CARDIVASCULAR DRUGS - medpharm
advertisement

CARDIVASCULAR
DRUGS
Sanjukta (2009)
CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE AND
DRUGS
►
►
Basic cardiovascular physiology and pathology depends on
the control of heart rate, cardiac output, blood pressure,
blood flow, ionic composition, RAAS, vascular endothelium,
regulation of tissue perfusion, hypertension, dislipidaemias,
atherosclerosis, blood clotting, ischaemic heart disease,
cardiomyopathies, cardiac arrhythmias and cardiac failure.
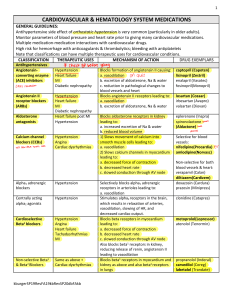
Cardiovascular drugs: inotropic agents, b blockers, calcium
antagonists, organic nitrates, anti-arrhythmics, ACE
inhibitors, ATII (=AT1) antagonists, diuretics, cholesterol
lowering drugs, clot-busters, anti-coagulants, anti-platelet
drugs.
DRUGS TO TREAT ANGINA
PECTORIS
► Angina
pectoris refers to a strangling or pressure
like pain caused by cardiac ischaemia.
► It’s a pain syndrome due to induction of an
adverse oxygen supply / demand situation in
portion of myocardium.
► Drugs used exploit two main strategies: reduction
of oxygen demand and increase of the oxygen
delivery to myocardium.
► Three types of anginal attack: stable angina,
unstable angina and variant angina.
ANTI ANGINAL DRUGS
►
1) ORGANIC NITRATES: Glyceryl trinitrate (Nitroglycerin), Isosorbide
dinitrate, etc
►
2) BETA BLOCKERS: Propranolol, Atenolol, Metroprolol, Carvedilol, etc
3) CALCIUM ANTAGONIST: Nifedipine, Diltiazem, Verapamil
4) SELECTIVE If- INHIBITORS: Ivabradine
►
►
ANTI ARRHYTHMIC DRUGS
Cardiac arrythmias commonly occur in presence of preexisting heart disease.
1) CLASS I: Membrane stabilizing drugs; sodium channel
blockersCLASS I a- Quinidine, disopyramide
CLASS I b- Lidocaine, Phenytoin
CLASS I c- Propafenone
2) CLASS II: BETA BLOCKERS- Acebutolol, Atenolol,
Esmolol,Metoprolol, Propranolol
3) CLASS III: POTASSIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERSAmiodarone, Sotalol
4) CLASS IV: CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS- Verapamil,
Diltiazem
CLINICAL CLASSIFFICATION OF
ANTIDYSRHYTHMIC DRUGS
►
►
►
►
►
I GROUP: (decrease AV conductance, for treatment of SV
tacharrhythmia)- Verapamil
II GROUP: (for treatment of ventricular tachyarrhythmia)Lidocaine (i.v.), Propafenone, Phenytoin
III GROUP: (for treating SV and V tachyarrhythmia)Amiodarone, Beta blockers
IV GROUP: (drugs for AV block)- Atropine {M-cholinolytic},
Ephedrine {indirect adrenomimetics}
V GROUP: (inhibitors of AV conduction)- Adenosine
[potassium channel opener], Digoxin [cardiac glycoside]
ANTIHYPERTENSIVE DRUGS
► DRUGS
AFFECTING RAAS [renin angiotensin
aldosterone system]RENIN INHIBITOR: Beta blockers
[Propranolol, Atenolol, etc]
ACE INHIBITORS: Enalapril, Ramipril
ANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR [AT1receptor] BLOCKERS: Eprosartan, Losartan
ALDOSTERONE ANTAGONIST [
potassium sparing diuretic ]: Spironolactone
► CALCIUM
ANTAGONIST: Nifedipine, Amlodipine,
Diltiazem, Verapamil
► DRUGS DECREASING SYMPATHETIC ACTIVITYBETA BLOCKERS: Nebivolol, Atenolol,
Bisprolol, Pindolol, Carvedilol
ALFA BLOCKERS: Prazosin, Phentolamine
OTHER: Reserpine, clonidine
► DIURETICS: Hydrochlorothiazide, Indapamide,
Furosemide
PERIPHERAL VASODILATORS
► Alfa
blockers- Prazosin, Ergotoxine
► Phosphodiesterase inhibitors- Pentoxifylline
► Prostaglandin analogue- [activators of AC]
Alprostadil (PG1), Iloprost (PG2)
► CEREBRAL VASODILATORS:
Nimodipine (calcium antagonist),
Naftidrofuryl (5-HT2 receptor blocker)
DRUGS TO TREAT HEART FALIURE
► Clinical
syndrome that
can result from any
structural or functional
cardiac disorder that
impairs the abilty of the
ventricle to fill with or
eject blood.
►
►
►
►
►
►
►
►
►
►
►
Therapeutic Uses of
Digitalis Compounds
Heart Failure
↑ inotropy
↑ ejection fraction
↓ preload
↓ pulmonary congestion/edema
Arrhythmias
↓ AV nodal conduction
(parasympathomimetic effect)
↓ ventricular rate in atrial flutter
and fibrillation
Digitalis compounds have historically been used in the treatment of
chronic heart failure owing to their cardiotonic effect.
Ex: Digoxin, digitoxin
► To
treat CHF:
Ionotropic drugs: Digoxin, Dobutamine
Diuretics: Furosemide, Thiazide
Vasodilators: ACE inhibitors,AT1
antagonist, Nitrate
Beta blockers: Metroprolol
THANK YOU
BY: SANJUKTA GHOSE