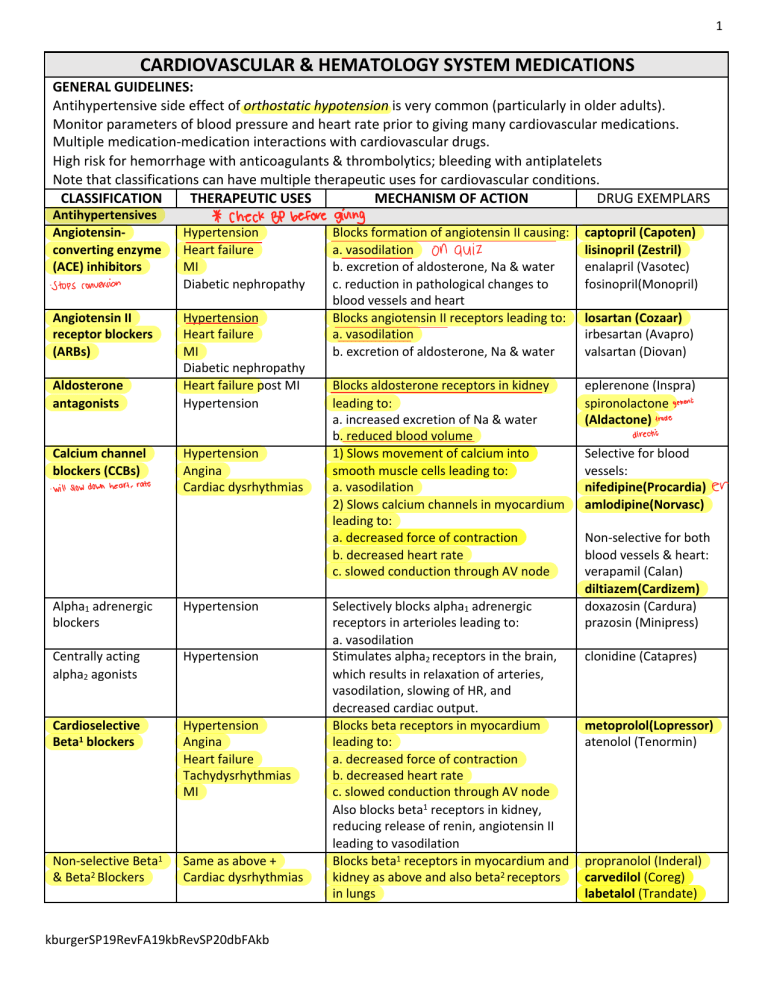
1 CARDIOVASCULAR & HEMATOLOGY SYSTEM MEDICATIONS GENERAL GUIDELINES: Antihypertensive side effect of orthostatic hypotension is very common (particularly in older adults). Monitor parameters of blood pressure and heart rate prior to giving many cardiovascular medications. Multiple medication-medication interactions with cardiovascular drugs. High risk for hemorrhage with anticoagulants & thrombolytics; bleeding with antiplatelets Note that classifications can have multiple therapeutic uses for cardiovascular conditions. CLASSIFICATION THERAPEUTIC USES MECHANISM OF ACTION DRUG EXEMPLARS Antihypertensives Angiotensinconverting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors - Stops conversion Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) Aldosterone antagonists Calcium channel blockers (CCBs) - will slow down heart - rate * check BP before Hypertension Heart failure MI Diabetic nephropathy Hypertension Heart failure MI Diabetic nephropathy Heart failure post MI Hypertension Hypertension Angina Cardiac dysrhythmias Alpha1 adrenergic blockers Hypertension Centrally acting alpha2 agonists Hypertension Cardioselective Beta1 blockers Hypertension Angina Heart failure Tachydysrhythmias MI Non-selective Beta1 & Beta2 Blockers Same as above + Cardiac dysrhythmias kburgerSP19RevFA19kbRevSP20dbFAkb giving Blocks formation of angiotensin II causing: a. vasodilation on quiz b. excretion of aldosterone, Na & water c. reduction in pathological changes to blood vessels and heart Blocks angiotensin II receptors leading to: a. vasodilation b. excretion of aldosterone, Na & water Blocks aldosterone receptors in kidney leading to: a. increased excretion of Na & water b. reduced blood volume 1) Slows movement of calcium into smooth muscle cells leading to: a. vasodilation 2) Slows calcium channels in myocardium leading to: a. decreased force of contraction b. decreased heart rate c. slowed conduction through AV node Selectively blocks alpha1 adrenergic receptors in arterioles leading to: a. vasodilation Stimulates alpha2 receptors in the brain, which results in relaxation of arteries, vasodilation, slowing of HR, and decreased cardiac output. Blocks beta receptors in myocardium leading to: a. decreased force of contraction b. decreased heart rate c. slowed conduction through AV node Also blocks beta1 receptors in kidney, reducing release of renin, angiotensin II leading to vasodilation Blocks beta1 receptors in myocardium and kidney as above and also beta2 receptors in lungs captopril (Capoten) lisinopril (Zestril) enalapril (Vasotec) fosinopril(Monopril) losartan (Cozaar) irbesartan (Avapro) valsartan (Diovan) eplerenone (Inspra) spironolactone generic (Aldactone) trade direction Selective for blood vessels: nifedipine(Procardia) amlodipine(Norvasc) er Non-selective for both blood vessels & heart: verapamil (Calan) diltiazem(Cardizem) doxazosin (Cardura) prazosin (Minipress) clonidine (Catapres) metoprolol(Lopressor) atenolol (Tenormin) propranolol (Inderal) carvedilol (Coreg) labetalol (Trandate) 2 Vasodilators Hypertensive emergencies Medications for Heart Failure Cardiac glycosides Heart failure Atrial fibrillation Centrally acting vasodilator that results in rapid reduction of blood pressure, preload, & afterload nitroprusside (Nitropress) mon Inhibits Na/K/ATPase (enzyme needed for digoxin pumping Na ions out of heart cells. As Na accumulates in the cells, calcium ions are released producing : a. increased force of contractions b. improved stroke volume & CO cardiac output Also acts to suppress SA – AV node conduction reducing heart rate Adrenergic agonists Emergency treatment Stimulates Beta1 receptors in myocardium epinephrine for cardiac arrest, heart to: dopamine patients dying need failure & shock a. increase heart rate dobutamine increases b. increase myocardial contractility c. increase cardiac output d. increase tissue perfusion Stimulates Beta1 receptors in kidney to release renin leading to: a. vasoconstriction and increased BP + Diuretics – See Urinary System Medication Information Sheet Antianginal Agents Organic nitrates Angina Dilates coronary arteries improving nitroglycerin perfusion of myocardium, reducing pain (Nitrostat)(Nitro-Bid) and coronary artery spasms. isosorbide (Isordil) Also dilates veins, reducing the amount of blood returning to the heart and reducing preload. Antidysrhythmics Class I: Sodium V-Tachycardia Blocks Na channels thereby slowing procainamide channel blockers A-Flutter cardiac conduction velocity (Pronestyl) A-Fibrillation Class II: BetaV-Tachycardia Prevents sympathetic nervous system propranolol (Inderal) adrenergic blockers A-Flutter stimulation of the heart See above under HTN A-Fibrillation Class III: Potassium V-Tachycardia Blocks K Channels thereby prolonging the amiodarone channel blockers A-Flutter action potential & refractory period of the (Cordarone) Which ahtidy A-Fibrillation cardiac cycle Class IV: Calcium V-Tachycardia Prolongs cardiac conduction verapramil (Calan) channel blockers A-Flutter Decreases oxygen demand of the heart diltiazem (Cardizem) A-Fibrillation See above under HTN Antilipemics HMG-CoA reductase Hypercholesterolemia Interferes with hepatic enzyme HMG-CoA atorvastatin (Lipitor) inhibitors (Statins) Prevention of MIs to reduce cholesterol precursors. bacon too much Decreases manufacture of LDL & VLDL Increases manufacture of HDL higher Cholesterol Same as above Inhibits intestinal absorption of ezetimibe (Zetia) absorption inhibitor cholesterol secreted in bile and food Bile-acid Same as above Binds to bile acids in intestine, causing colesevelam (Welchol) sequestrants increased excretion of cholesterol. mom - to - - basal dilation = BP 'srhmicsmedj • • kburgerSP19RevFA19kbRevSP20dbFAkb less than 100 then 60 high Nicotinic acid (Niacin) Fibrates Direct thrombin inhibitors Direct factor Xa inhibitors Thrombolytics Antiplatelets 1)Salicylic 2)Glycoprotein inhibitors 3)ADP inhibitors 3 take niacin Same as above Decreases LDL & triglycerides synthesis niacin Same as above Decreases triglyceride production and transport. Increases HDL precursors gemfibrozil (Lopid) Activates antithrombin leading to: a. inhibition of thrombin & factor Xa b. inhibition of fibrin formation heparin when fondaparinux (Arixtra) enoxaparin (Lovenox) (Low molecular weight heparin) warfarin (Coumadin) Medications that affect Coagulation Parenteral Therapy for Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary emboli (PE) Prevent DVT & PE and stroke Oral triglycerides ? Therapy for DVT & PE Prevent thrombus formation in persons with A-fib to prevent DVT, PE, stroke, MI Prevent thrombus formation in persons with A-fib to prevent DVT, PE, stroke, MI Same as above Dissolves clots in conditions of: CVA, MI, PE Prevention of MI & CVA Hematopoietic Medications Iron Supplements Iron-deficiency Anemia Vitamin Supplement B12 – Erthyropoiesis Growth Factors Leukopoietic Growth Factors Anemia r/t kidney disease, chemotherapy Neutropenia Pernicious Anemia Folate -Folic acid Anemia - count too we give those? DVTandPE-3gwthoraly-.is# .NSAlDS-! Antagonizes vitamin K leading to: a. prevention of synthesis of factor VII, IX, X, and prothrombin Directly inhibits thrombin formation dabigatran (Pradaxa) Directly inhibits factor Xa and fibrin formation Dissolves clots. Converts plasminogen to plasmin resulting in: a. destruction of fibrinogen b. destruction of other clotting factors rivaroxaban (Xarelto) apixaban (Eliquis) Alteplase (Activase) (tissue plasminogen activator tPA) Inhibit enzymes and factors of normal arterial clotting to: a. prevent platelet aggregation b. prevent platelet clumping 1)aspirin 2)abciximab (Reopro) 3)clopidogrel (Plavix) Provides iron for hemoglobin composition ferrous sulfate (Feosol) Provides supplemental vitamins necessary for normal RBC production cyanocobalamin (B12) folic acid (Folate) Stimulates bone marrow to increase production of RBCs Stimulates bone marrow to increase low production of WBCs not making marrow bone - enough production kburgerSP19RevFA19kbRevSP20dbFAkb do epoetin alfa (Epogen) Filgrastim (Neupogen)