reproductive system notes
advertisement

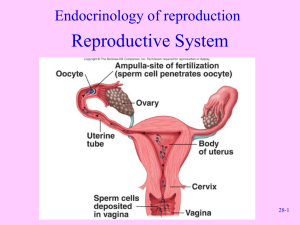
Reproductive System Honors Anatomy & Physiology Male Anatomy Structures & Their functions External Genetialia: Penis – copulatory organ Shaft, glans (enlarged tip), prepuce (foreskin) Erectile (spongy) tissue – connective tissue, smooth muscle, and vascular spaces Erection – sexual arousal triggers parasympathetic release of NO causing arterioles to dilate, engorgement restricts drainage Testes (gonads)-1.5” x 1” sperm & testosterone production Scrotum – maintain testes temp 3oC lower than body temp (retractable) Duct System (sympathetic control over ejaculation) Epididymis –20 ft long, 20 days for sperm to become motile, may be stored for months (ejaculated by smooth muscle or phagocytized) Ductus deferens – 18” long, thick smooth muscle Ejaculatory duct – through the prostate and empties into urethra Urethra – both urine & sperm (has priority!) 3 regions: prostatic urethra, membranous, spongy Semen Semen – milky white, sticky secretion of sperm & secretions 2-5mL per ejaculation 20-150milliom sperm per mL Catabolism of fructose provides ATP for flagella Prostaglandins stimulate uterine peristalsis Accessory Glands Seminal vesicles – 60% of semen: yellow, viscous alkaline fluid w/fructose, ascorbic acid, prostaglandins enhancing sperm motility Prostate Gland – 30% of semen: milky acidic fluid w/enzymes to activate sperm Bulbourthral glands – pea sized glands secrete a thick clear mucus to neutralize acidic urine in urethra “pre-ejaculate” Structure of the testis Surrounded by 2 membranes: Tunica vaginalis Tunica albuginea Divided into 250-300 lobules Ea/w 1-4 seminiferous tubules (sperm production) Surrounded by myoid cells – contract to squeeze sperm out of testis into rete testis Spermatogenesis Begins @ age 14 Makes ~400million sperm/day Spermatogonia – divide by mitosis @puberty some become primary spermatocytes generating secondary spermatocytes Producing non motile spermatotids Female Anatomy Female External Genitalia Vagina – 3-4” birth canal & copulation organ 3 layers: outer fibroelastic, smooth muscle, ridged mucosa Acidic pH – antimicrobial but hostile to sperm Hymen – vascular membrane in virgins Mons pubis – fatty ridge Labia: majora & minora – enclose the vestibule or entrance Vestibular glands – secrete mucus Clitoris – innervated erectile tissue hooded by prepuce Ovaries Produce Ova (eggs) & Sex hormones Ovarian ligament anchor to uterus & suspensory ligament to pelvic wall Ovarian follicles ea/contains oocyte surrounded by follicle cells Primordial follicle – 1 layer cells surround oocyte Primary follicle – 2 + layers of cells Secondary follicle – fluid filled cavity appears Graafian follicle – follicle bulges from ovary surface, mature oocyte Ovulation – oocyte ejected from ovary Corpus luteum – follicle degenerates into scars/pits Oogenesis Fetal period – oogonia divide by mitosis (7 million) Primary oocytes in primary follicles begin meiosis I, and stall in prophase I (2 milion) Puberty 250,000 oocytes remain 1 selected every 28 days to complete meiosis I, first polar body undergoes apoptosis, secondary oocyte is suspended in metaphase II when ovulated <500 released over 40 years After fertilized, it completes meiosis II, creating a second polar body that deteriorates and 1 large ovum Ovarian Cycle @puberty pituitary releases FSH & LH stimulating ovaries Follicular Phase (days 1-14) Menstration (days 1-5 ) endometrium sheds Low estrogen & progesterone Proliferative Phase (day 6-14) FSH & LH follicle growth estrogen (- feedback on release FSH & LH, + feedback on estrogen) Endometrial lining thickens Cervical mucus thins Ovulation (day 14) estrogen causes surge of LH & FSH, then drops Ovary expels 2o oocyte w/corona radiata Mittlschmerz – abdominal pain due to ovarian wall stretching 21-40 days, avg 28 days) Luteal /Secretory Phase (days 14-28) estrogen progesterone (thickens endometrium) Corpus luteum degenerates Female Duct System Uterine (fallopian) tubes Receive ovulated oocyte About 4” long Fimbraie – ciliated finger like projections on distal end create current to capture oocytes Infundibulum – funnel shaped structure Smooth muscle (peristalysis) & mucosa ciliated lining Uterous (womb)- nourish fertilized ovum Inverted pear in size and shape 3 regions: fundus, body, & cervix 3 layers of wall: Perimetrium – outermost layer Myometrium – smooth muscle Endometrium – 2 layers of mucosal lining (inner layer sheds) Menopause 20’s reproductive peak 30’s ovarian function (quality of oocytes) declines, still ~100,000 oocytes left By 50, only ~3 oocytes left Estrogen production declines Menstrual periods erratic & shorter, until ovulation & menstruation ceases Menopause reached after 1 year w/o menstruation Mammary Glands Produce milk by modified sweat glands Areola – ring of pigmented skin surrounding nipple Ea gland/ 15-25 lobes consisting of lobules containing alveoli that produce milk Milk passes into lactiferous ducts which open at nipple