Reproductive endocrinology
advertisement
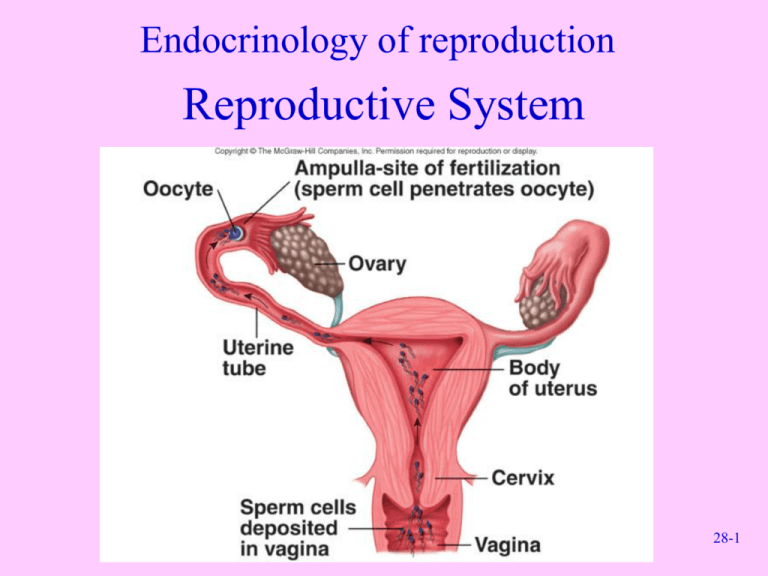
Endocrinology of reproduction Reproductive System 28-1 Anatomy of Male Reproductive System • Testes • Series of ducts – Epididymides – Ductus deferentia – Urethra • Accessory glands – Seminal vesicles – Prostate gland – Bulbourethral glands • Supporting structures – Scrotum • 2 chambered sac that contains testes • Dartos and cremaster muscles help regulate temperature – Penis • Perineum – Diamond-shaped areas between thighs 28-2 Male Pelvis 28-3 Testes • Glands – Exocrine – Endocrine • Compartments divided by septa – Seminiferous tubules • Empty into rete testis • Empties into efferent ductules – Interstitial or Leydig cells • Descent – Pass from abdominal cavity through inguinal canal to scrotum • Cryptorchidism – Failure of of one or both of testes to descend into scrotum – Prevents normal sperm development 28-4 Histology of Testis 28-5 Descent of Testes 28-6 Sperm Cell Development • Spermatozoa produced in seminiferous tubules • Spermatogonia divide (mitosis) to form primary spermatocytes • Primary spermatocytes (first division of meiosis) divide to form secondary spermatocytes • Secondary spermatocytes (second division of meiosis) divide to form spermatids • Spermatids develop an acrosome and flagellum • Sertoli cells nourish sperm cells and form a blood-testis barrier and produce hormones 28-7 Spermatogenesis 28-8 Meiosis 28-9 Ducts • Epididymis – Site of sperm cell maturation • Ductus deferens or vas deferens – Passes from epididymis into abdominal cavity • Ejaculatory duct – Joining of ductus deferens and seminal vesicle • Urethra – Extends from urinary bladder to distal end of penis – Passageway for urine and male reproductive fluids – 3 parts • Prostatic urethra • Membranous urethra • Spongy or penile urethra 28-10 Male Reproductive Structures 28-11 Penis • Three columns of erectile tissue that engorge with blood – Corpora cavernosa (2) – Corpus spongiosum (1) • Glans penis – Prepuce or foreskin covers • Circumcision: Surgical removal • External urethra orifice 28-12 Penis 28-13 Accessory Glands • Bulbourethral glands • Seminal vesicles – Empty into ejaculatory duct – Produce about 60% of semen • Prostate gland – Produces about 30% of semen – Contribute about 5% to semen • Secretions – Semen • Composite of sperm cells and secretions – Emission • Discharge of semen into prostatic urethra – Ejaculation • Forceful expulsion of semen from urethra 28-14 Regulation of Sex Hormone Secretion • Hypothalamus releases – GnRH or LHRH which stimulates • LH or ICSH to produce testosterone • FSH to stimulate sperm cell formation • Inhibin inhibits FSH secretion from anterior pituitary 28-15 Puberty and Testosterone • Puberty – Age at which individuals become capable of sexual reproduction • Before puberty small amounts of testosterone inhibit GnRH release • During puberty testosterone does not completely suppress GnRH release, resulting in increased FSH,LH, and testosterone • Testosterone – Produced by interstitial cells, adrenal cortex and sustentacular cells – Causes development of male sex organs in embryo, stimulates descent of testes, causes enlargement of genitals and necessary for sperm cell formation 28-16 Male Sexual Behavior and Male Sex Act • Male sexual behavior – Testosterone required to initiate and maintain • Male sex act – Complex series of reflexes that result in erection of penis, secretion of mucus into urethra, emission, ejaculation – Sensations result in orgasm associated with ejaculation and then resolution 28-17 Neural Control of Erection • Stimulation – Tactile or psychological – Parasympathetic • Erection due to vasodilation of blood vessels – Sympathetic • Causes erection, emission, ejaculation • Erectile Dysfunction 28-18 Anatomy of Female Reproductive System • Female reproductive organs – – – – – – Ovaries Uterine tubes Uterus Vagina External genital organs Mammary glands 28-19 Female Pelvis 28-20 Uterus, Vagina, Uterine Tubes, Ovaries and Supporting Ligaments 28-21 Ovary Histology 28-22 Maturation of Follicle and Oocyte 28-23 Maturation and Fertilization of Oocyte 28-24 Follicle and Oocyte Development • Oogenesis is the production of a secondary oocyte in ovaries • Oogonia are cells from which oocytes develop • Primary oocytes are surround by granulosa cells and called a primordial follicle • Primordial follicle becomes a primary follicle when oocyte enlarges and cells change • Primary follicle becomes secondary follicle and enlarges to form mature or graafian follicle – Usually only one is ovulated, others degenerate • Primary oocyte completes first meiotic division to produce secondary oocyte and a polar body • Secondary oocyte begins second meiotic division, which stops in metaphase II 28-25 Ovulation and Follicle Fate • Ovulation – Follicle swells and ruptures, secondary oocyte is released from ovary – Second meiotic division completed when secondary oocyte unites with sperm cell to form zygote • Fate of the follicle – Graafian follicle become corpus luteum – If fertilization occurs, corpus luteum persists – If no fertilization, becomes corpus albicans 28-26 Uterine Tubes and Uterus • Uterine or fallopian tubes or oviducts – Open directly into peritoneal cavity to receive oocyte from ovary – Transport oocyte or zygote from ovary to uterus • Uterus – Parts: Body, isthmus, cervix – Composed of 3 layers • Perimetrium: Serous membrane • Myometrium: Smooth muscle • Endometrium: Mucous membrane 28-27 Vagina and Perineum • Perineum • Vagina – Female organ of copulation – Allows menstrual flow and childbirth – Hymen covers the vaginal opening or orifice – Divided into two triangles • Urogenital: Contains the external genitalia • Anal triangle • Clinical perineum – Region between vagina and anus – Episiotomy: Incision to prevent tearing during childbirth 28-28 Female External Genitalia • Vulva or pudendum or external female genitalia – Vestibule: Space • Labia minora: Form borders on sides • Clitoris: Erectile structure – Corpora cavernosa – Corpora spongiosa – Labia majora • Unite to form mons pubis 28-29 Female Perineum 28-30 Mammary Glands • Organs of milk production located within mammae or breasts – Consist of glandular lobes and adipose tissue – Cooper’s ligaments support the breasts 28-31 Puberty and Menstrual Cycle • Menstrual Cycle • Puberty – Begins with menarche or first episode of menstrual bleeding – Begins when GnRH levels increase – About 28 days long – Phases • • • • Menses Proliferative phase Secretory phase Menses – Amenorrhea: Absence of a menstrual cycle – Menopause: Cessation of menstrual cycles 28-32 Menstrual Cycle 28-33 Hormone Regulation during Menstrual Cycle 28-34 Female Sexual Behavior and Sex Act • Female sexual behavior – Depends on hormones • Androgens and steroids – Depends on psychological factors • Female sex act – Parasympathetic stimulation • Blood engorgement in clitoris and around vaginal opening • Erect nipples • Mucouslike fluid extruded into vagina and through wall – Orgasm not necessary for fertilization to occur 28-35 Female Fertility and Pregnancy • Female fertility – Sperm ejaculated into vagina during copulation and transported through cervix and uterine tubes to ampulla – Sperm cells undergo capacitation • Pregnancy – Oocyte can be fertilized up to 24 hours after ovulation – Sperm cells can be viable for up to 6 days in female tract – Ectopic pregnancy: Implantation occurs anywhere other than uterine cavity 28-36 Sperm Cell Movement 28-37 Changes in Hormones During Pregnancy 28-38 Control of Pregnancy • Behavioral methods – Abstinence – Coitus interruptus – Rhythm method • Barrier methods – Condom • Male and female – Diaphragm – Cervical cap – Spermicidal agents • Lactation • Chemical methods – Oral contraceptives – Injections as DepoProvera – Implants – Morning-after pills • Surgical methods – Vasectomy – Tubal ligation – Abortions 28-39 Effects of Aging • Male – Decrease in size and weight of testes – Decrease in sperm production – Prostate gland enlarges and increase in cancer – Impotence is agerelated – Decrease in sexual activity • Female – Menopause – Decrease in size of uterus and vaginal wall thins – Age related increase in breast, uterine, ovarian cancer 28-40










