CGS – 1100 Introduction to Computer Applications
advertisement

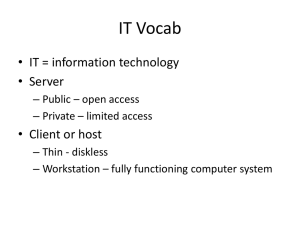
CGS – 1100 Introduction to Computer Applications Computer Concepts Computer System Component Computer: A programmable electronic device that can store, retrieve, and process data. The word “Computer” emerged during WWII, people who operated desk calculators were called: Computers. History of the Modern Computer Human: Could add a two 10 digit number in 10 seconds, with Calculator, in 4 Seconds. Mark 1: Also called “Harvard Mark 1” Could add two 10digit numbers in about 0.3 seconds. 30 times faster than Pencil and paper. ENIAC: Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer. The world's first electronic digital computer was developed by Army Ordnance to compute World War II ballistic firing Tables. Could add the same in 0.0002 seconds, 50,000 times faster than a human, and 1,500 times faster than the Mark 1. General Vocabulary and Units Bit: "Binary digIT" Computers happen to operate using the base-2 number system, also known as the binary number system ( 0, 1) Byte: 8-bit collections (single, double precision) Digital: Send – Receive 0’s and 1’s Analog: AM - FM Hertz: Unit of Frequency Kilo-Hertz: 1000 Cycles Mega-Hertz: 1 million Cycles Giga-Hertz: 1 Billion Cycles Components of a Computer System Computer Hardware Motherboard Floppy Hard Drive Software Operating System Office 2003 Internet Explorer Components of a Computer System Storage Input Information Processing Cycle Output Process Components of a Computer System Input Process Storage Output Types of Computer Supercomputer Minicomputer Computers Microcomputer Mainframe Types of Computer Microcomputer Desktop Laptop / Notebook PDA Personal Digital Assistant Hardware Devices Input Device Storage Device Printer Output Device Peripheral System Unit Input Device Monitor Output Device Peripheral Memory Memory RAM ROM SRAM PROM DRAM EPROM Memory Random Access Memory SRAM: Static RAM DRAM: Dynamic RAM Read Only Memory EPROM: Erasable Programmable ROM PROM: Programmable ROM Memory Size in MB 1 MB 2 MB 4 MB 8 MB 16 MB 32 MB 64 MB 128 MB 256 MB 512 MB 1024 MB Extra Points: What mathematical equation describes the pattern? Monitors Output device, Soft-Copy Output Resolution is given by the amount of “Pixels” Two categories: CRT (Cathode Ray Tubes) and LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) Printers Output Devices Hard Copy Output Resolution is given in “dsi”. Dots per Inch. Two Categories: Laser (B&W, Color) uses Toner. Inkjet (Color) uses ink cartridges. Types of Software and Their Uses Operating System Software (OS): Tell the computer how to work and what to do. Windows, Linux and Macintosh. Driver: Software that tells a hardware component how to work. Application Software: Accomplish a task Using a computer. Word, Excel, PowerPoint Networks and Configuration Computer Network: Two or more computer connected in some way in order to share their resources. Bus Network, Star Network, Ring Network. Network Vocabulary Server/Host: Client/Workstation: Topology: Star Network A star network is a local area network (LAN) in which all nodes (workstations or other devices) are directly connected to a common central computer. Every workstation is indirectly connected to every other through the central computer. In some star networks, the central computer can also operate as a workstation. Bus Network A bus network is an arrangement in a local area network (LAN) in which each node (workstation or other device) is connected to a main cable or link called the bus. Ring Network A ring network is a local area network (LAN) in which the nodes (workstations or other devices) are connected in a closed loop configuration. Adjacent pairs of nodes are directly connected. Other pairs of nodes are indirectly connected, the data passing through one or more intermediate nodes. Local Area Network A local area network (LAN) is a group of computers and associated devices that share a common communications line or wireless link and typically share the resources of a single processor or server within a small geographic area (for example, within an office building). Usually, the server has applications and data storage that are shared in common by multiple computer users. A local area network may serve as few as two or three users (for example, in a home network) or as many as thousands of users Wide Area Network A wide area network or WAN is a computer network covering a wide geographical area, involving a vast array of computers. WANs are used to connect local area networks (LANs) together, so that users and computers in one location can communicate with users and computers in other locations. Test 1