Oogenesis and the Ovarian Cycle
advertisement

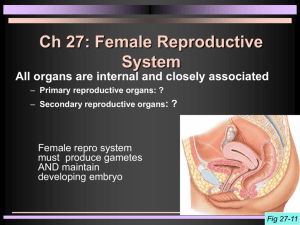
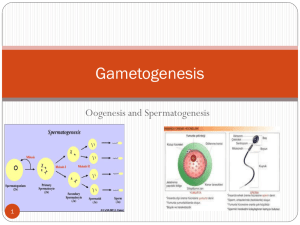
Oogenesis and the Ovarian Cycle Overview Oogenesis and the Ovarian Cycle The total supply of eggs are present at _________ Ability to release eggs begins at puberty Reproductive ability ends at _________ Stage 1 Oocytes are matured in developing ovarian _________ Oogonia—female stem cells found in a developing fetus _________ undergo mitosis to produce primary oocytes Primary oocytes are surrounded by cells that form primary follicles in the ovary Oogonia no longer exist by the time _________ Have approximately 700,000 primary oocytes. Stage 2 Primary oocytes are inactive until puberty _________ _________ hormone (FSH) causes some primary follicles to mature each month Cyclic monthly changes constitute the ovarian cycle Follicle is prodded by FSH, it accumulates fluid in central chamber called the _________ . Meiosis starts inside maturing follicle Stage 3 Produces a secondary oocyte and the first _________ Huge _________ difference. Follicle development to the stage of a vesicular follicle takes about _________ days Protrudes like an angry boil from the external surface of the ovary. Stage 4 Ovulation of a secondary oocyte occurs with the release of _________ hormone (LH) Secondary oocyte is released and surrounded by a _________ _________ – like a second follicle The are several primary follicles that start the process. Only one will finish and be released for _________ . It is _________ how it is determined which one will complete the process Luteinizing Hormone also causes the ruptured follicle to change into the _________ _________ Responsible for hormone production later Ovulation Pain Some women experience a twinge of abdominal pain when ovulation occurs. Called mittelschmerz, meaning “middle pain” Aused by the intense stretching of the ovarian wall during ovulation. Ovulation Stage 5 Meiosis is completed after ovulation only if _________ _________ Ovum is produced Two additional polar bodies are produced Once ovum is formed, the ______ chromosomes can be combined with those of the sperm to form the fertilized egg (zygote) If the secondary oocyte is not penetrated by a sperm, it ________ and does not complete meiosis to form an ovum Male and Female Differences Meiosis Males—produces _________ functional sperm Females—produces one functional ovum and three polar bodies Sex cell size and structure Sperm are tiny, _________ , and equipped with nutrients in seminal fluid Egg is large, non-motile, and has _________ _________ to nourish the embryo until implantation Growing follicle MeiosisPrimary II completed (only if sperm follicle penetration occurs) Ovu Primary oocyte Childhood Sper Primary oocyte (arrested in prophase I; present at birth) Primary Ovulation follicle Second polar body Primary follicle Secondary oocyte (arrested in metaphase II) Mature vesicular (Graafian) follicle Oocyt Ovulated secondary oocyte Follicle Polar bodies (all polar bodies degenerate) Meiosis II of polar body (may or may not occur) Growth Oogonium (stem cell) Mitosis 2n (ovary inactive) 2n Each month from2n First polar Meiosis I (completed by one puberty to menopause primary oocyte each month) Primary oocyte (still arrested in prophase I)