user to have many programs in operating at the same time. Microsoft’s Windows and Apple’s MacOS are good examples of this type of system. 5 Multi-user: This allows multiple users to use the computer’s resources at the same time. This system has to control the requirements of each user so a problem that one single user might have doesn’t affect the whole community. PCs usually use Windows 7 or 8 and Macintosh computers use MacOS. WHAT IS HARDWARE? Hardware is the physical components of your computer, which you can feel and touch. Hardware is used to run and store the software. Without hardware, you cannot use software. Likewise, hardware functions once software is installed. Hardware can wear out over time. A hardware upgrade is when a piece of hardware is replaced or a piece of hardware is added. There is external hardware and internal hardware. Examples of external hardware include the mouse, the keyboard, and the monitor. Examples of internal hardware include the hard drive, the RAM (Random Access Memory) and the video card. See figure 3. Figure 3. Computer hardware WHAT IS SOFTWARE? 6 Software enables your computer to do certain tasks. Without software, your computer would be useless. Without Internet browser software, you wouldn’t be able to go on the Internet. Software must be installed onto hardware. It can’t do anything on its own. Software does not wear out over time, but Bugs can be found in software. It can be fixed, though. There are two main categories for software: system software and application software. System software normally comes Pre-Installedin the computer and it controls the basic functions of the computer. See figure 4. These functions are invisible to the user. Application software is the software that handles specialized tasks such as word processors and email. Figure 4: Application software GIVE SOME EXAMPLES OF SOFTWARE: SEE FIGURE 4 Web browsers: Internet Explorer, Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox E-mail: Gmail, Yahoo, Hotmail Games: World of Warcraft, League of Legends, The Sims Presentation: Microsoft PowerPoint Photo editors: Photoshop Word processors: Microsoft Word Operating systems: Microsoft Windows Presentation : Powerpoint 7 Figure 5. Samples of System software HOW SHOULD A COMPUTER WORKSTATION BE SET UP TO MAXIMIZE THE COMFORT OF THE USER? When setting up a computer workstation, the chair must be positioned so that you aren’t craning your neck looking down at the computer screen or looking up at it. You must be seated far enough from the computer so that you aren’t straining your eyes, but if they’re too far away you won’t be able to sit comfortably. Your face should be at least 40cm away from the screen. The brightness and contrast of the computer can’t be too high or too low because it may give you a headache or strain your eyes. The keyboard of the computer should be positioned so that your arms can rest comfortably when typing, not having to reach too far to get to the keys, but not so close that it your arms would be forced back. You should have a 90110 degree angle from your shoulder to your elbow to your wrist. You should have a comfortable seat that allows you to lean backwards if needed. See figure 6. Any documents should be placed close to you so that you don’t have to reach very far and put yourself in uncomfortable positions to get them. 8 Figure 6. Computer Workstation Set-Up IDENTIFY COMMON USER INTERFACE ELEMENTS AND DESCRIBE THEIR FUNCTIONS Interface elements include: Input controls: checkboxes, radio buttons, dropdown lists, list boxes, buttons, toggles, text fields, date field Navigational Components: breadcrumb, slider, search field, pagination, slider, tags, icons Informational Components: tooltips, icons, progress bar, notifications, message boxes, modal windows Containers: accordion CHECKBOXES: Checkboxes allow the user to select something from multiple choices. See Figure 7. Figure 7. Example of Checkboxes 9 TEXT FIELDS: Text fields allow the user to enter text. It can either be one line or multiple lines. See Figure 8. Figure 8. Example of Text Fields SEARCH FIELD: A search field/box that allows the user to type in a word or phrase in order to get back the most relevant results from an index. See Figure 9. Figure 9: Example of a Search Field ICONS: An icon is a simple image to help users identify and navigate the system. Icons are typically hyperlinked. See Figure 10. 10 Figure 10: Examples of Icons 11 REVOLUTIONS IN COMPUTING TIMELINE Year What is it? Why is it important? Interesting fact Abacus 300 B.C It is a calculation device. It was used before the invention of Arabic numerals. It was used for addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Abacus comes from the Greek word ABAX which means calculating table. Antikythra mechanism At least 2000 years old A mechanical computer used to calculate the movements of stars and planets. At that time, it provided people with the astronomical knowledge. It was like an encyclopedia. It was recovered in1900-1901. It is displayed at the National Archaeological Museum of Athens. John Napier, Calculation Tables 1614 It was the world’s first calculator. Napier developed what would be the backbone of modern mathematics. John Napier entered St. Andrew’s university at the age 13 but never graduated. Joseph-Marie Jacquard, Punchcard controlled loom 1801 A weaving loom that used punch cards to create elaborate and complicated designs. The weaving profession was a tiring job but this invention made it less tedious and you were able to make intricate designs. It reduced the amount of human labour. The French Government considered the loom to be public property therefore giving Jacquard a small pension. Charles Babbage, Difference Engine 1822 A mechanical calculator used to solve polynomial functions. It was a better and more effective way of solving math equations. Charles Babbage invented the Difference Machine because he was tired of people making mathematical errors. Samuel Morse, Telegraph 1837 Machine used to transmit messages using Telegraphs made it possible to communicate to people The telegraph became more 12 Sir Charles Wheatstone, paper tapes electrical impulses. quickly over vast distances. famous when it was used a catch a murderer boarding a train in London. It records data. It helped people connect with one another. Sir Charles Wheatstone also invented the accordion. Stoles, Glidden and Soule, typewriter 1866 It allows the user to print letters one by one onto a medium such as paper/ It increased the production of books, newspapers and other written documents. This also increased the literacy rate in many countries. Typewriter is the longest word that you can spell using only one row of letters. Herman Hollerith, Tabulating Machine 1881 It helps summarize information and it also does accounting. Since it recorded medical information in the late 1880s to the 1960s, it was very important to doctors and nurses Without the tabulating machine, it was hard to count the population. It took 7 years to complete the 1880 census. Electronic computing devices used to help British code breakers read encrypted German messages It was the first large scale electronic computer. It helped British soldiers and code breakers prevent attacks from Germans. Since many machines used in WWII were destroyed or hidden, the Colossus was only recently fully recognized. Transistors control the movement of electrons. The Transistor was probably the most important electronic invention in the 20th century. It was the basis of modern technologies. Today, billions of transistors are manufactured every week. A small electronic device made of a transistor and other components in a piece of germanium. Integrated Circuits are used in practically every electronic device today. Pure silicon is the basis for most integrated circuits. Mainframe computer system It changed the way people thought of computers and it was said to be the company’s most important product Within 8 weeks of its announcement, customers ordered well over two Colossus Bell Labs, the Transistor 1947 Texas Instruments and Fairchild Semiconductor, Integrated Circuit IBM 360 1964 13 announcement ever. thousand machines. Word Processor invented 1979 Software capable of creating, printing and storing documents. Word processing has had a huge impact on education. It saves time and you are able to share documents. Ribbon Hero and Ribbon Hero 2 are games that are designed that help people learn the features of Microsoft Word, a word processor. ARPANET 1966 It was a wide area network (WAN) that connected several universities and research centers. It was the beginning of the Internet. Email capabilities were introduced to ARPANET in 1977. Intel, 1K RAM CHIP (the 4004) 1971 It is a microprocessor that was first designed for a printing calculator. It is Intel’s first microprocessor. This microprocessor (the size of a fingernail) delivered the computing power as the first computer (built in 1946) which took up a whole room. Today, it is slimmer than a human hair. Jonathan Titus, Mark 8 1973 Mark 8 is a computer that was invented by the student Jonathan Titus. It can be used to manipulate data, send data to the mainframe and control experiments. Mark 8 has caused a significant impact in the amateur community. It has been used for applications in instrumentation for nuclear reactors. Jonathan and his brother have designed several other parts of computer equipment. BBN, Telenet 1948 This is a company that has been very involved in the invention of new communication technologies in the internet. Thanks to all that they have done the internet is much bigger and more developed. They were full of different research to advance the technology to communicate with the Internet. In 1968, BBN ARPAnet has clinched a contract. 14 Paul Allen and Bill Gates invent BASIC 1975 This is a programming language that has been created for use of the personal computer. Thanks to this invention, the computing world is different and highly developed. They have begun to do that because they had a vision for a long period or the chip could go. USENET 1979 This is a network that allowed to swap the information as before internet was a network of private exploited sites. Usenet has provided a network for the general public. Thanks to Usenet people could have access to information that had not with newspapers. It is on the Usenet emoticons, some expressions, trolls, etc., it was invented. The archives provided by Usenet is a good source of information on the most recent decades of computing. The history of Usenet is not only relevant to social networks, but many concepts and high-tech innovations. TCP/IP 1974 TCP/IP stands for Transmission Control Protocol/ Internet Protocol. They are 2 separate things, but they are used together so often that TCP/IP has become the standard term The TCP/IP govern the rules over passing along information on the internet. Without the TCP/IP you would need direct connections to the other computers to get any information from them. IP addresses follow the Internet Protocol. Everything connected to the internet has an IP address and its how they can find one another through the massive network that is known as the internet. Apple Macintosh 1984 The macintosh is a computer that was made from the company apple. The macintosh was the very first computer that used a mouse. Computers before the macintosh were “text-based” and you operated them by typing words into the keyboard. The macintosh runs by clicking icons, which we do now. It was considered to be the first computer to successfully use a GUI (Graphical User Interface). The macintosh has the signatures of the designers on the inside of the case. Microsoft Windows 1.0 1985 Microsoft windows is an operating system. It The Microsoft windows operating system allows you The official code name is Interface 15 The Internet 19691972 came after the MS-DOS (Microsoft Disk Operating System), and is much more advanced. to use a mouse instead of needing to type up commands for your computer. You can point and click through screens instead of Manager and it is considered to be the final name, but the name Windows prevailed because it best described the boxes needed for the new system. The internet is the largest computer network in the world. It is the physical network of all computers and it connects them. Without the internet, it would be harder to gather information and communicate with others from around the world (example: family living in a different country). If you were to store all of the information that is on the internet, you would need more than 1 billion dvds or 200 million blu-ray discs. Apple iPod 2001 A portable device that plays music and depending on the version, you might be able to play games and go on the internet with it. With an iPod, you can listen to music and watch videos on the go. This way, you don’t have to carry a cd player or a radio with you when going for a run. In France, it is illegal to play anything on your iPod louder than 100 decibels. Apple iPhone 1983 (the very first one) An iPhone is a phone with a touchscreen that is a lot like the later versions of an iPod. Unlike the iPod, the iPhone can make calls and text people. It can also take pictures. (depending on the version) An iPhone is easy to open and close. Since it’s a touchscreen, you feel in control at all times and it gives easy access to games, photos, contacts, and other stuff. When typing, you have a computer-like keyboard, with buttons for numbers and symbols. If needed, you can also rotate the display so that it’s sideways. The very first iPhone was not the kind of iPhones that we have today. It was actually a white landline phone with a built in screen controlled by a stylus. 2007 (the cell phone) Amazon Kindle 2007 This is an electronic tablet that measures 6 inches with 250 GB of memory. The price is much cheaper than the Apple Ipad. This is a convenient way to have multiple books, newspapers and applications in a single tablet. It is light and easy to carry. When Kindle was launched, it became very popular and all of them had been sold in a few hours. They were out of stock for months. Apple iPad 2010 This is an electronic This is very advanced The Ipad manages 16 tablet that lets you send email, watch or take pictures, play games or listen to music. It allows users to physically interact with the applications and content. technology which allows for all that we need and we want in one device. With the iPad, Apple allows users to have new means of interaction that are fun and intuitive. almost all of the Apple store, with over 11 million songs, 50,000 TV series episodes and over 8,000 films. Android 2008 Android is a software that google engineered, so google’s apps run best on it. With the widgets, you can look at photos, email, and more without needing to leave your home screen or open different apps. On certain devices, there is a thing called “Face Unlock” which allows you to unlock your device with a facial expression. Android is very intuitive and creative and will continue to think of ideas like these. Each version of android is names after a dessert. The most recent one was Jellybean and the next version is said to be named Kitkat. 3D Printing 1980 A 3D printer uses Computer Aided Designs (CAD) to create 3D objects. 3D printers can make a variety of things including furniture, sculptures, and toys. It can print plastic, metal, nylon, and over a hundred other materials. 3D printers can create models and prototypes, allowing people to make quick changes in their designs. On top of that, 3D printing can save money, because it doesn’t waste a lot of material, unlike when material needs to be cut, shaved off, or drilled. There are certain 3D printers that can be used for applying things in other forms, such as liquids and pastes (ex. icing and chocolate). The French Culinary Institute has been using one of these to make artistic delicacies. Leap Motion Controller 2013 The Leap motion controller is a small and light motion sensor that conects to your computer and lets you control it without using a mouse or a trackpad, and without touching the screen. Instead, you put your hands over it (without touching it) and you can interact with your computer based on how your This gives you much more control over your actions. If, for example, you like art and you want to draw on your computer you can use your fingers instead of a mouse or a trackpad, which can be tricky to use. If you’re playing the piano or a guitar on the computer, you can do many more things than just hit one note at a time or strum. You can play chords, pieces, or pluck the strings! There is a store for apps designed for the Leap Motion Controller called “Airspace”. It’s created by the same people who created the Leap Motion Controller. 17 hands and fingers move. The Cloud 1969 The Cloud is all of the things you can remotely access over the internet. The Cloud allows things to be stored on servers on the internet instead of just your computer. That way, you can access your email and many other things from any computer with an internet connection. If something happens to your computer, like it gets a virus, or it gets wiped, you will still be able to access your email, important files, and anything else that has been saved over the internet, just on a different computer. This is extremely helpful, especially if you need to retrieve a file with, let’s say, work on it, and you can only access it by A. Your computer or B. Your email. Some cloud applications that have been researched at intel include decoding brainwave patterns and creating new user interfaces. EVALUATION OF A WEBSITE The website "Internet 101" is very useful and easy to use. It was created by a non-profit organization. The purpose of this website is to teach others about the basics of the internet and it is full of helpful information. The pages are small enough so that they aren't boring and some pages are interactive. There are colourful pictures that make it easier to understand and it has a font that is big enough so that it is easy to read. 18 I can't tell when it was last modified, but that doesn't matter because the facts aren't going to change. Especially not the history facts. The site is very well maintained, though, seeing as this is a website with nice, calm colours that aren't too loud and there isn't a dizzying pattern that makes the background too busy. None of the links are broken and that's great because with the fun interactive page, you don't have to keep reloading the page. When you click on the interactive buttons, you don't have to move to a new website. Overall, it is very easy to read and navigate, and it is well designed and organized. 19 GLOSSARY Bugs: Bugs are little glitches or problems in the program or software. They can normally be fixed. Components: A part or an element of something that is complete/whole. For example, a component could be a part of a car or a toaster. Desktop: The background picture of a display screen where images, icons and windows appear. Device: Something created or made for a certain task. For example, it can be some sort of mechanism or electronic. Keyboard: A keyboard helps input data onto your computer and it allows you to be able to type. Mouse: A mouse is an electronic device that controls the coordinates of your cursor on your computer screen when moved around on a mouse pad. Pre-Installed: The program or software has already been installed so that you don’t have to do it yourself. Printer: A printer is a machine that allows you to print text and/or pictures onto paper. Printers must be connected to a computer. Program: A sequence of instructions that the computer can understand and execute. Screen: The screen is part of the monitor that allows you to see the output of the computer to the user. 20 System: A set of things working together as parts of a mechanism or a network. 21 BIBLIOGRAPHY Franklin, Curt, and Dave Coustan. "How Operating Systems Work." HowStuffWorks. N.p., n.d. Web. 4 Oct. 2013. <http://computer.howstuffworks.com/operating-system.htm>. Winkelman, Roy. "What Is a Network?" Florida Center For Instructional Technology, n.d. Web. 5 Oct. 2013. <http://fcit.usf.edu/network/chap1/chap1.htm>. Allen, Martin. "Why Is It So Important?" The Antikythera Mechanism Research Project. N.p., 17 June 2008. Web. 5 Oct. 2013. <http://www.antikythera-mechanism.gr/faq/general-questions/why-is-it-soimportant>. "Abacus." Cultural China. N.p., n.d. Web. 5 Oct. 2013. <http://www.culturalchina.com/chinaWH/html/en/10Kaleidoscope6.html>. Bartolome, Eric. "The Antikythera Mechanism." Stunning And Interesting Facts. N.p., n.d. Web. 5 Oct. 2013. <http://www.stunninginterestingfacts.com/2012/10/the-antikythera-mechanism-first-computer.html>. Hansen, Jim. "Napier's Bones." John Napier's Bones. N.p., n.d. Web. 5 Oct. 2013. <http://www.17centurymaths.com/contents/napier/jimsnewstuff/Napiers%20Bones/NapiersBones.ht ml>. "User Interface Elements." Usability.gov. N.p., n.d. Web. 9 Oct. 2013. <http://www.usability.gov/how-toand-tools/methods/user-interface-elements.html>. "What Is a Computer." Webopedia. Itsbusinessedge, n.d. Web. 10 Oct. 10. <http://www.webopedia.com/TERM/C/computer.html>. "What Is a Peripheral." Webopedia. Itsbusinessedge, n.d. Web. 10 Oct. 10. <http://www.webopedia.com/TERM/P/peripheral_device.html>. "Computer Hardware Peripherals." English4it. N.p., n.d. Web. 10 Oct. 10. <http://www.english4it.com/reading/31>. "Who Built the First Modern Computer?" Computer Science For Fun. N.p., n.d. Web. 10 Oct. 10. <http://www.cs4fn.org/history/colossus.php>. "Fun Facts." Typewriter. N.p., n.d. Web. 10 Oct. 10. <http://typewriterdg.weebly.com/interestingfacts.html>. "The Story of the Intel 4004." Intel. N.p., n.d. Web. 10 Oct. 10. <http://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/history/museum-story-of-intel-4004.html>. "Mark 8." Jonathan A. Titus. Florida Gulf Coast University, 2007. Web. 11 Oct. 2013. <http://chc61.fgcu.edu/mark8.aspx>. "Bill Gates, Paul Allen and Basic." Stanford, n.d. Web. 11 Oct. 2013. <http://facultygsb2.stanford.edu/mendelson/computer_history/software.htm>. "Usenet History." Giganews. N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Oct. 2013. <http://www.giganews.com/usenet-history/>. 22 "BBN Internet Engineering Timeline." Xbbn. N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Oct. 2013. <http://xbbn.weebly.com/bbninternet-engineering-timeline.html>. "Hardware vs Software." - Difference and Comparison. N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Oct. 2013. <http://www.diffen.com/difference/Hardware_vs_Software>. "Hardware." What Is Hardware? N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Oct. 2013. <http://www.computerhope.com/jargon/h/hardware.htm>. "IT English." IT English. University of Victoria, n.d. Web. 11 Oct. 2013. <http://web2.uvcs.uvic.ca/elc/sample/ite/u01/u1_1_03.html>. "Online Resources." Examples Of Computer Software. N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Oct. 2013. <http://www.streetdirectory.com/etoday/examples-of-computer-software-apjju.html>. "Software." BusinessDictionary.com. N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Oct. 2013. <http://www.businessdictionary.com/definition/software.html>. "How to Make Your Computer Workstation Fit You." Worksafebc.com. N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Oct. 2013. <http://www.worksafebc.com/publications/health_and_safety/by_topic/assets/pdf/comptr_wrk stn.pdf>. "How Does the Internet Work?" HowStuffWorks. N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Oct. 2013. <http://computer.howstuffworks.com/internet/basics/internet1.htm>. "TCP/IP - Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol." About.com Wireless / Networking. N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Oct. 2013. <http://compnetworking.about.com/cs/basictcpip/g/bldef_tcpip.htm>. "Who Created the Internet Network?" About.com Wireless / Networking. N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Oct. 2013. <http://compnetworking.about.com/od/history_networking/f/internet_create.htm>. "A History of Windows." Windows.microsoft.com. N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Oct. 2013. <http://windows.microsoft.com/en-CA/windows/history>. 23 "Macintosh Computer." Macintosh Computer. N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Oct. 2013. <http://oldcomputers.net/macintosh.html>. "3D Printing: What You Need to Know." Pcmag.com. N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Oct. 2013. <http://www.pcmag.com/article2/0,2817,2394722,00.asp>. "Cloud Computing Fun Facts." Download.intel.com. N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Oct. 2013. <http://download.intel.com/newsroom/kits/istcs/pdfs/CloudFunFacts.pdf>. "13 Fun Facts." : About Your IPod. N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Oct. 2013. <http://13-funfacts.blogspot.ca/2011/05/13-fun-facts-about-your-ipod.html>. "Apple Press Info." Apple. N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Oct. 2013. <http://www.apple.com/pr/products/ipodhistory/>. "A Complete History of Android." TechRadar. N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Oct. 2013. <http://www.techradar.com/news/phone-and-communications/mobile-phones/a-completehistory-of-android-470327>. "A History of Cloud Computing." A History of Cloud Computing. N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Oct. 2013. <http://www.computerweekly.com/feature/A-history-of-cloud-computing>. "Internet 101." GCFLearnFree.org. N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Oct. 2013. <http://www.gcflearnfree.org/internet101/1.5>. "Introducing Android." Android. N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Oct. 2013. <http://www.android.com/about/>. "It Goes Where No Device Has Gone Before." Leap Motion. N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Oct. 2013. <https://www.leapmotion.com/product>. "Leap Motion Controller Released at Last." Leap Motion Controller Released at Last. N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Oct. 2013. <http://www.gizmag.com/leap-motion-released-at-last/28418/>. 24 "Mashable." Mashable. N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Oct. 2013. <http://mashable.com/2011/12/30/apple-iphone1983/>. "Who Invented The IPhone?" About.com Inventors. N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Oct. 2013. <http://inventors.about.com/od/istartinventions/a/iPhone.htm>. 25 INDEX components, 2, 4, 10 Internet, 3, 5, 10, 11, 12, 14, 17, 18, 19 computer, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 16, 17, 18 Navigational Components, 7 hardware, 2, 3, 4, 5, 18 Informational Components, 7 Input controls, 7 Interface, 7, 12, 17 network, 3, 10, 11, 12, 16, 17 peripherals, 1, 2 software, 3, 4, 5, 6, 13, 16, 17, 18 system, 2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 10, 12, 17 workstation, 6 26